Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2015; 21(28): 8615-8628
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615
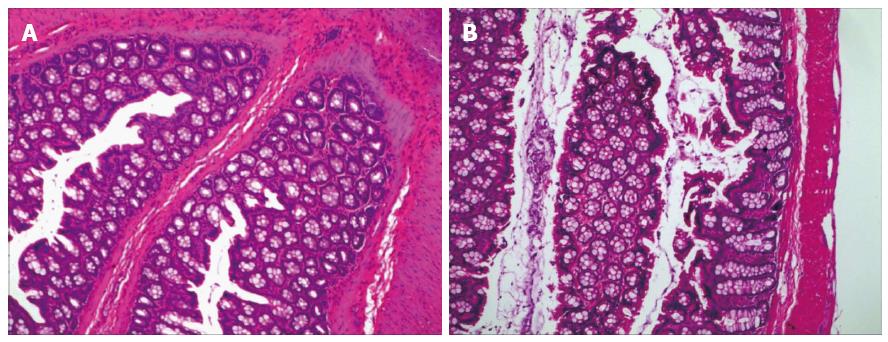
Figure 1 Effect of neonatal acetic acid treatment on colons of adult rats.
Photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections from colons of P10 normal saline-treated (A) and P10 acetic acid-treated rats (B).
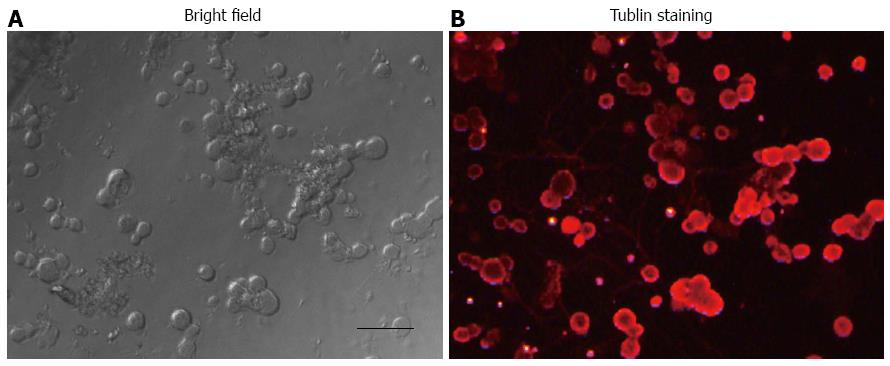
Figure 2 Bright-field of acutely dissociated dorsal root ganglion cells (A), and image of the same dorsal root ganglion cells (B) in (A) stained with β-tubulin (red).
Bar = 50 μm.
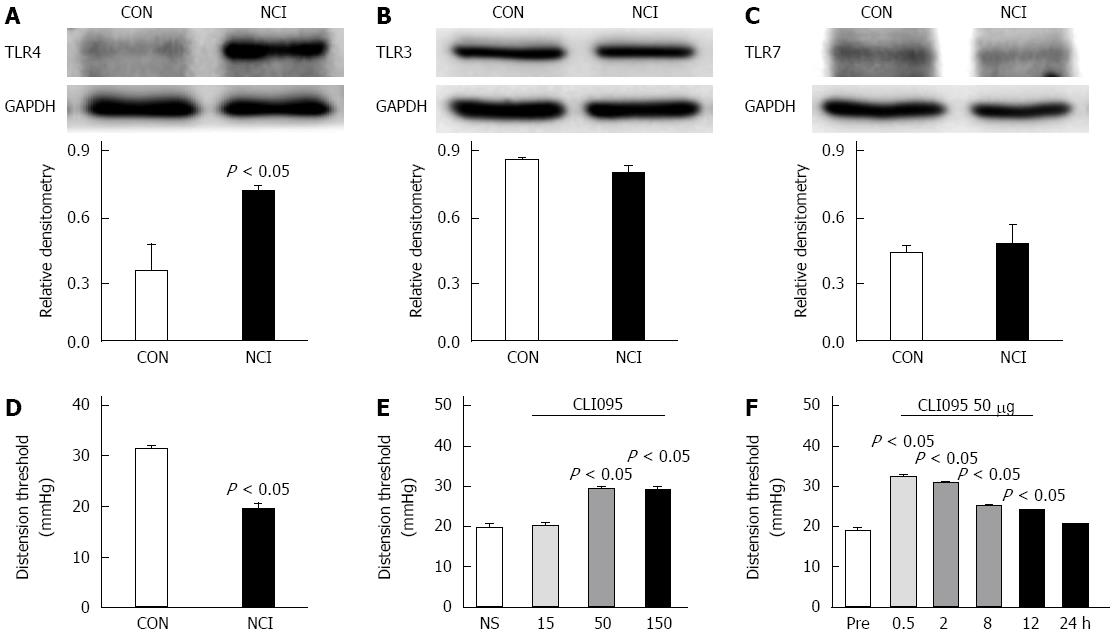
Figure 3 Neonatal colonic inflammation upregulates toll-like receptor 4 expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats with visceral hypersensitivity.
