Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
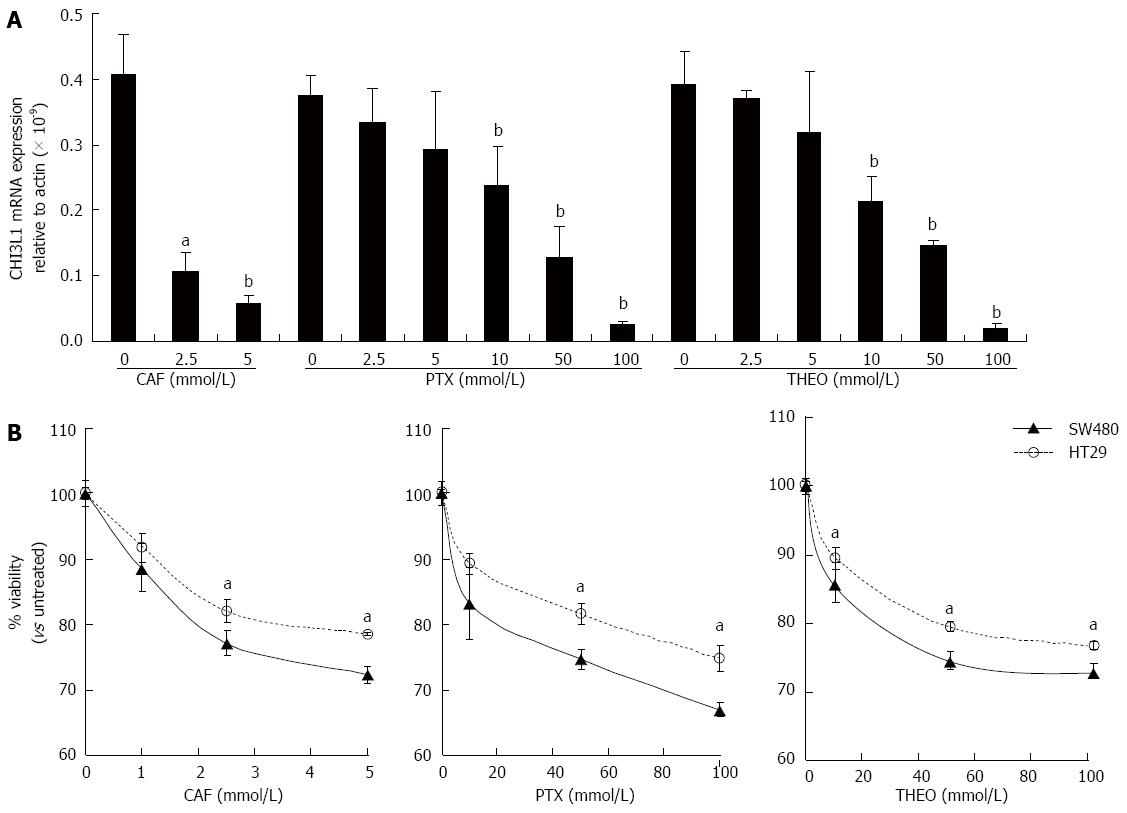
Figure 1 Caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline down-regulate chitinase 3-like 1 mRNA expression and reduce cell viability in human colonic epithelial cells.
A: SW480 cells were stimulated with caffeine (CAF) at 0, 2.5 or 5 mmol/L or pentoxifylline (PTX) or theophylline (THEO) at 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 50 or 100 mmol/L for 48 h and detected for the chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) mRNA expression by quantitative-polymerase chain reaction. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control; B: SW480 and HT29 cells were treated with either CAF (0, 1, 2.5 or 5 mmol/L), PTX or THEO (0, 10, 50 or 100 mmol/L) for 48 h and cell viability were determined using trypan blue exclusion test. CAF, PTX and THEO were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, United States). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
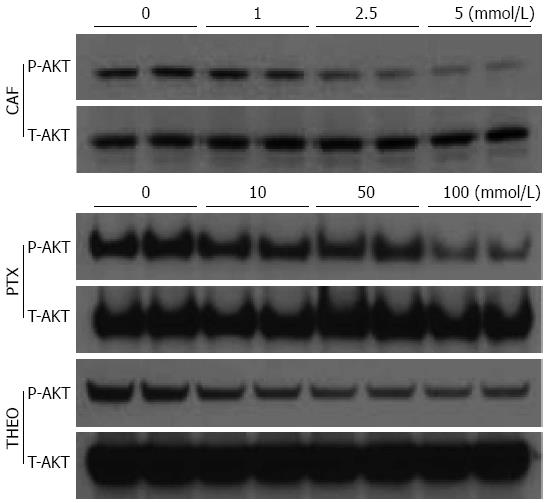
Figure 2 Caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline suppress protein kinase B signaling pathway activation in mouse colonic epithelial cells.
CMT93 mouse colonic epithelial cells were stimulated with caffeine (CAF) (0, 1, 2.5 or 5 mmol/L), pentoxifylline (PTX) or theophylline (THEO) (0, 10, 50 or 100 mmol/L) for 48 h. Twenty five micro grams of total protein were resolved using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Western blot using anti-phospho/total protein kinase B (AKT) Abs purchased from cell signaling technology (Danvers, MA, United States) .
