Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2015; 21(17): 5336-5344
Published online May 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5336
Published online May 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5336
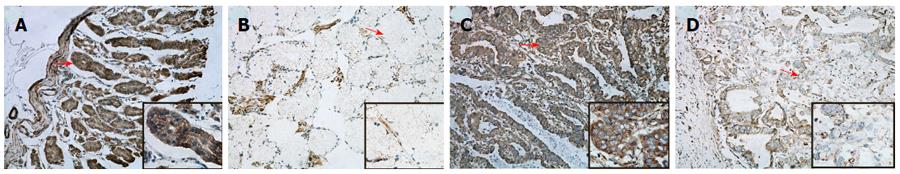
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining of pyruvate dehydrogenase in gastric samples.
The typical diffuse cytoplasmic staining of the protein can be found in many gastric carcinoma and normal gastric tissues. A: PDH positivity was observed in the cytoplasm of NNM; B: PDH negativity was observed in NNM; C: PDH positivity was observed in the cytoplasm of well-differentiated gastric cells; D: Low expression of PDH was observed in gastric well-differentiated cancer cells. PDH: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; NNM: Non-neoplastic mucosa.
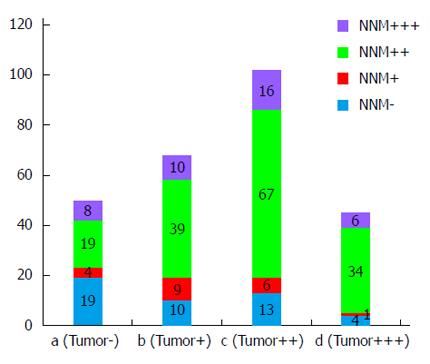
Figure 2 Relationship between pyruvate dehydrogenase expression level in cancer and non-neoplastic mucosa tissue from the same patient.
The results showed that 123 patients had pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) co-expression (GC+/NNM+), 24 patients had GC+/NNM- single expression, 76 patients had GC-/NNM+ single expression, and 42 patients had double PDH negative expression; 147 cases (55.47%) showed positive PDH staining (Tumor ++ and Tumor +++) and 118 (44.53%) specimens displayed negative staining (Tumor - and Tumor +). PDH expression was much higher in the NNM tissue with positive staining in 199 (75.09%) specimens and negative staining in 66 (24.91%) specimens; P < 0.001. NNM: Non-neoplastic mucosa; GC: Gastric cancer.
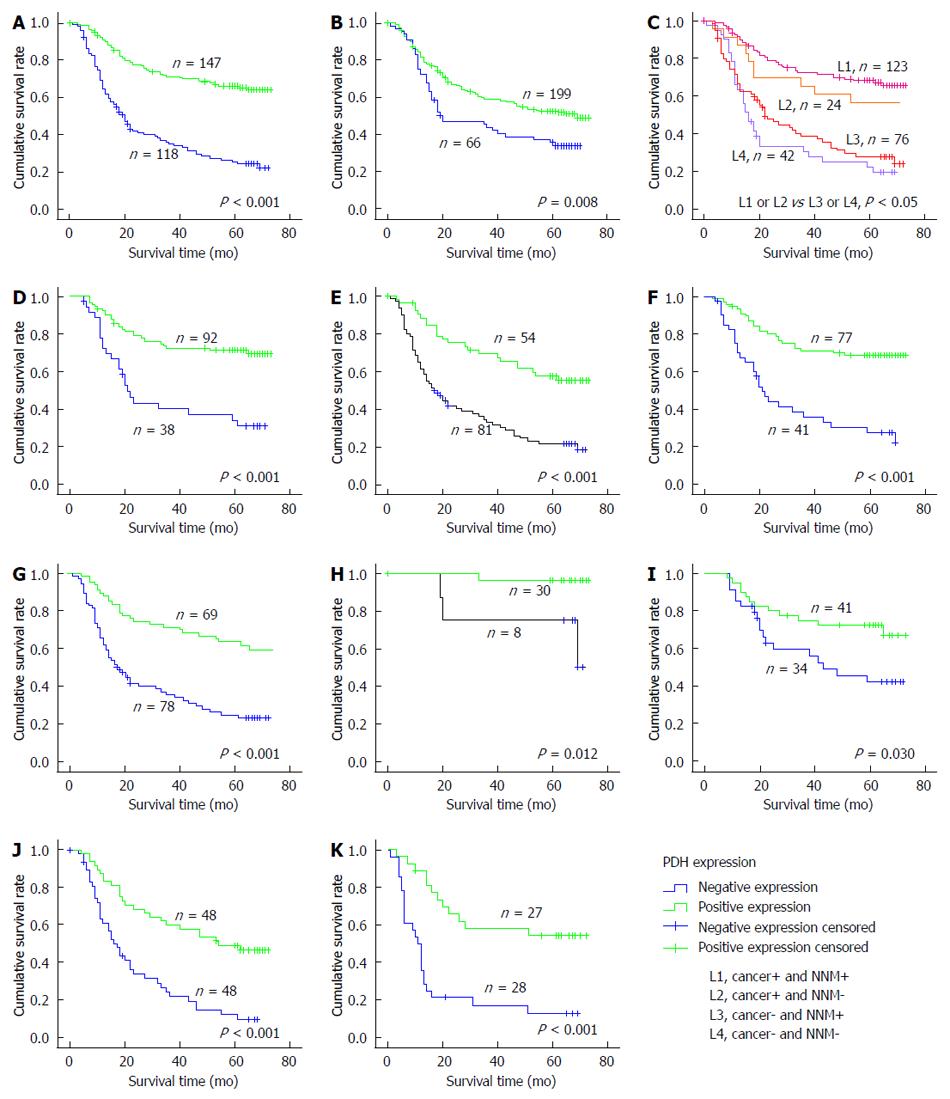
Figure 3 Correlation between pyruvate dehydrogenase expression and prognosis of gastric cancer patients.
Kaplan-Meier curves for cumulative survival of patients with gastric cancer (GC) according to GC tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) expression shows that PDH expression in GC (A), in non-neoplastic mucosa (NNM) (B) and in both GC and NNM (C) was significantly associated with better overall survival. The Kaplan-Meier curves for cumulative survival rate stratified by Lauren grade, histological type and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage also show that PDH expression was significantly associated with a better overall survival in each subtype of GC: intestinal-type GC (D), diffuse-type GC (E), differentiated type GC (F), undifferentiated type GC (G), and TNM stage I (H), II (I), III (J), and IV (K) subgroups.
- Citation: Sun XR, Sun Z, Zhu Z, Guan HX, Li CY, Zhang JY, Zhang YN, Zhou H, Zhang HJ, Xu HM, Sun MJ. Expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase is an independent prognostic marker in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(17): 5336-5344
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i17/5336.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5336