Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2014; 20(30): 10457-10463
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10457
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10457
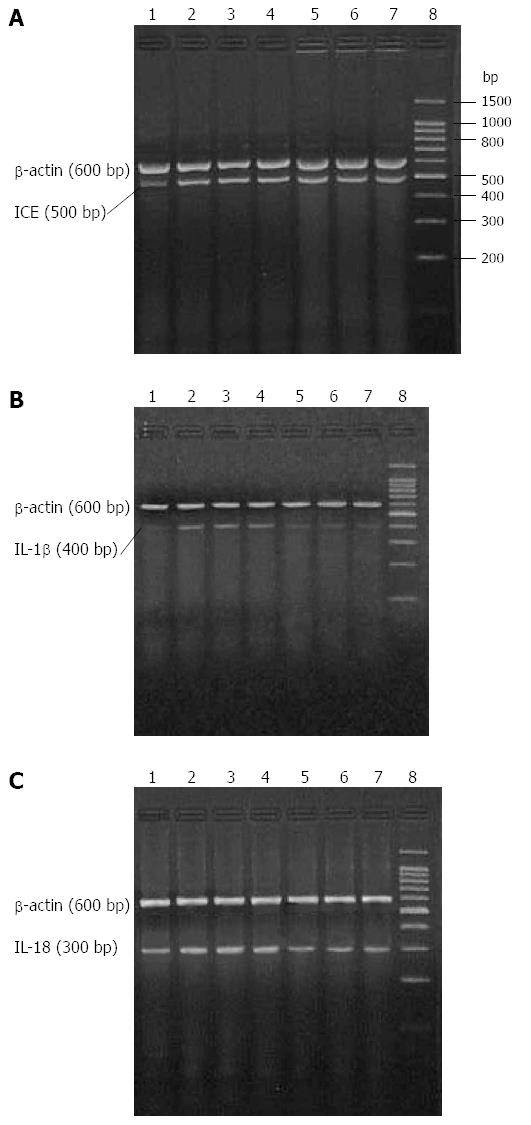
Figure 1 Expression levels of renal caspase-1, interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 mRNAs in cases of acute pancreatitis.
Agarose gel electrophoresis revealed mobility and size of real-time polymerase chain reaction products for A: Caspase-1; B: Interleukin (IL)-1β; and C: IL-18 in kidney tissues from healthy controls (HC), severe acute pancreatitis (SAP-S) rats treated with saline, and SAP rats treated with a caspase-1 inhibitor (SAP-ICE-I). The DNA fragments from each group were of expected size. Lane 1: HC; lanes 2-4: SAP-S; lanes 5-7: SAP-ICE-I; lane 8: Marker.
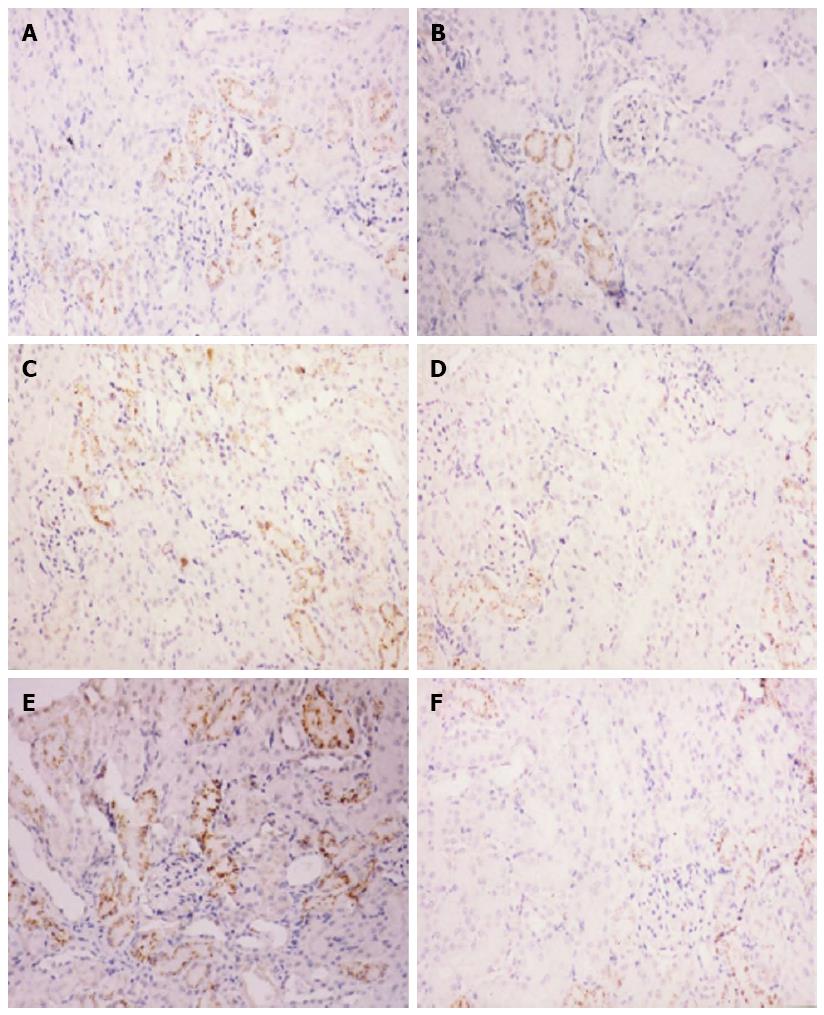
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical detection of interleukin-1β.
Representative micrographs showing interleukin (IL)-1β immunoreactivity in hematoxylin counterstained kidney sections from animals with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) (magnification × 200). Saline treatment A: 6 h; C: 12 h; and E: 18 h after SAP induction. Caspase-1 inhibitor treatment B: 6 h; D: 12 h; and F: 18 h after SAP induction.
- Citation: Zhang XH, Li ML, Wang B, Guo MX, Zhu RM. Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates acute renal injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(30): 10457-10463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i30/10457.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10457