Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2014; 20(32): 11297-11304
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297
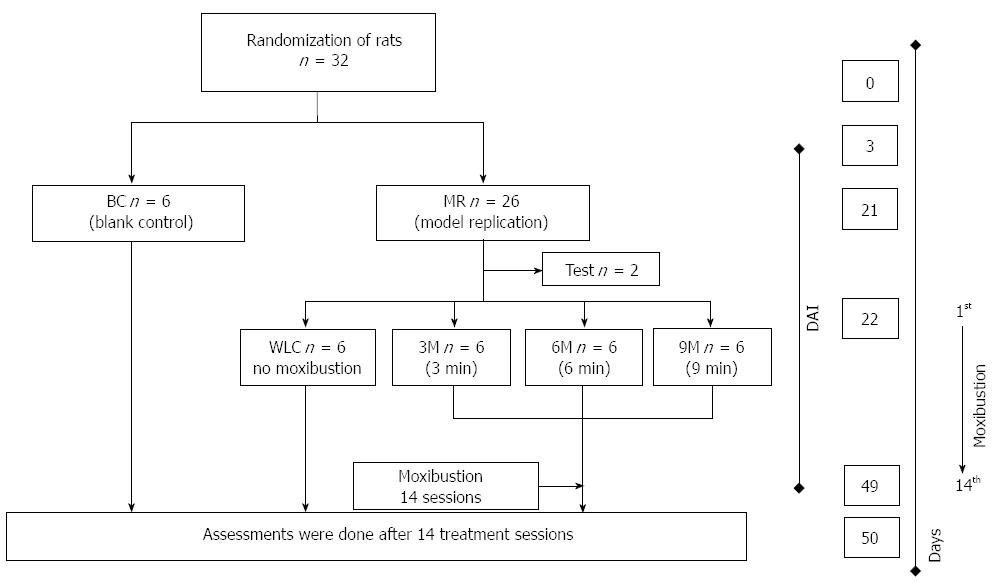
Figure 1 Study design of moxibustion treatment in ulcerative colitis rats.
Blank control (BC) indicates control group with normal rats. Model replication (MR) is rat model of ulcerative colitis (UC). Waiting list control (WLC) is the control group in which UC rats did not receive moxibustion treatment. 3-min moxibustion (3M), 6-min moxibustion (6M) and 9-min moxibustion (9M) are 3-moxa, 6-moxa, and 9-moxa groups in which UC rats received different durations of moxibustion (3, 6 and 9 min) in each session (2 d). The whole moxibustion treatment course included 14 sessions from days 22 to 49. DAI: Disease activity index.
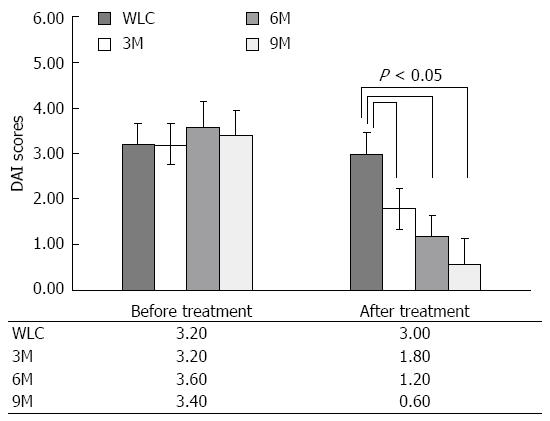
Figure 2 Comparison of disease activity index in ulcerative colitis rats before and after moxibustion treatment.
Ulcerative colitis (UC) rats in the waiting list control (WLC) group did not receive moxibustion treatment. UC rats in the 3-min moxibustion (3M), 6-min moxibustion (6M) and 9-min moxibustion (9M) groups received 3, 6 and 9 min, respectively, in each treatment session. Values are the average of 14 sessions. Before treatment, there was no significant difference in disease activity index (DAI) among the groups. After treatment, significant differences (P < 0.05) in disease activity were found. In the 3M, 6M and 9M groups, DAI markedly decreased after moxibustion treatment. Error bar represents SD, and significance was assessed using least significant difference.
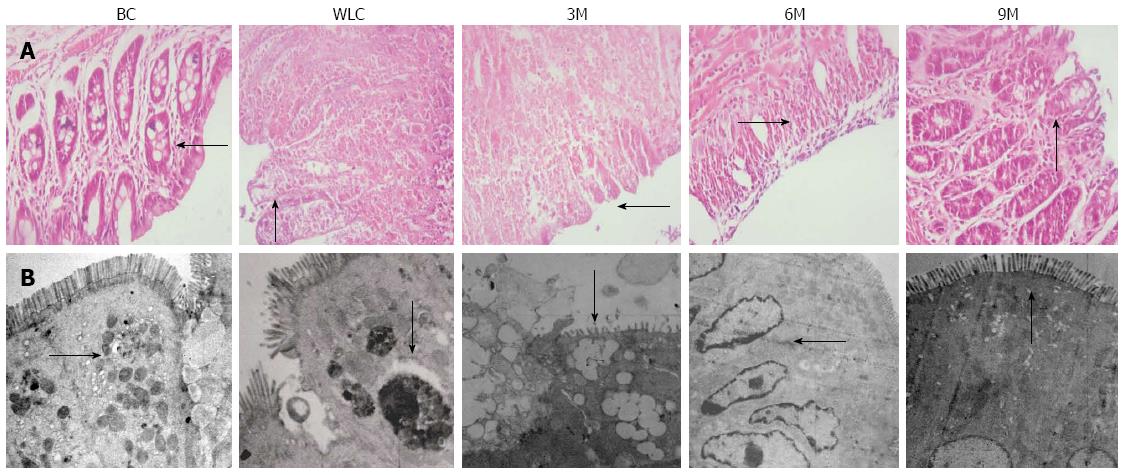
Figure 3 Histological features and morphology of colonic tissue.
