Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7955-7963
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7955
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7955
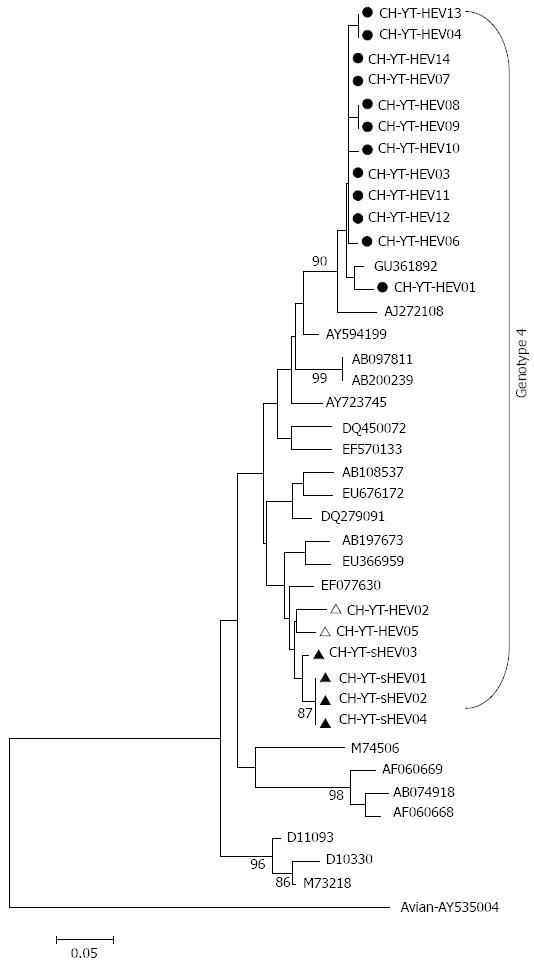
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree based on partial ORF2 sequences.
An avian hepatitis E virus (HEV) strain (AY535004) is included as an outgroup. The strains CH-YT-HEV01 to CH-YT-HEV12 were isolated from human patients, and the strains CH-YT-HEV13 and CH-YT-HEV14 were isolated from the general human population. The strains CH-YT-sHEV01 to CH-YT-sHEV04 were isolated from swine bile.
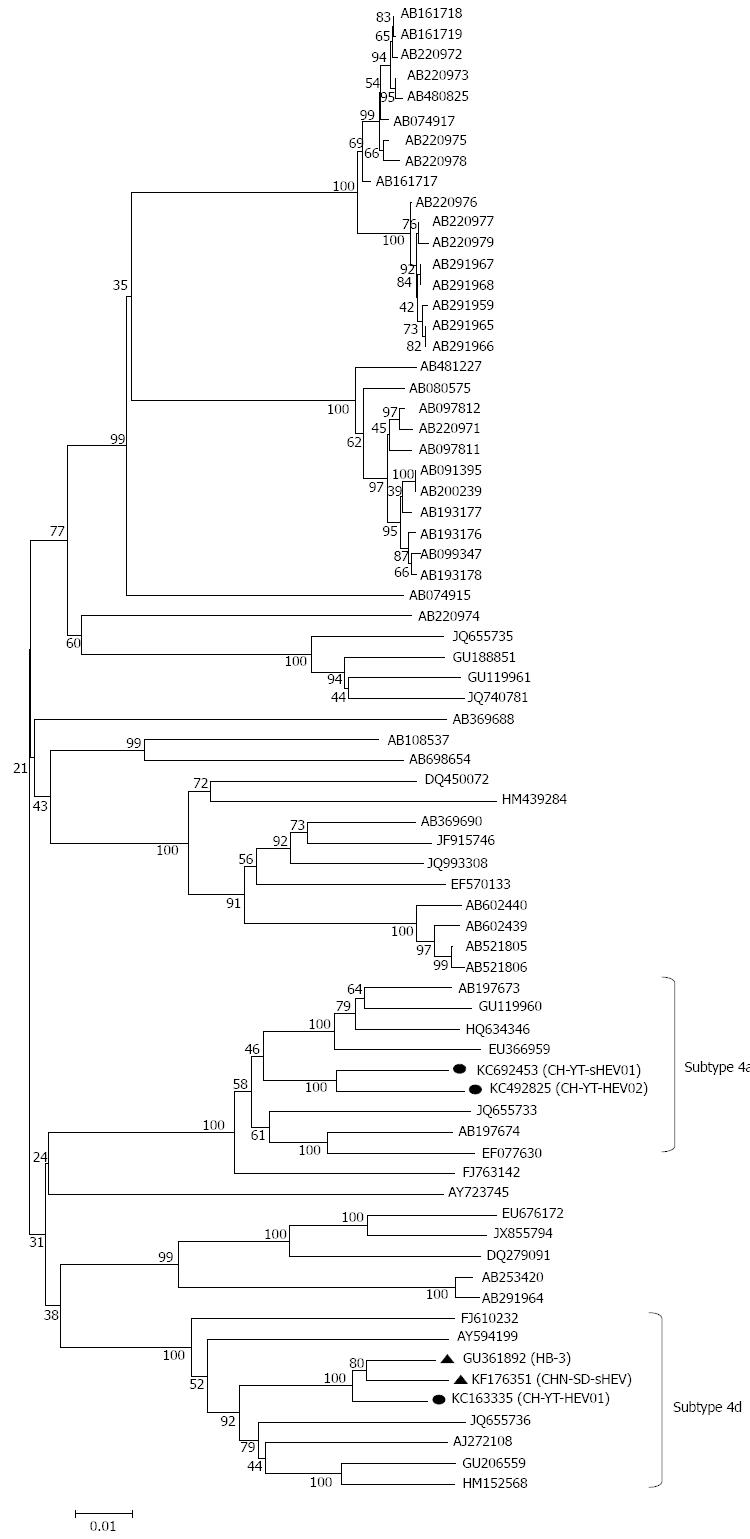
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree depicting sub-genotypic status of all 72 genotype 4 hepatitis E virus isolates based on full-length sequences.
