Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2014; 20(3): 804-813
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.804
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.804
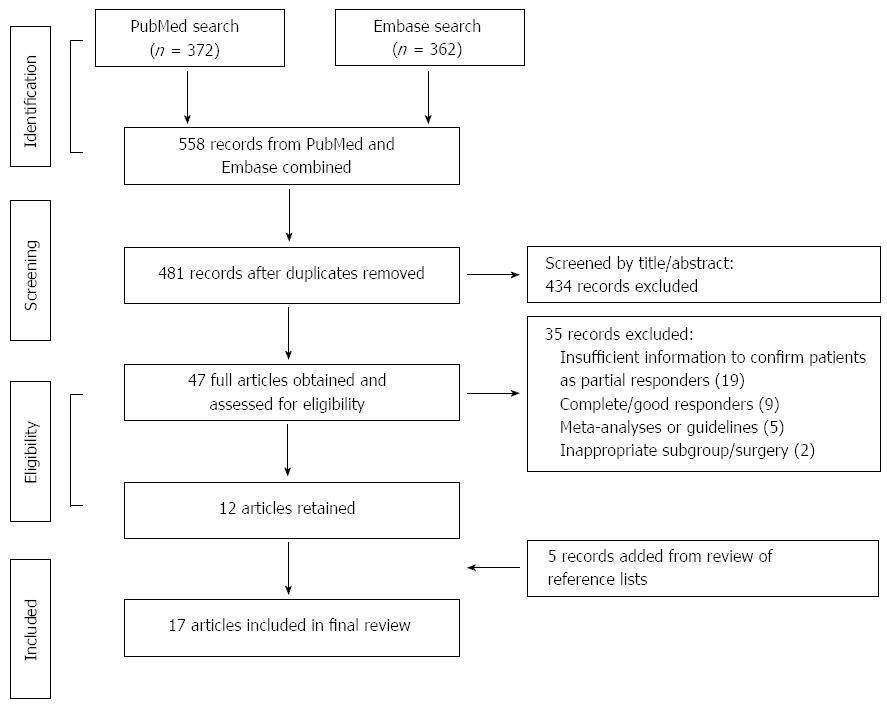
Figure 1 Search strategy.
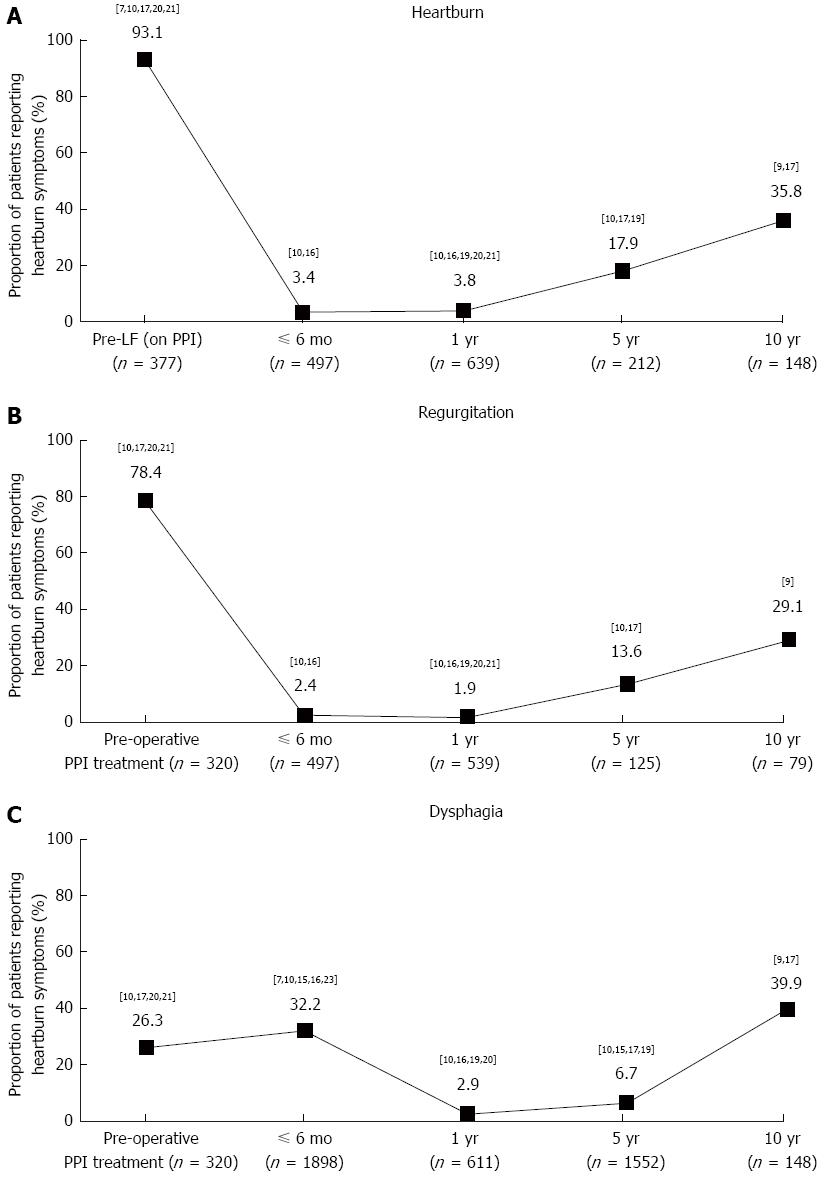
Figure 2 Proportion of patients reporting heartburn, regurgitation and dysphagia symptoms during preoperative proton pump inhibitor treatment and at follow-up after laparoscopic fundoplication.
