Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2016; 22(12): 3341-3354
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i12.3341
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i12.3341
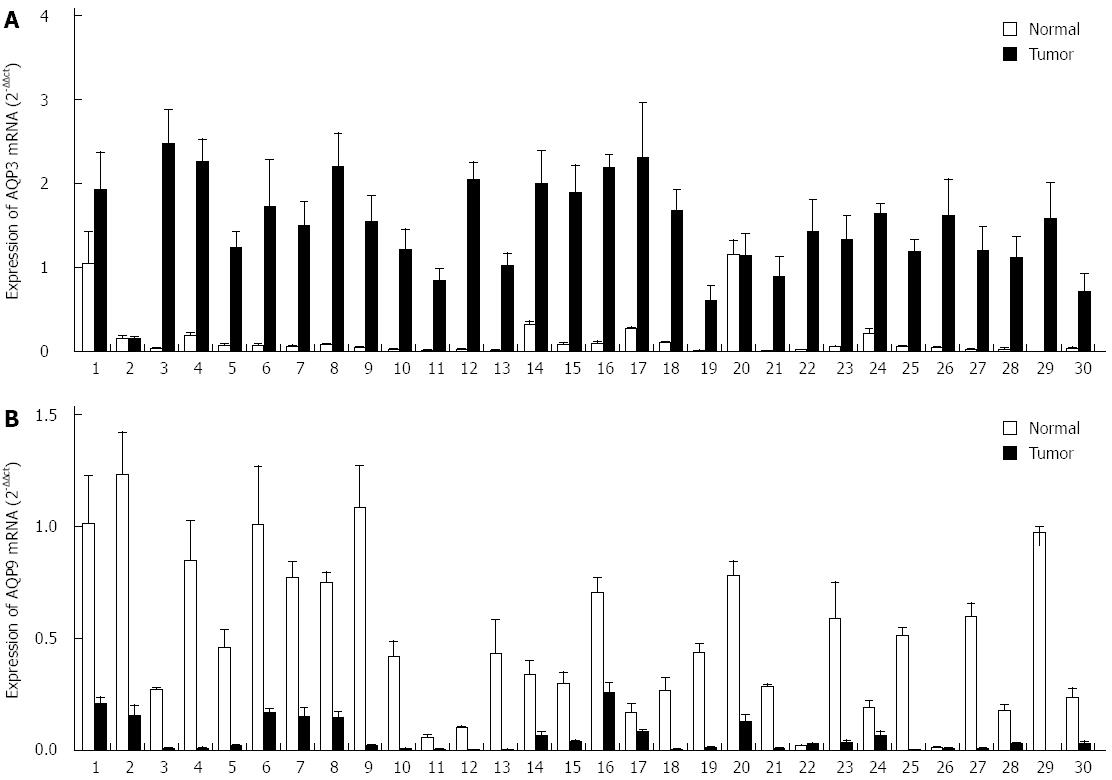
Figure 1 mRNA levels of AQP3 and AQP9 in hepatocellular carcinoma and normal liver tissues.
A: mRNA levels of AQP3 in 30 paired HCC tissues and normal liver tissues measured by RT-PCR; B: mRNA levels of AQP9 in 30 paired HCC tissues and normal liver tissues measured by RT-PCR. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; N: Normal liver tissues; T: HCC tissues.