Western blotting analysis for TLR4 (A), TLR3 (B), TLR7 (C) and GAPDH (A, B, C) protein levels in T13-L2 DRGs from CON or NCI rats (n = 4 for each group); D: NCI significantly reduced the distension threshold of rats at the age of 6 wk (n = 8 for each group); E: The TLR4 selective inhibitor CLI095 significantly increased the distention threshold of NCI rats at doses of 50 and 150 μg/kg body weight. n = 8 for each group, Tukey’s post hoc test following one-way ANOVA, compared with NS; F: The time course of the effects of CLI095 at a dose of 50 μg/kg body weight, Tukey’s post hoc test following one-way repeated ANOVA. CON: Control; TLR: Toll-like receptor; NCI: Neonatal colonic inflammation.
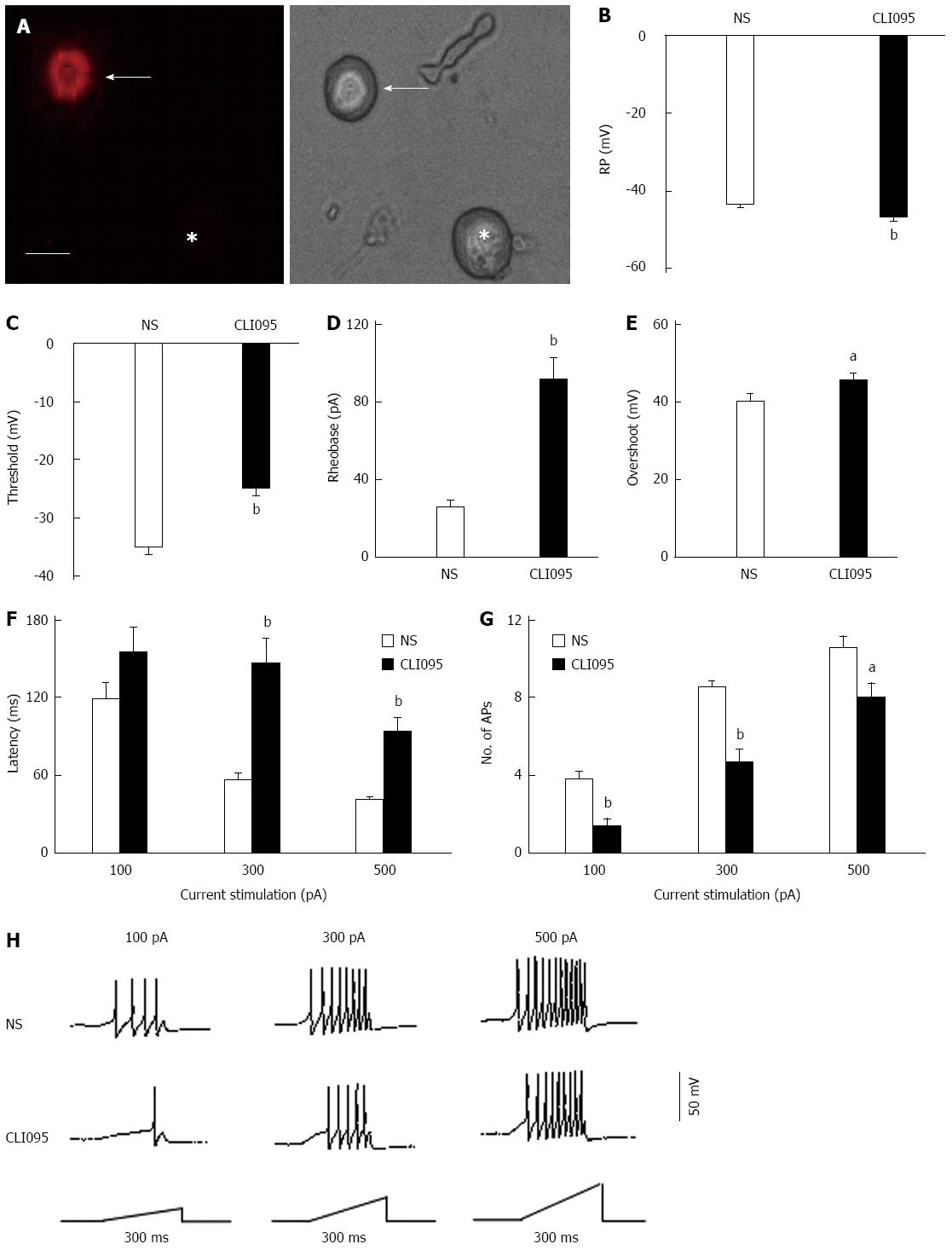
Figure 4 Toll-like receptor 4 inhibition reduces the hyperexcitability of dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the colon.
A: DiI fluorescence (left) and bright-field (right), images of acutely dissociated DRG neurons. Colon-specific neurons are shown in red in the DiI-fluorescence image; B: The administration of CLI095 significantly hyperpolarized the RP of colon-related neurons (bP < 0.01, vs NS); C: CLI095 treatment notably depolarized the AP threshold (bP < 0.01, vs NS); D: CLI095 also markedly increased rheobase (bP < 0.01, vs NS); E: CLI095 also significantly increased overshoot (aP < 0.05, vs NS); F: CLI095 treatment significantly increased the response latencies to stimulation with 300 and 500 pA current ramps (aP < 0.05, vs NS); G, H: CLI095 greatly decreased the number of APs evoked by 100, 300 and 500 pA current ramps (100 pA, bP < 0.01, vs NS, two-sample t-test; 300 pA, bP < 0.01 vs NS, two-sample t-test; 500 pA, aP < 0.05, vs NS, two-sample t-test). Bar = 50 μm. DRG: Dorsal root ganglion; NS: Normal saline; RP: Resting membrane potential; AP: Action potential.