The Arabic numbers and the Roman letters outside the square bars indicate potential sub-genotypic designations.
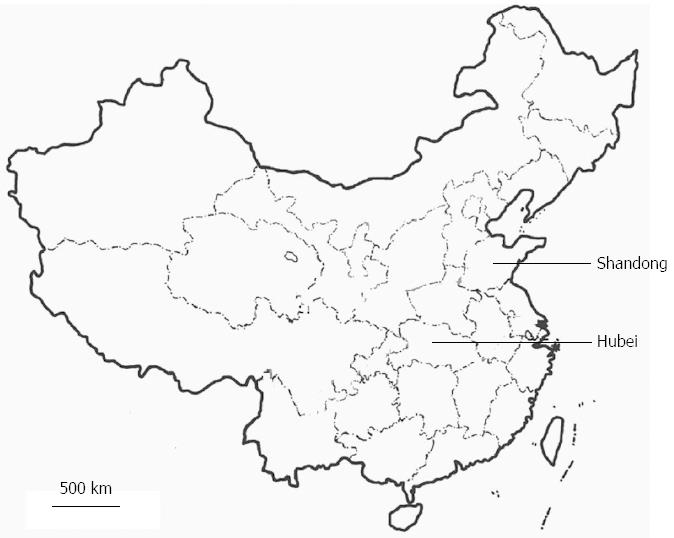
Figure 3 Map showing the geographic distribution of Shandong and Hubei in China.
Shandong Province is located 380 km northeast of Hubei Province.
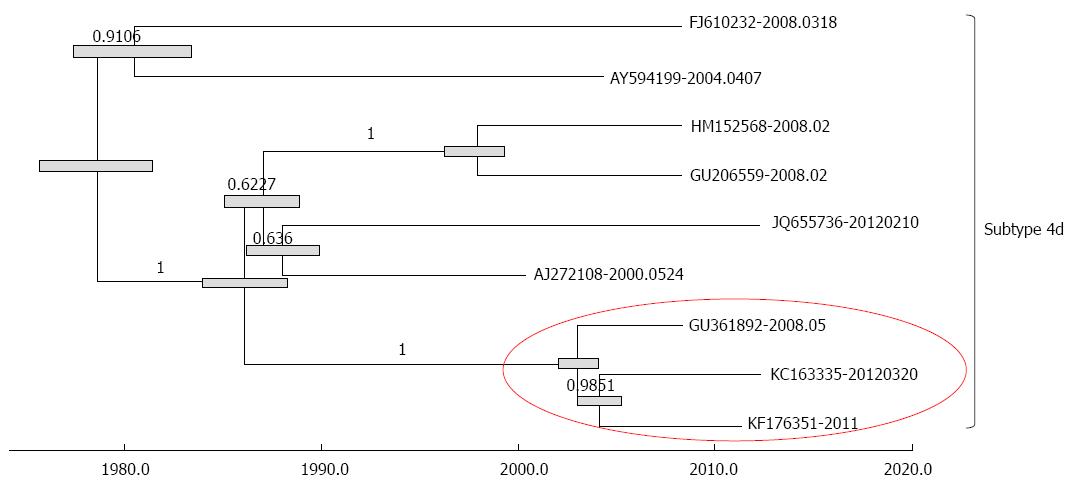
Figure 4 Maximum clade support phylogeny for the dated China-indigenous (subtype 4d) isolates of complete genome sequences.
The branch lengths and node heights are in units of years.
- Citation: Yang D, Jiang M, Jin M, Qiu ZG, Shen ZQ, Cui WH, Wang DN, Gong LF, Li B, Wang XW, Li JW. Seroprevalence and evolutionary dynamics of genotype 4 hepatitis E virus in Shandong Province, China. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7955-7963
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7955.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7955