Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2016; 22(11): 3261-3267
Published online Mar 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3261
Published online Mar 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3261
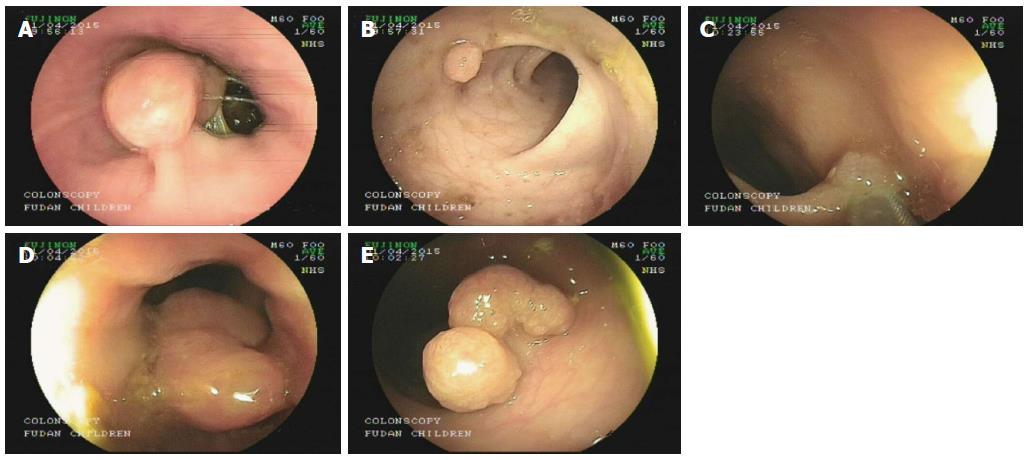
Figure 1 Endoscopic images of the five polyps located in different parts of the intestine (A-E).
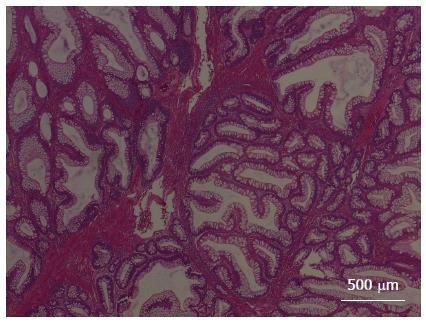
Figure 2 Hematoxylin-eosin stained image showing the pathological characteristics of the hamartomatous polyps in the infant with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
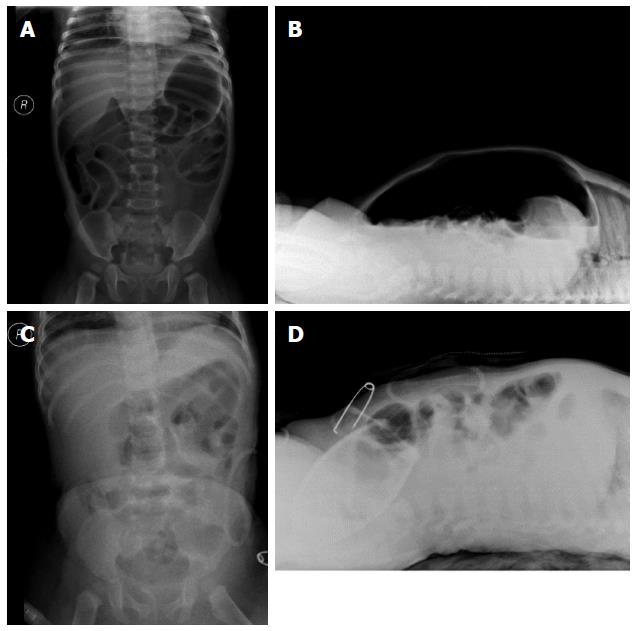
Figure 3 X-ray images of the abdomen.
A, B: Images showing the pneumoperitoneum; C, D: Images showing recovery of pneumoperitoneum after intestinal repair.
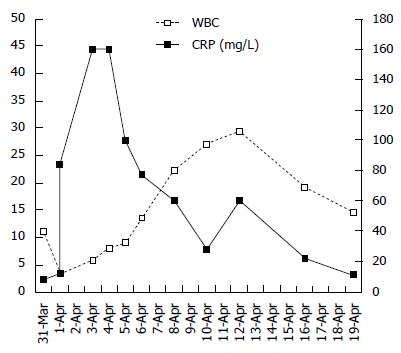
Figure 4 Changes in the white blood cell and C-reactive protein preoperatively and postoperatively.
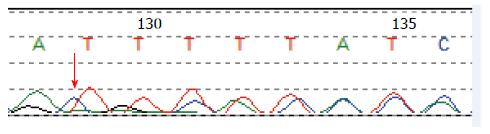
Figure 5 Infant had a frameshift mutation in codon 64 (64_65het_delAT) in exon 1.
The arrow indicates the mutation site.
- Citation: Huang ZH, Song Z, Zhang P, Wu J, Huang Y. Clinical features, endoscopic polypectomy and STK11 gene mutation in a nine-month-old Peutz-Jeghers syndrome Chinese infant. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(11): 3261-3267
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i11/3261.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3261