Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3769-3776
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3769
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3769
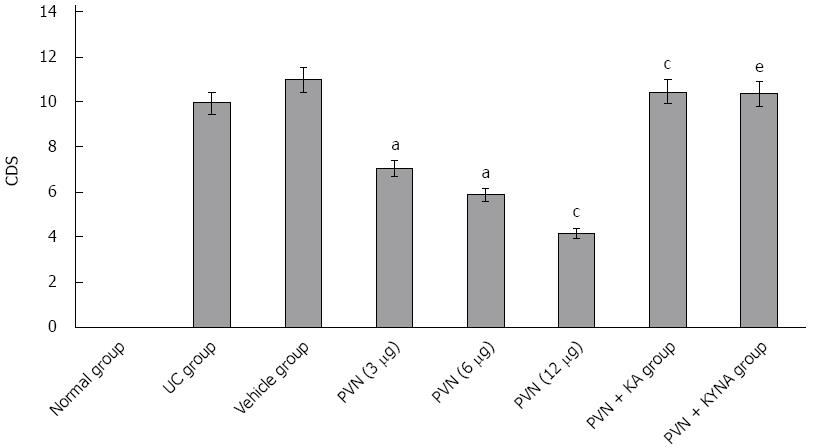
Figure 1 Colonic damage scores in colons of rats with ulcerative colitis in each group after glutamic acid stimulation and chemical damage to the paraventricular nucleus.
aP < 0.05, PVN (12 μg) group vs each group; cP < 0.05, PVN (12 μg) group vs the PVN + KA group; eP < 0.05, PVN (12 μg) group vs the PVN + KYMA group. CDS: Colonic damage score; PVN: Paraventricular nucleus; KA: Kainic acid.
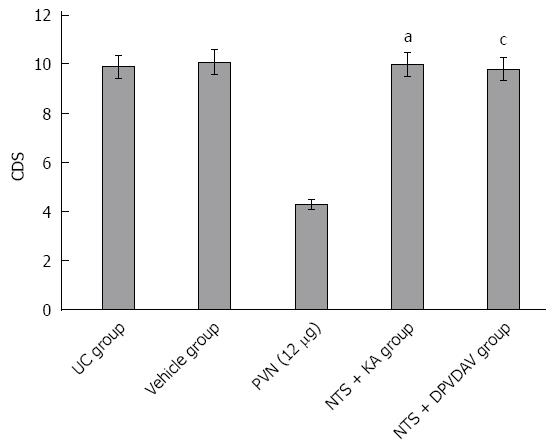
Figure 2 Influence of chemical damage to the nucleus tractus solitarius and injection of AVP-Vl receptor antagonist into the nucleus tractus solitarius on alleviated ulcerative colitis injury in rats by stimulation of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus with glutamic acid.
aP < 0.05, PVN (12 μg) group vs the NTS + KA group; cP < 0.05, PVN (12 μg) group vs the NTS + DPVDAV group. DPVDAV: Damage in nucleus tractus solitarius and injection of AVP-Vl receptor antagonist; NTS: Nucleus tractus solitaries; KA: Kainic acid; PVN: Paraventricular nucleus.
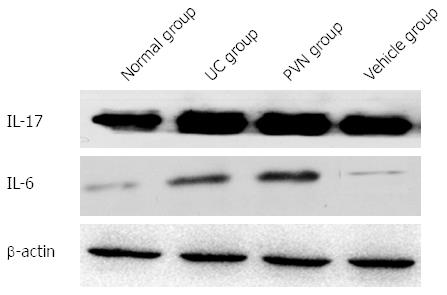
Figure 3 Interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 contents in colon tissue of rats with ulcerative colitis.
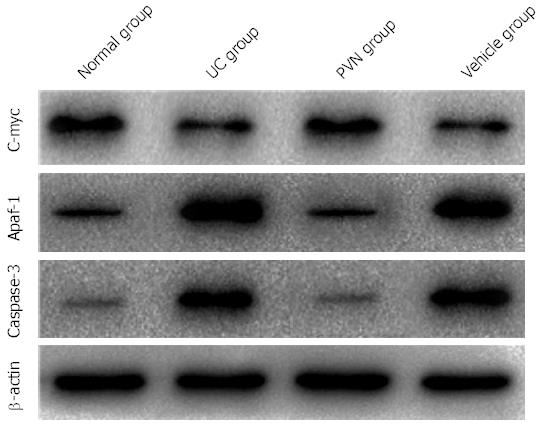
Figure 4 C-myc, Apaf-1 and caspase-3 protein expression in colon tissues of rats with ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Deng QJ, Deng DJ, Che J, Zhao HR, Yu JJ, Lu YY. Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus stimulation reduces intestinal injury in rats with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3769-3776
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3769