Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2014; 20(5): 1340-1347
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1340
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1340
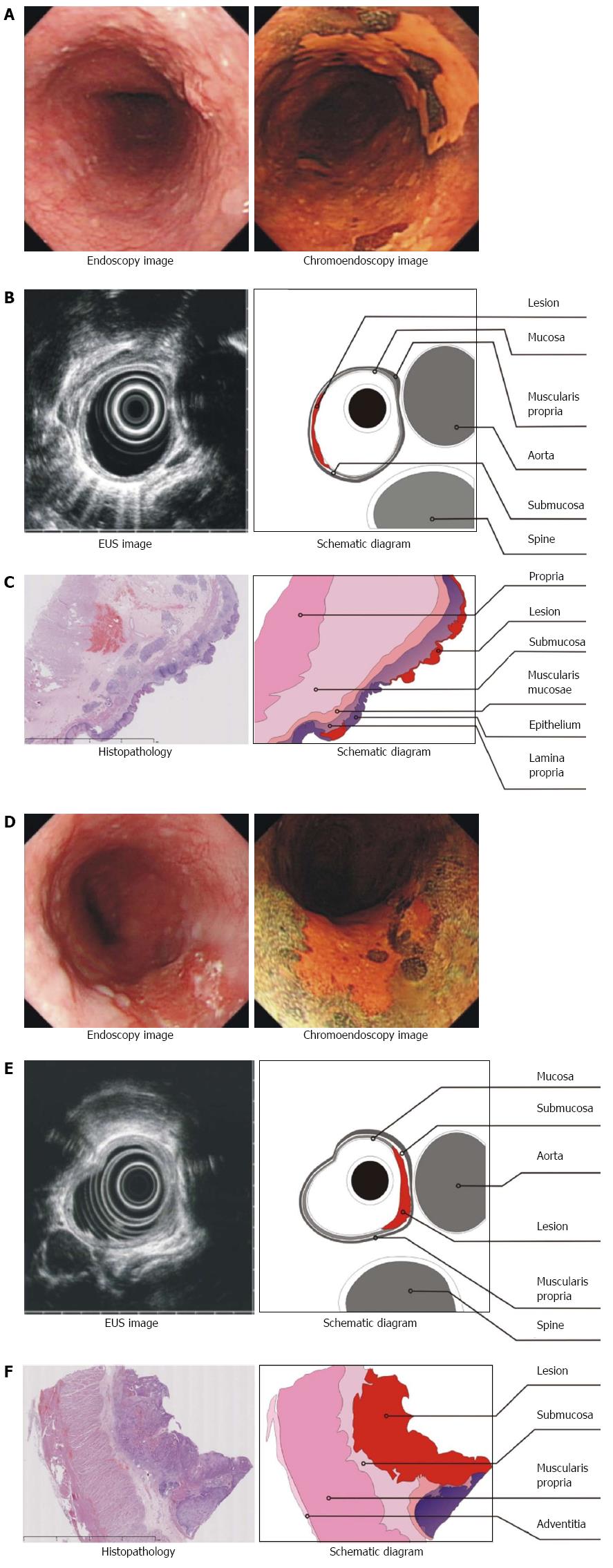
Figure 1 Images of patients with stage T1a or T1b early esophageal squamous carcinoma.
A-C: Stage T1a early esophageal squamous carcinoma; A: The lesion visualized by endoscopy and chromoendoscopy with iodine staining; B: The lesion visualized by ultrasonography. The lesion appeared as a hypoechoic line in the first layer, and the outside edge of the second layer was smooth; these two layers represent the mucosa and muscularis mucosa, and thus, the lesion was limited to the mucosa. The third layer (hyperechoic), which represented the submucosa, was intact; C: The post-operative pathology revealed that the tumor had invaded the lamina propria; therefore, this case was confirmed as T1a stage; D-F: Stage T1b early esophageal squamous carcinoma; D: The lesion visualized by endoscopy and chromoendoscopy with iodine staining; E: The lesion visualized by ultrasonography appeared as a hypoechoic line not only in the first and second layers but also in the third layer (hyperechoic), which represents the submucosa; the fourth layer (hypoechoic), which represents the muscularis propria, was intact; F: The postoperative pathology confirmed that the lesion covered the mucosa and had invaded into the submucosa; therefore, the patient was staged as T1b.
- Citation: He LJ, Shan HB, Luo GY, Li Y, Zhang R, Gao XY, Wang GB, Lin SY, Xu GL, Li JJ. Endoscopic ultrasonography for staging of T1a and T1b esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(5): 1340-1347
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i5/1340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1340