Superscript numbers indicate individual studies. A: Heartburn; B: Regurgitation; C: Dysphagia.
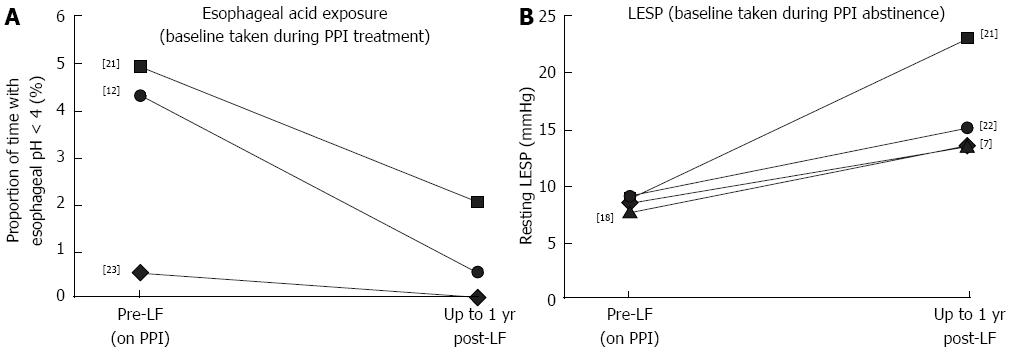
Figure 3 Effects of laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal acid exposure (assessed by ambulatory 24-h H measurement) and resting lower esophageal sphincter pressure (assessed by esophageal manometry).
Data are shown for before and after laparoscopic fundoplication (LF) (follow-up period: 0.25-1 year). A: Esophageal acid exposure [baseline taken during proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) treatment]; B: Lower esophageal sphincter pressure (LESP) (baseline taken during PPI abstinence).
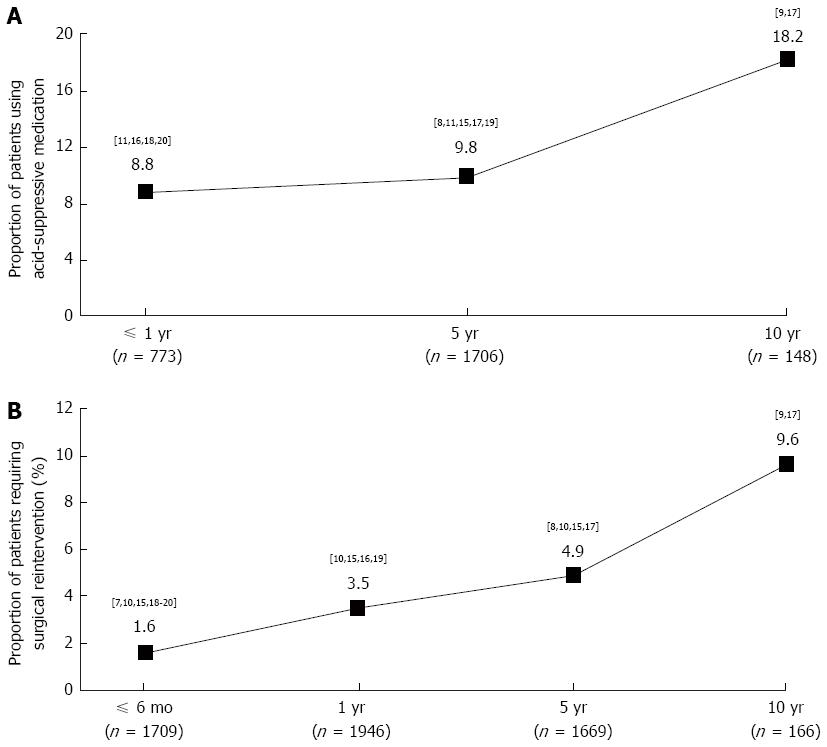
Figure 4 Proportion of patients using acid-suppressive medication (A) and requiring surgical reintervention (B) after laparoscopic fundoplication.
- Citation: Lundell L, Bell M, Ruth M. Systematic review: Laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease in partial responders to proton pump inhibitors. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(3): 804-813
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i3/804.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.804