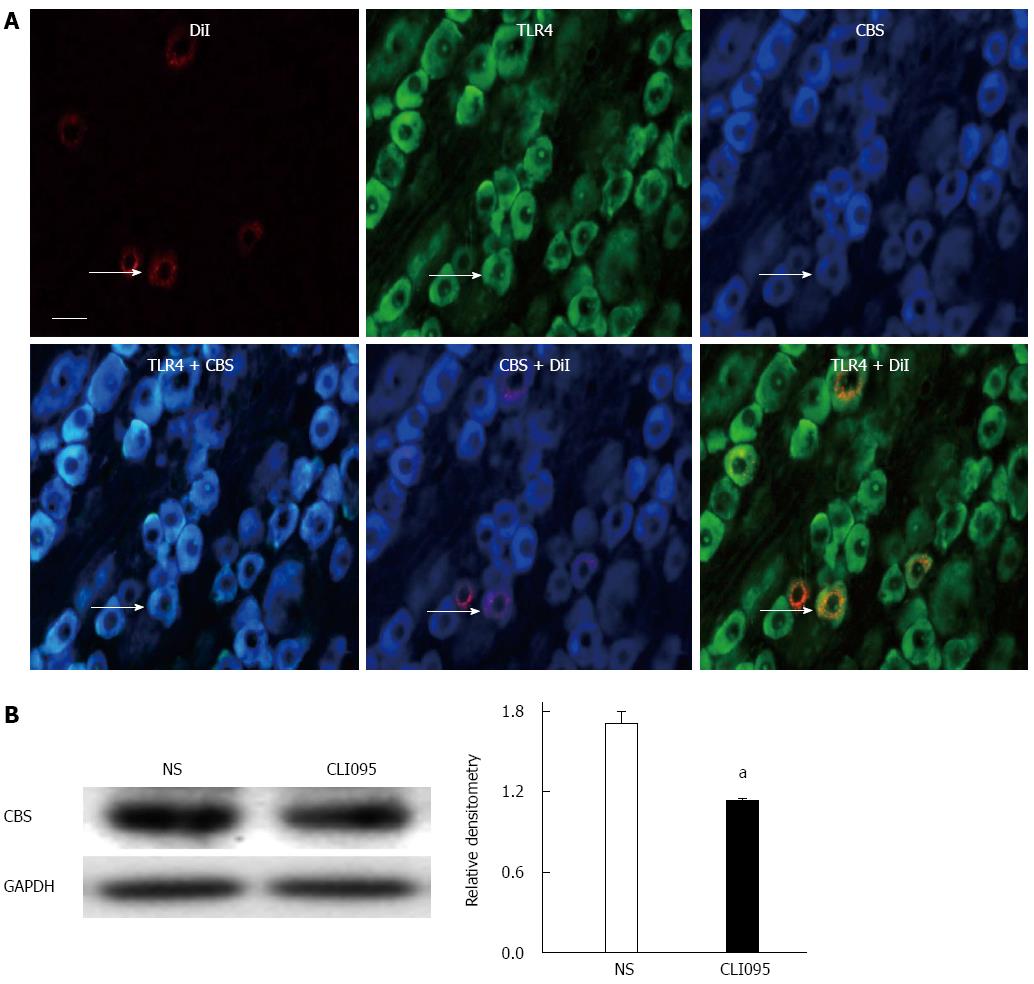
Figure 5 Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 suppresses cystathionine β synthetase expression in neonatal colonic inflammation rats.
A: Immunofluorescence analysis of TLR4 expression in CBS-positive, colon-specific DRG neurons; B: Western blotting analysis for CBS after CLI095 treatment in NCI rats. Normal saline was used as a control. n = 6 for each group, aP < 0.05, vs NS. Bar = 50 μm. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; CBS: Cystathionine β synthetase.