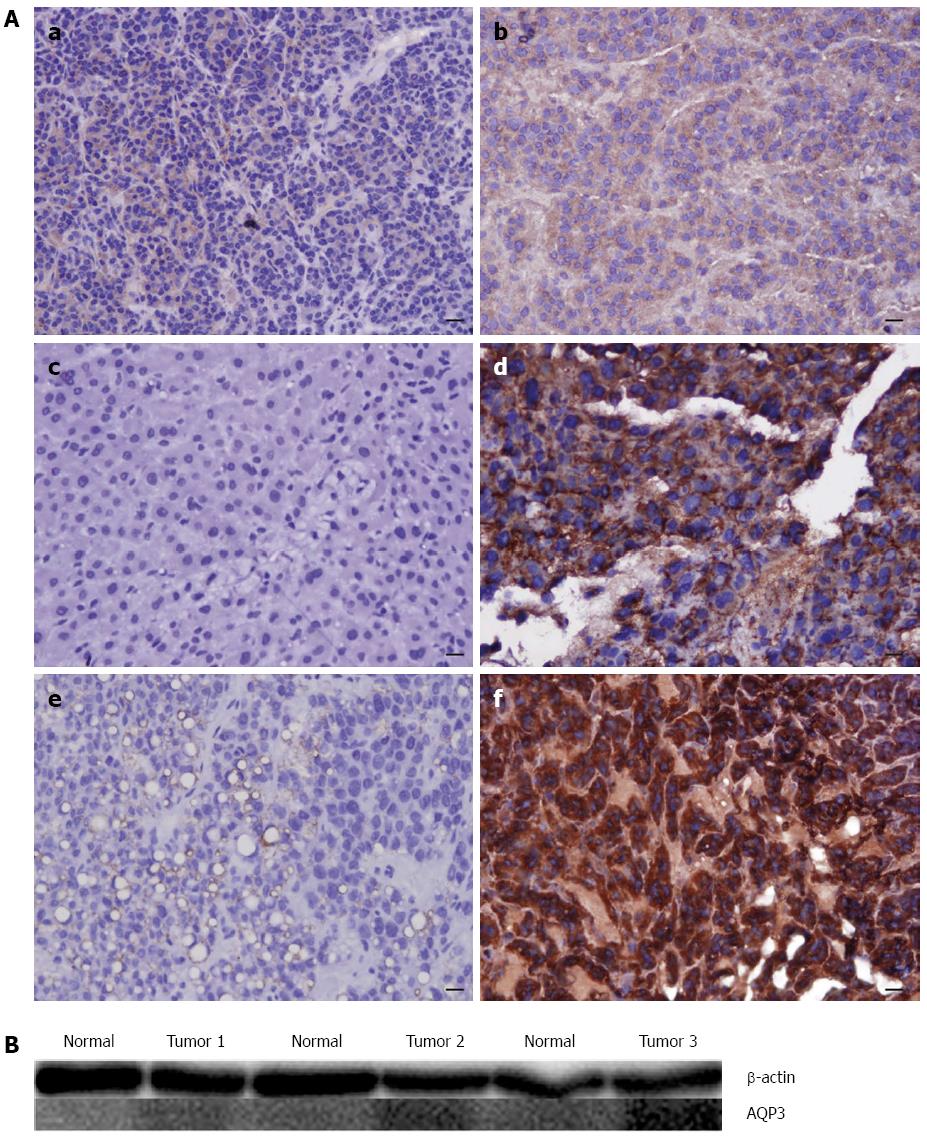
Figure 2 Levels of AQP3 in hepatocellular carcinoma of different differentiation.
A: Analysis of AQP3 protein expression by immunohistochemistry. a: AQP3 expression decreased in normal liver tissues; b: AQP3 expression was weak in well-differentiated HCC samples; c: AQP3 expression decreased in normal liver tissues; d: AQP3 expression was moderate in moderately differentiated HCC samples; e: AQP3 expression decreased in normal liver samples; f: AQP3 expression was high in poorly differentiated HCC samples. B: The protein levels of AQP3 in HCC of different degrees of differentiation corresponded to their immunohistochemistry results. Tumor 1, well-differentiated HCC sample; tumor 2, moderately differentiated HCC sample; and tumor 3, poorly differentiated HCC sample. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
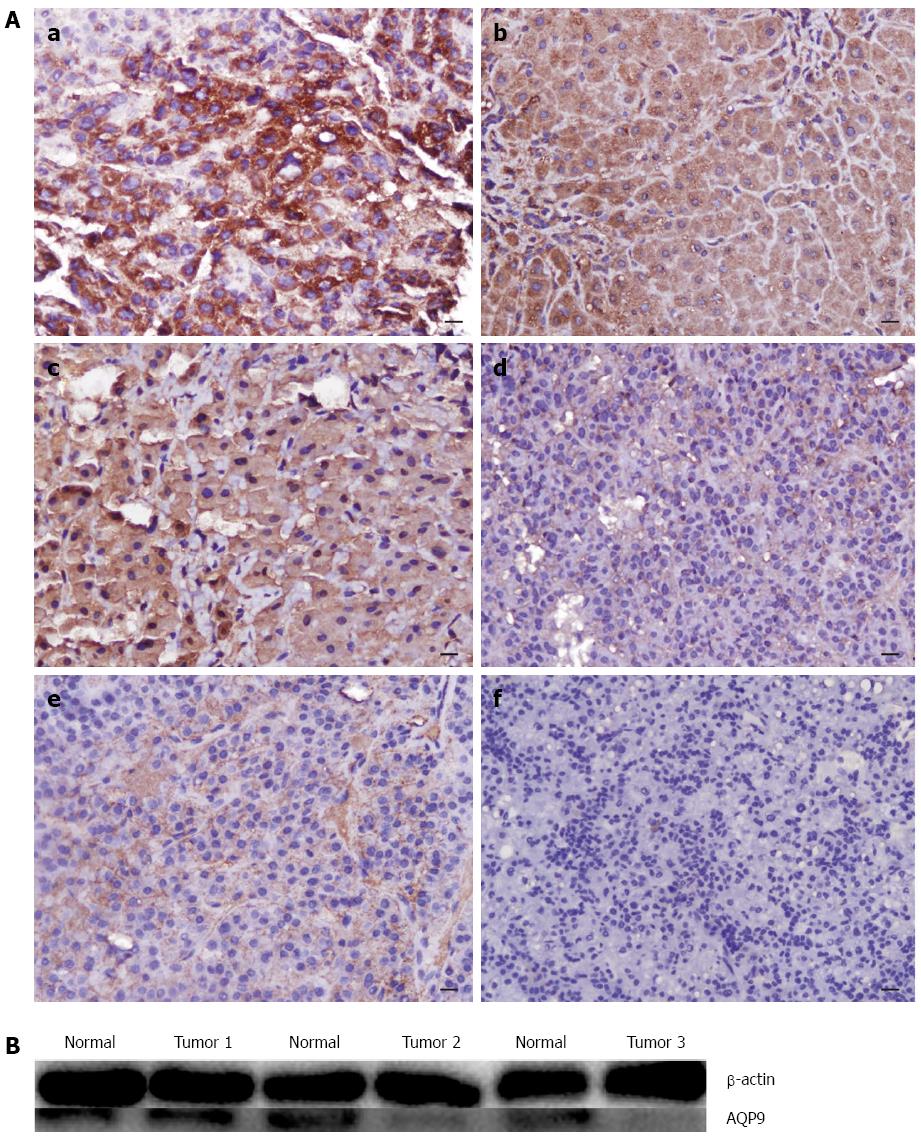
Figure 3 Levels of AQP9 in hepatocellular carcinoma of different differentiation.
