Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2793-2799
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2793
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2793
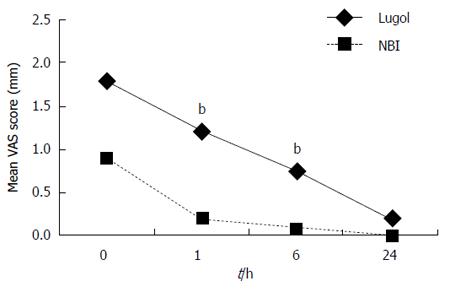
Figure 1 Mean visual analogue scale scores for heartburn at corresponding measure points immediately, 1 h, 6 h and 24 h after examination in the narrow band imaging group and Lugol group.
Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores in the narrow band imaging (NBI) group were significantly better than those in the Lugol group (P = 0.004, Lugol group vs NBI group, ANOVA for repeated measures). VAS scores for heartburn at 1 h and 6h after the examinations were better in the NBI group than those in the Lugol group (bP < 0.01, Lugol group vs NBI group, Wilcoxon’s rank sum test).
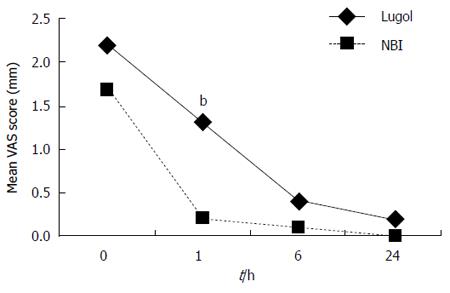
Figure 2 Mean visual analogue scale scores for retrosternal pain.
Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores in the NBI group were significantly better than those in the Lugol group (P = 0.024, Lugol group vs NBI group, ANOVA for repeated measures). VAS scores for heartburn at 1 h after the examinations were better in the NBI group than those in the Lugol group (bP < 0.01, Lugol group vs NBI group, Wilcoxon’s rank sum test).
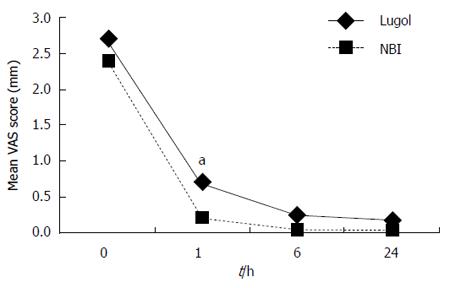
Figure 3 Mean visual analogue scale scores for dyspnea.
There were no differences between the two groups (ANOVA for repeated measures). Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for dyspnea at 1 h after the examinations were better in the NBI group than those in the Lugol group (aP < 0.05, Lugol group vs NBI group, Wilcoxon’s rank sum test).
- Citation: Yamasaki Y, Takenaka R, Hori K, Takemoto K, Kawano S, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Fujiki S, Yamamoto K. Tolerability of magnifying narrow band imaging endoscopy for esophageal cancer screening. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2793-2799
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2793