Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2015; 21(31): 9317-9327
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9317
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9317
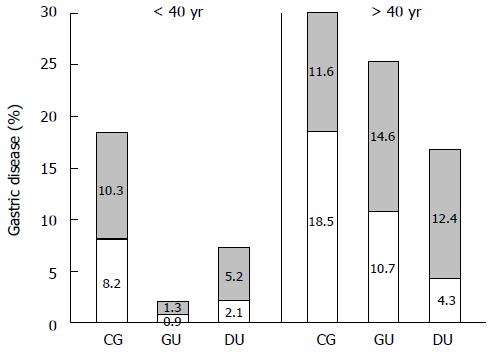
Figure 1 Gastric disease cases are more prevalent in patients > 40 years of age.
The percentages of the 233 Helicobacter pylori-positive patients are plotted according to disease diagnosis (CG: Chronic gastritis: GU: Gastric ulcer; and DU: Duodenal ulcer), age (< 40 years and > 40 years), and sex (male: White bars; female: Shaded bars).
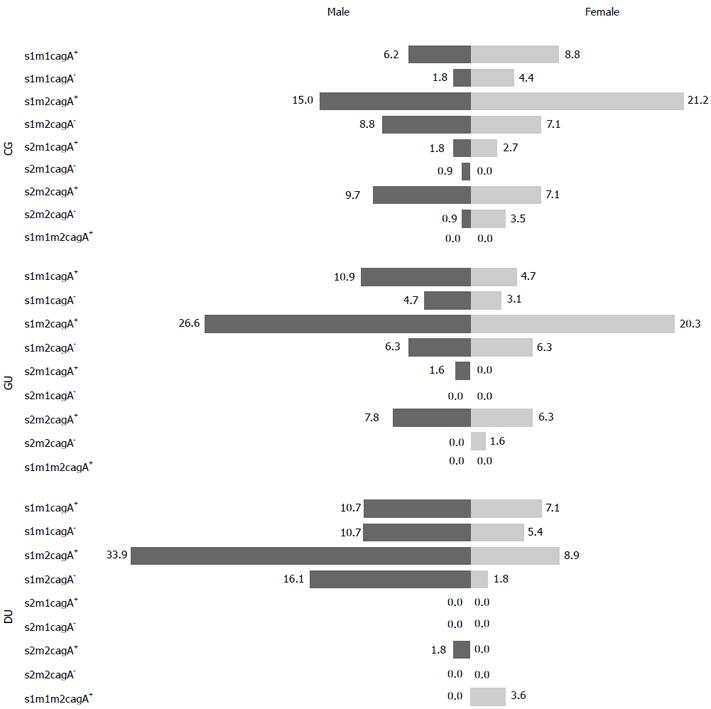
Figure 2 Distribution of Helicobacter pylori genotypes according to sex.
vacA s1m2 cagA+ was the most common genotype in both males (dark bars) and females (light bars) of all three gastric diseases. CG: Chronic gastritis; GU: Gastric ulcer; DU: Duodenal ulcer.
-
Citation: Honarmand-Jahromy S, Siavoshi F, Malekzadeh R, Nejad Sattari T, Latifi-Navid S. Reciprocal impact of host factors and
Helicobacter pylori genotypes on gastric diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(31): 9317-9327 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i31/9317.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9317