A: Analysis of AQP9 protein expression by immunohistochemistry. a: AQP9 expression was high in normal liver samples; b: AQP9 expression was weak in well-differentiated HCC samples; c: AQP9 expression was high in normal liver samples; d: AQP9 expression was moderate in moderately differentiated HCC samples; e: AQP9 expression was high in normal liver samples; f: AQP9 expression was low in poorly differentiated HCC samples (magnification × 200, bar = 50 μm). B: The protein levels of AQP9 in HCC of different differentiation corresponded to their immunohistochemistry results: Tumor 1, well-differentiated HCC sample; tumor 2, moderately differentiated HCC sample; and tumor 3, poorly differentiated HCC sample. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
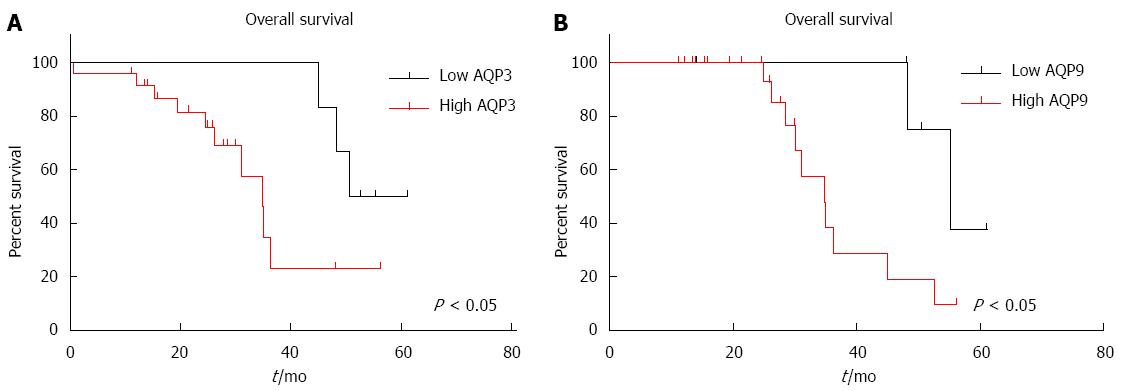