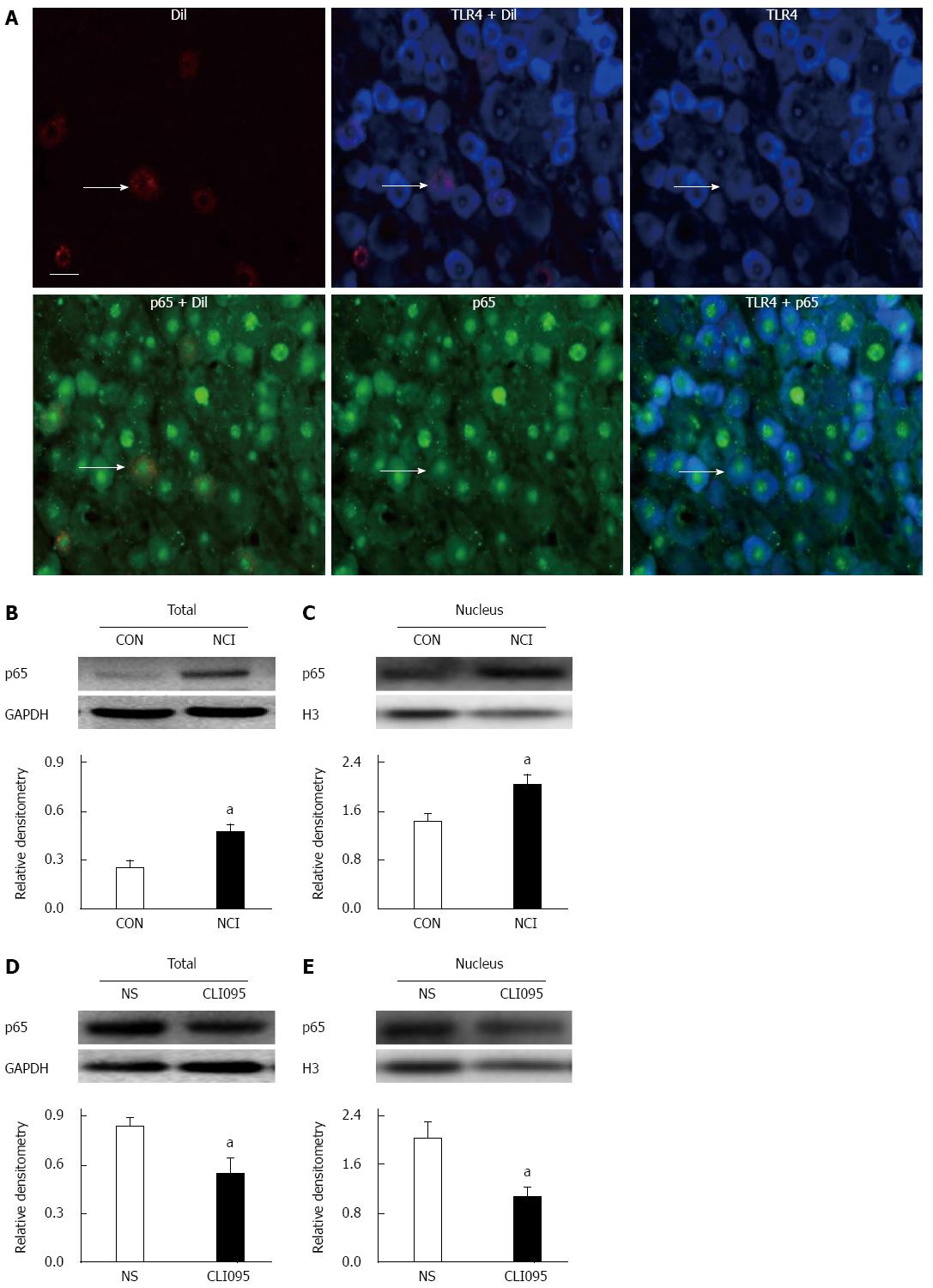
Figure 6 Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 reduces nuclear p65 expression in neonatal colonic inflammation rats.
A: Immunofluorescence analysis of TLR4 expression in p65-positive, colon-specific DRG neurons; Total protein (n = 4) (B) and nuclear protein (n = 5) (C) were used for p65 western blotting in NCI rats (both aP < 0.05, vs CON). Western blotting analysis for p65 from (D) total (n = 5) and (E) nuclear (n = 4) protein after CLI095 treatment in NCI rats (both aP < 0.05, vs CON). Bar = 50 μm.