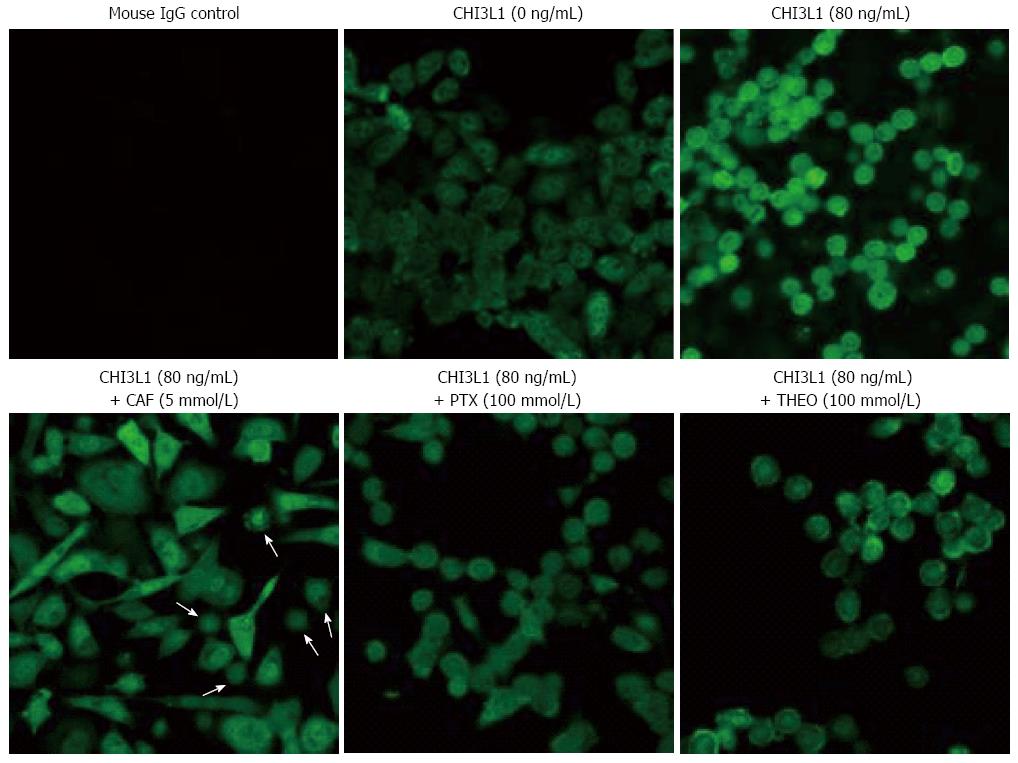
Figure 3 Caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline inhibit β-catenin nuclear translocation with different degrees.
SW480 colonic epithelial cells were cultured on lab-tec chamber slide. After reached to 90% confluency, the cells were stimulated with or without purified human chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) (80 ng/mL) in combination with caffeine (CAF) (5 mmol/L), pentoxifylline (PTX) (100 mmol/L) or theophylline (THEO) (100 mmol/L) for 24 h. Human CHI3L1 protein was purchased from Quidel (San Diego, CA). β-catenin was then detected using mouse anti-human β-catenin monoclonal primary Ab (BD Biosciences, CA) and FITC-horse anti-mouse Immunoglobulin G (Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA) and analyzed by confocal microscope (magnification, objective 40 ×). White arrows show the limited numbers of completely nuclear translocated β-catenin positive cells after caffeine treatment.
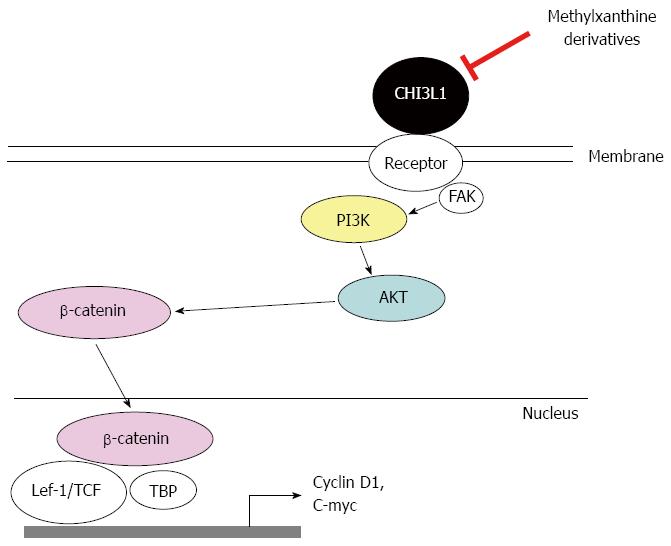
Figure 4 Schematic representation of chitinase 3-like 1-associated β-catenin activation signaling pathway, which is inhibited by methylxanthine derivatives.
Binding of extracellular chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) to a putative receptor on plasma membrane activates the intracellular phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway, which leads to β-catenin activation by translocating this protein from cytoplasm into nucleus. Methylxanthine derivatives, including caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline, directly down-regulate CHI3L1 mRNA expression and inhibit CHI3L1 protein functions, leading to reduced CHI3L1-associated AKT activation and prevent down-stream β-catenin nuclear translocation with different degrees of efficacy.
- Citation: Lee IA, Kamba A, Low D, Mizoguchi E. Novel methylxanthine derivative-mediated anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i5/1127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127