Figure 4 High AQP3 and low AQP9 expression predict worse survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A and B: Survival of 30 hepatocellular carcinoma patients, including both untreated and HCC-treated patients using Kaplan-Maier analysis. High AQP3 and low AQP9 levels resulted in lower patient survival. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
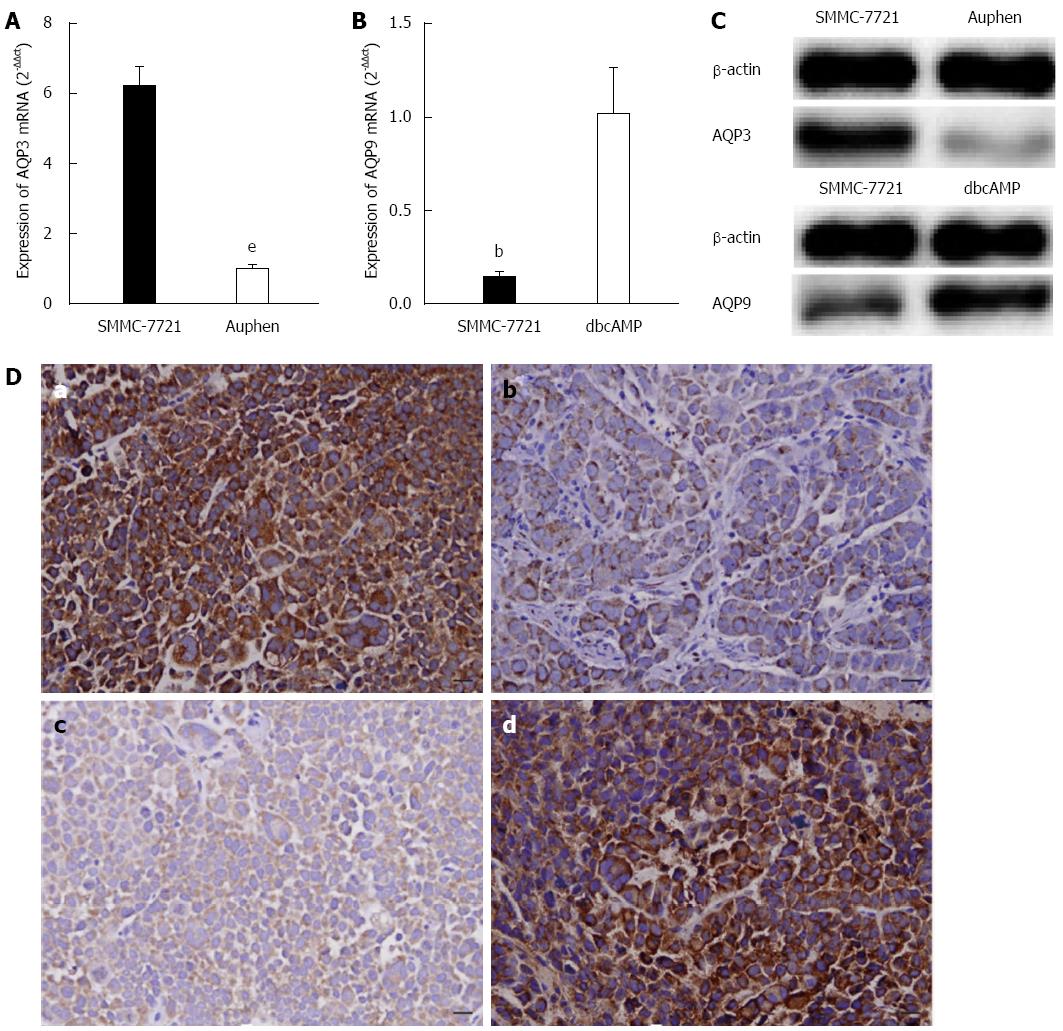
Figure 5 Effects of Auphen and dibutyryl cAMP on AQP3 and AQP9 expression.
A: mRNA levels of AQP3 in tumors from nude mice; B: mRNA levels of AQP9 in tumors from nude mice; C: Protein levels of AQP3 and AQP9 in tumors from nude mice; D: Immunohistochemical analysis of a subcutaneous tumor: a: Analysis of AQP3 expression in the control group; b: Analysis of AQP3 expression in the Auphen group; c: Analysis of AQP9 expression in the control group; d: Analysis of AQP9 expression in the dbcAMP group. (magnification × 200, bar = 50 μm). All data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). bP < 0.01 vs the control; eP < 0.001 vs the control. dbcAMP: Dibutyryl cAMP.