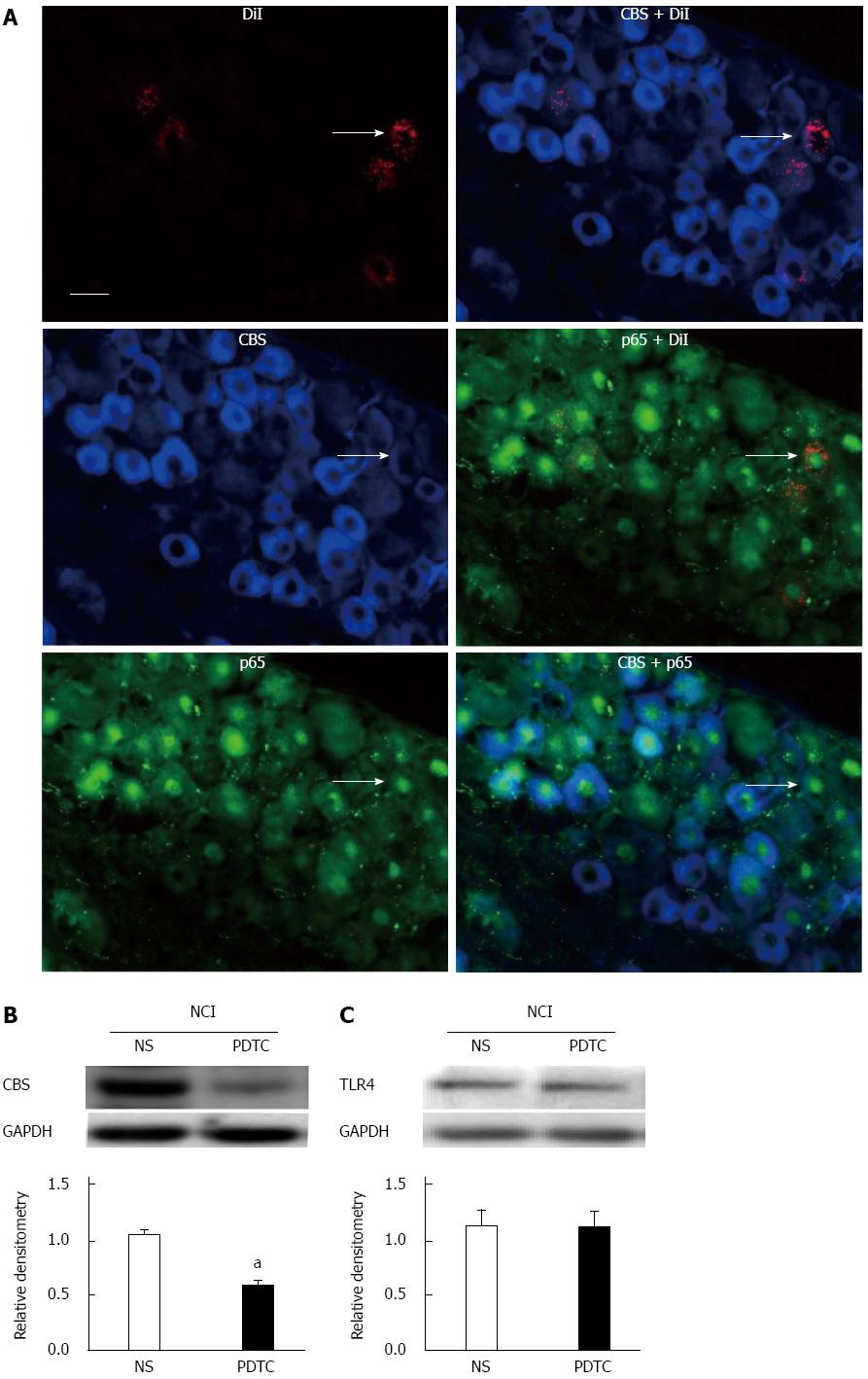
Figure 7 Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB suppresses cystathionine β synthetase expression.
A: Immunofluorescence analysis of p65 expression in CBS-positive, colon-specific DRG neurons. Bar = 50 μm; B: Western blotting analysis for CBS expression after PDTC treatment in NCI rats (n = 6 for each group, aP < 0.05, vs NS); C: In contrast, PDTC treatment did not significantly alter TLR4 expression in NCI rats (n = 6 for NS, n = 7 for PDTC, two-sample t-test). PDTC: Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.
