Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18177-18188
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18177
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18177
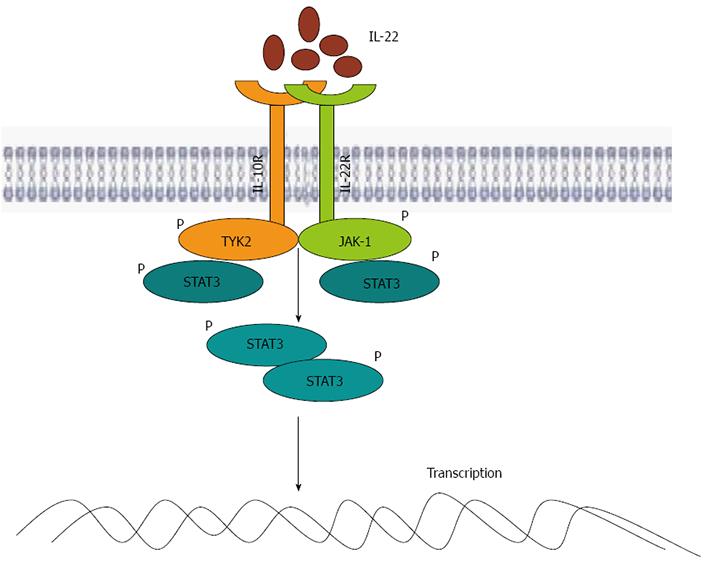
Figure 1 Interleukin-22 signaling pathway.
IL-22 binds to a heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-10R2 and IL-22R1, activating JAK1 and TYK2, which self-phosphorylate, resulting in binding and phosphorylation of STAT3. Then, STAT3 translocates to the nucleus and induces target genes. IL: Interleukin; JAK: Janus kinase; TYK: Tyrosine protein kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
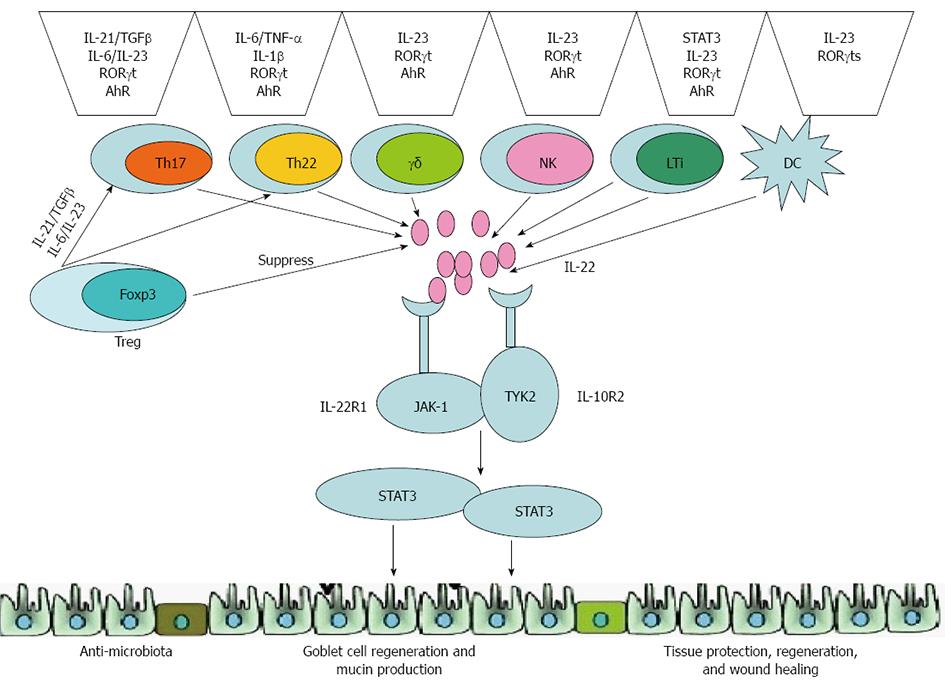
Figure 2 Protective function of interleukin-22 in inflammatory bowel disease.
In the intestine, innate and adaptive immune cells, cytokines and many of the transcriptional factors can induce and regulate expression of IL-22. Through activation of STAT3 signaling cascades, IL-22 induces antimicrobial molecules and proliferative and antiapoptotic pathways, and helps regenerate goblet cells and produce mucin proteins, which could prevent tissue damage and aid in its repair. IL: Interleukin; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
- Citation: Li LJ, Gong C, Zhao MH, Feng BS. Role of interleukin-22 in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18177-18188
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18177