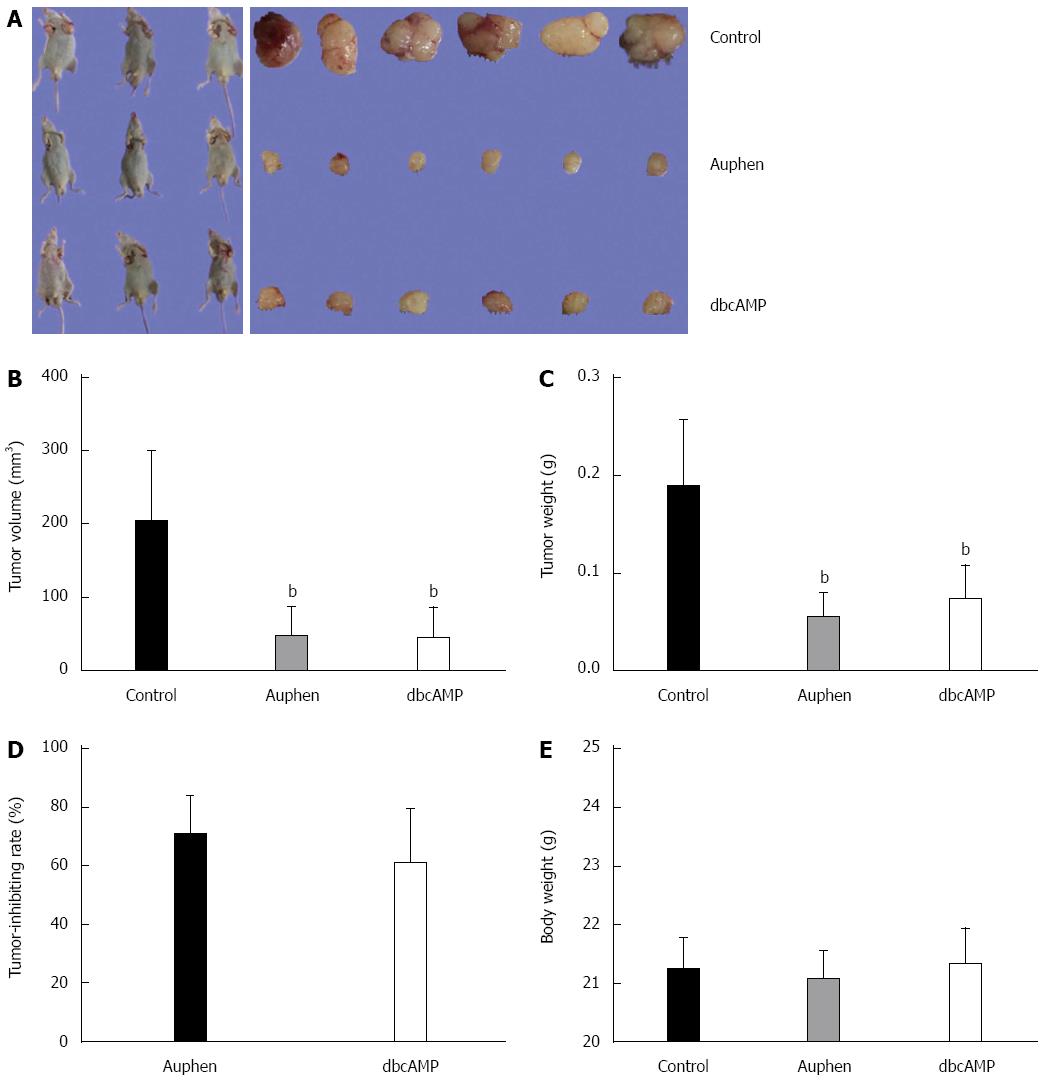
Figure 6 Auphen and dbcAMP suppress hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth.
A: Tumor volumes of control (NS), Auphen-treated (Auphen), and dbcAMP-treated (dbcAMP) groups; B: Tumor volumes of control, Auphen-treated, and dbcAMP-treated groups; C: Tumor weights of control, Auphen-treated, and dbcAMP-treated groups; D: Tumor suppression rates of Auphen-treated, and dbcAMP-treated groups; E: Body weights of control, Auphen-treated, and dbcAMP-treated groups. All data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). bP < 0.01 vs the control. dbcAMP: Dibutyryl cAMP.
