Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2015; 21(36): 10253-10261
Published online Sep 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10253
Published online Sep 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10253
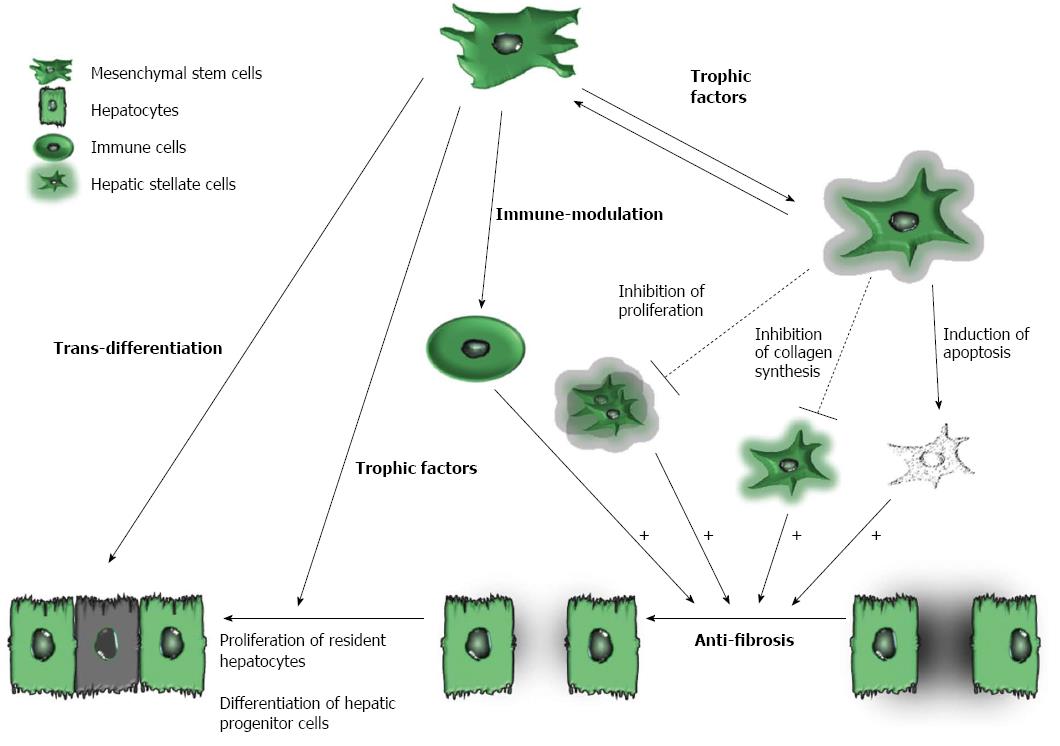
Figure 1 Potential role of mesenchymal stem cells in cirrhosis.
Potential protective mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) include the following: (1) trans-differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells; (2) suppression of immune reactions; (3) secretion of trophic factors to suppress activated hepatic stellate cells and to increase the proliferation of both resident hepatocytes and hepatic progenitor cells; and (4) anti-fibrotic action that results from the regulation of activated hepatic stellate cells and immune cells. Solid lines and dashed lines indicate stimulatory and inhibitory modifications, respectively. The + sign represents tentative stimulatory effects. The shadows represent extracellular matrix (ECM) that is secreted from hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Eom YW, Kim G, Baik SK. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for cirrhosis: Present and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(36): 10253-10261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i36/10253.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10253