A: Histological analysis of colonic tissue sections stained with HE. The finer details of the epithelial cells can be seen clearly; B: Morphology of colonic mucosal epithelia observed by electron microscopy. From left to right in both A and B: Blank control (BC), waiting list control (WLC), 3-min moxibustion (3M), 6-min moxibustion (6M) and 9-min moxibustion (9M) groups. Treatment in the 9M group gave the best results, which were close to that of the normal rats without ulcerative colitis. Black arrow: Representative features of colonic tissue (magnification: A: 400 ×; B: 2000 ×).
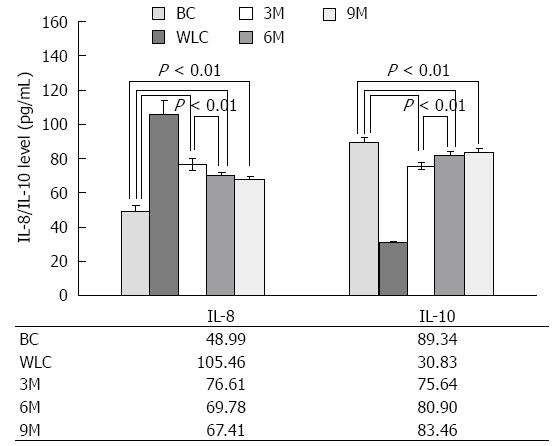
Figure 4 Interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 serum levels in normal rats (blank control), ulcerative colitis rats without (waiting list control) and with (3-min, 6-min and 9-min) moxibustion treatment.
The measurements were done by ELISA. Moxibustion treatment increased secretion of interleukin (IL)-8 and inhibited that of IL-10. Significant differences in IL-8 and IL-10 of 3-min moxibustion (3M) vs blank control (BC), 6-min moxibustion (6M) vs BC, 9-min moxibustion (9M) vs BC, 3M vs waiting list control (WLC), 6M vs WLC, and 9M vs WLC were found with P < 0.01 for each comparison. For parallel comparisons, the differences in IL-8 and IL-10 levels were significant for 3M vs 6M (P < 0.01) and 3M vs 9M (P < 0.01). For better presentation, only partial comparisons are marked here. For 6M vs 9M, although the difference was no longer significant (P > 0.05), the tendency for IL-8 level to decrease and IL-10 level to increase was still noticeable.
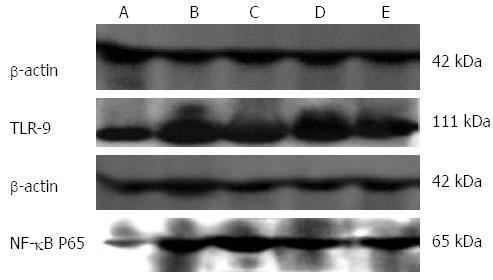
Figure 5 Expression of Toll-like receptor 9 and nuclear factor-κB p65 in colonic tissue of rats.
A-E corresponds to the expression in colonic tissue of rats from blank control, waiting list control, 3-min, 6-min and 9-min moxibustion groups, respectively. Extracts of colonic tissues (approximately 25 μg) from normal or ulcerative colitis rats were assessed by sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and were probed with Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 as well as nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 antibody. Antibody against β-actin was used as a loading control.
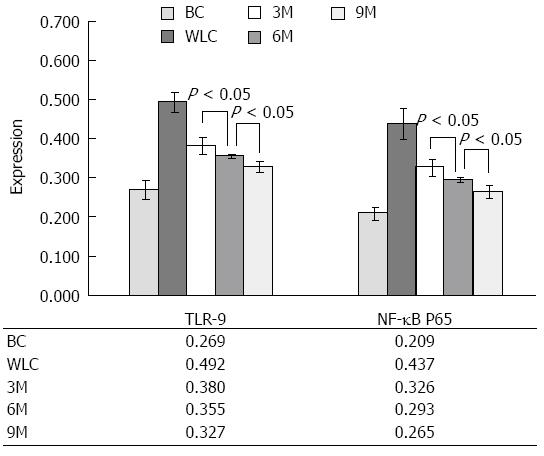
Figure 6 Effect of moxibustion on expression of Toll-like receptor 9 as well as nuclear factor-κB p65.
Expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)9 as well as nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 showed significant differences among all moxibustion-treated groups [3-min moxibustion (3M), 6-min moxibustion (6M) and 9-min moxibustion (9M)] and moxibustion-free groups [blank control (BC) and waiting list control (WLC)] with P < 0.01 for each comparison. For parallel comparisons between the moxibustion-treated groups, the differences were still significant for 3M vs 6M (P < 0.05), 3M vs 9M (P < 0.05), and 6M vs 9M (P < 0.05). The results for ulcerative colitis (UC) rats in the 9M group were the closest to the normal rats (BC). The results implied that 9 min moxibustion treatment resulted in the best improvement of UC within the physical tolerance of UC rats.
- Citation: Han Y, Ma TM, Lu ML, Ren L, Ma XD, Bai ZH. Role of moxibustion in inflammatory responses during treatment of rat ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(32): 11297-11304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i32/11297.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297