Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2016; 22(19): 4757-4765
Published online May 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4757
Published online May 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4757
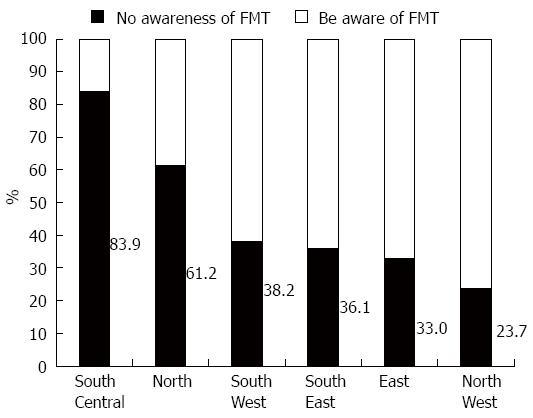
Figure 1 Physicians’ awareness of fecal microbiota transplantation in different regions.
FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation.
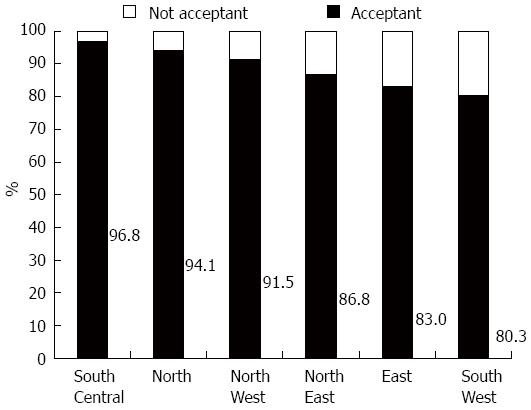
Figure 2 Physicians’ acceptance of fecal microbiota transplantation in different regions.
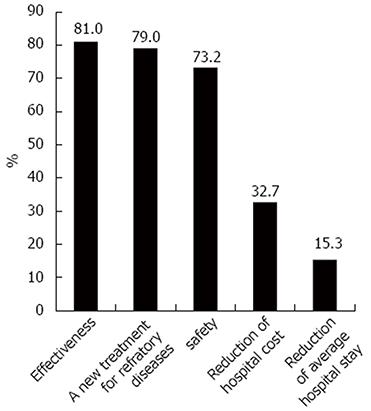
Figure 3 Physicians’ concerns about choosing fecal microbiota transplantation as a treatment.
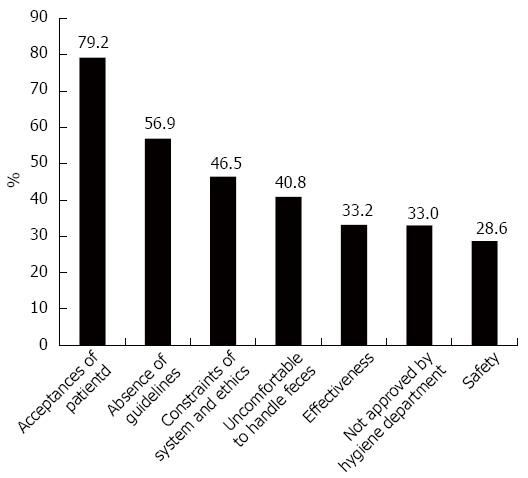
Figure 4 Barriers against clinical applications of fecal microbiota transplantation.
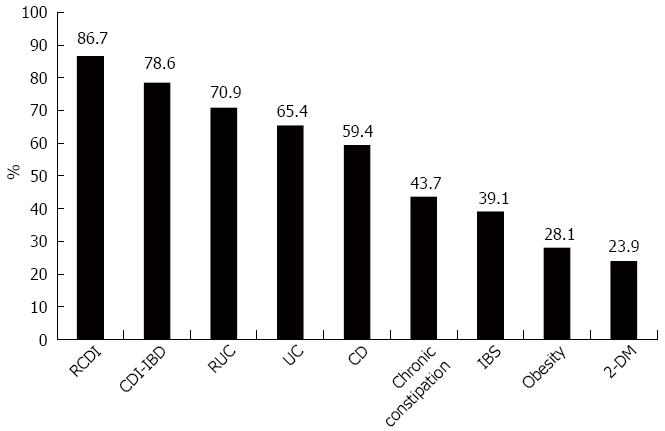
Figure 5 Fecal microbiota transplantation indications.
RCDI: Refractory Clostridium difficile infection; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s Disease; RUC: Refractory ulcerative colitis; CDI-IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease with Clostridium difficile infection; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; 2-DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
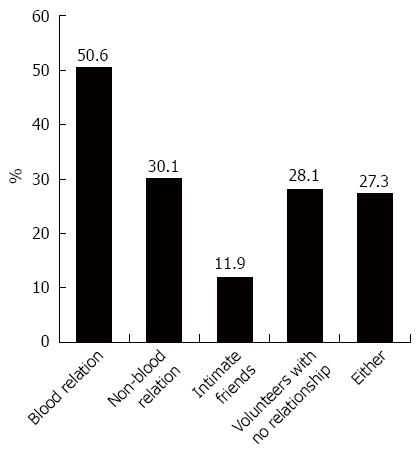
Figure 6 Selection of donors.
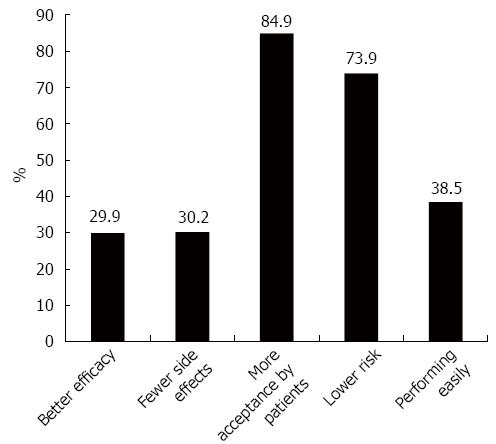
Figure 7 Reasons for lower gastrointestinal tract selection.
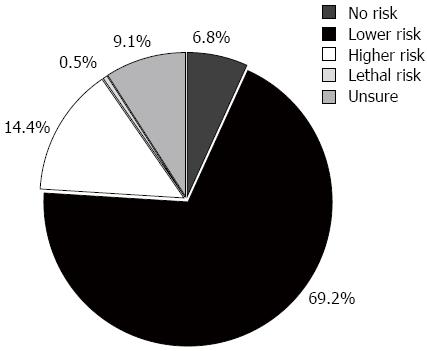
Figure 8 Physicians’ perceptions of fecal microbiota transplantation risk.
- Citation: Ren RR, Sun G, Yang YS, Peng LH, Wang SF, Shi XH, Zhao JQ, Ban YL, Pan F, Wang XH, Lu W, Ren JL, Song Y, Wang JB, Lu QM, Bai WY, Wu XP, Wang ZK, Zhang XM, Chen Y. Chinese physicians’ perceptions of fecal microbiota transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(19): 4757-4765
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i19/4757.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4757