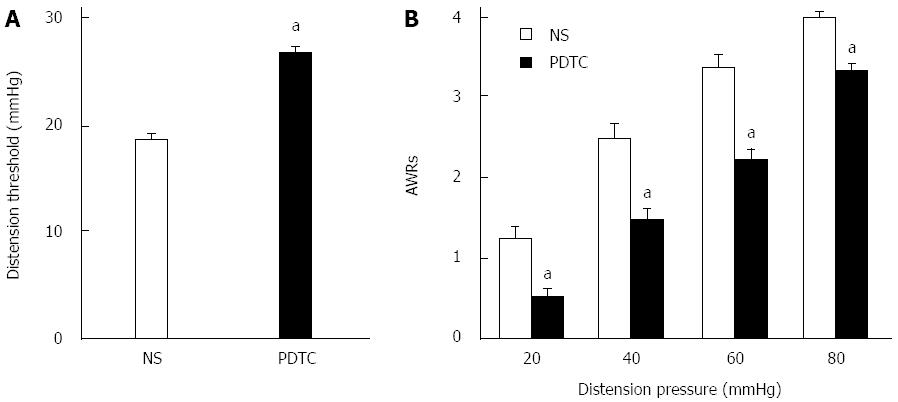
Figure 8 Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB attenuates visceral hypersensitivity.
A: PDTC treatment greatly increased the distention threshold in NCI rats (n = 6 for each group, aP < 0.05, vs NS); B: PDTC significantly reduced the abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores of NCI rats (n = 6 for each group, aP < 0.05, vs NS).
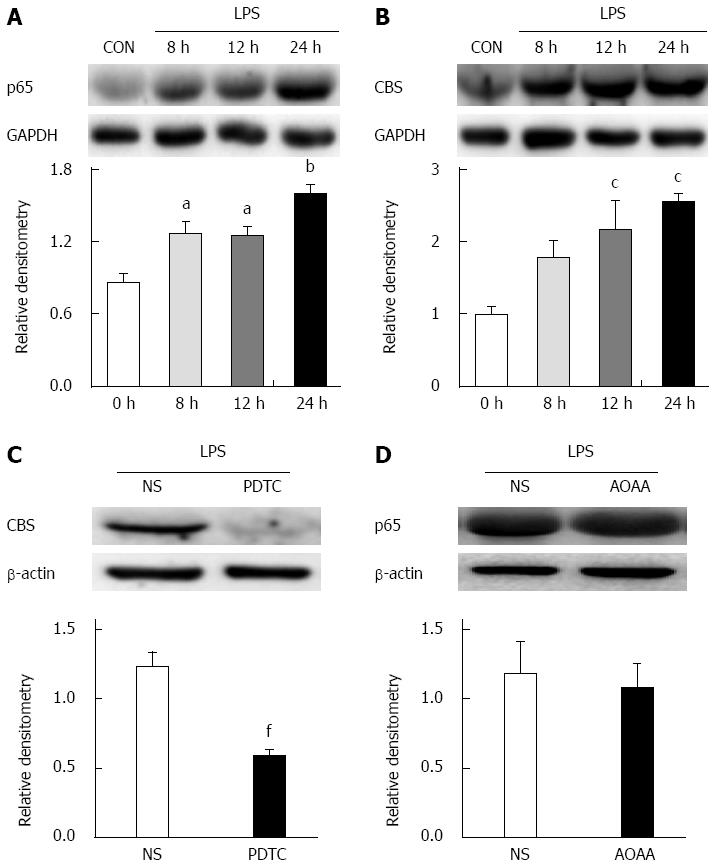
Figure 9 Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB reverses toll-like receptor 4-induced upregulation of cystathionine β synthetase expression in cultured dorsal root ganglion cells.
A: Western blotting analysis for p65 expression in DRG neurons incubated with LPS for 8 h, 12 h and 24 h (n = 3 for each group, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs CON; B: LPS notably upregulated CBS expression at 12 h and 24 h (n = 3 for each group, cP < 0.05, compared with CON); C: PDTC significantly downregulated CBS expression (n = 4 for each group, fP < 0.01, vs NS, two-sample t-test); D: AOAA did not alter the upregulation of p65 induced by LPS incubation for 12 h. AOAA: O-(carboxymethyl)-hydroxylamine hemihydrochloride.
- Citation: Yuan B, Tang WH, Lu LJ, Zhou Y, Zhu HY, Zhou YL, Zhang HH, Hu CY, Xu GY. TLR4 upregulates CBS expression through NF-κB activation in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome with chronic visceral hypersensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(28): 8615-8628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i28/8615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615