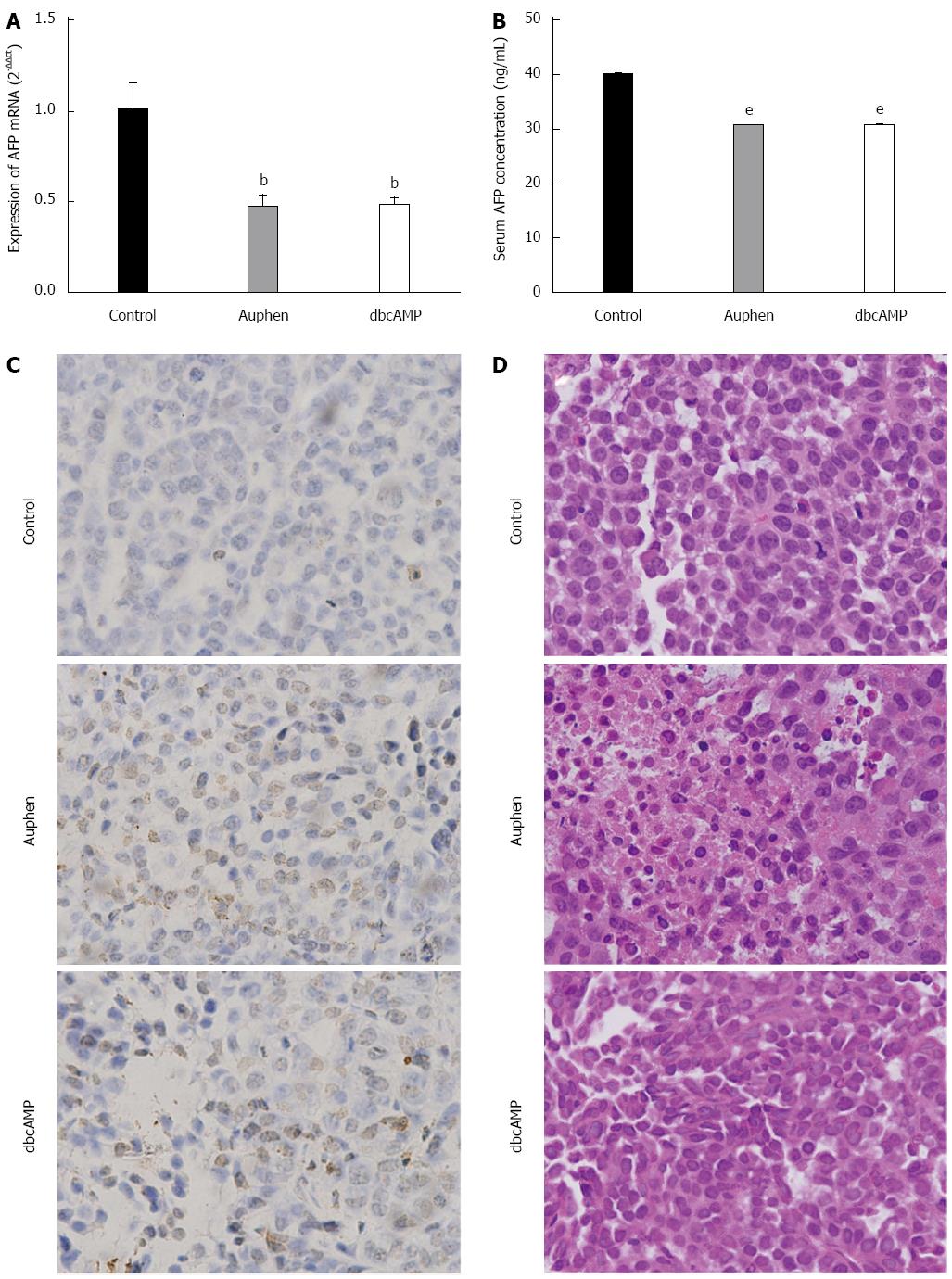
Figure 7 Effects of Auphen and dbcAMP on hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.
A: mRNA levels of α-fetoprotein (AFP) in tumors from nude mice; B: AFP concentration in blood of control (NS), Auphen-treated (Auphen), and dbcAMP-treated (dbcAMP) groups. All data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). bP < 0.01 vs the control; eP < 0.001 vs the control; C: Testing of apoptosis by TUNEL assay in tumor samples of nude mice in different treated groups (magnification, × 400). The nuclei of positive cells were stained brown; D: Tumor samples from nude mice in different treated groups (HE, magnification, × 400). Pathological traits of positive cells were revealed as karyopyknosis, and had a cytoplasmic red color.
- Citation: Peng R, Zhao GX, Li J, Zhang Y, Shen XZ, Wang JY, Sun JY. Auphen and dibutyryl cAMP suppress growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating expression of aquaporins 3 and 9 in vivo. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(12): 3341-3354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i12/3341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i12.3341