Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7675-7685
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7675
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7675
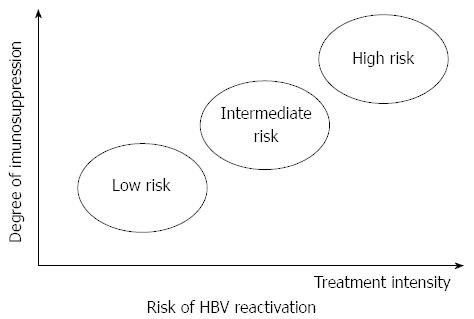
Figure 1 Role of treatment intensity and the degree of immunosuppression in hepatitis B virus reactivation during cancer therapy.
The risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is proportionate to treatment intensity and the degree of immunosuppression.
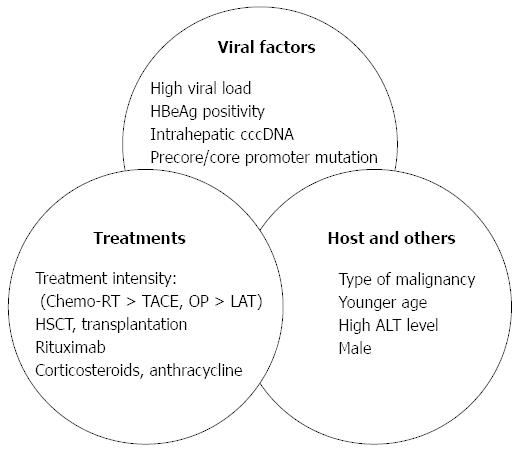
Figure 2 Risk factors of hepatitis B virus reactivation in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers with or without hepatocellular carcinoma.
Modified from Jang et al[8]. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; OP: Operation; LAT: Local ablation therapy; HSCT: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
- Citation: Jang JW. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing anti-cancer therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7675-7685
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7675.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7675