Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7325-7338
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7325
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7325
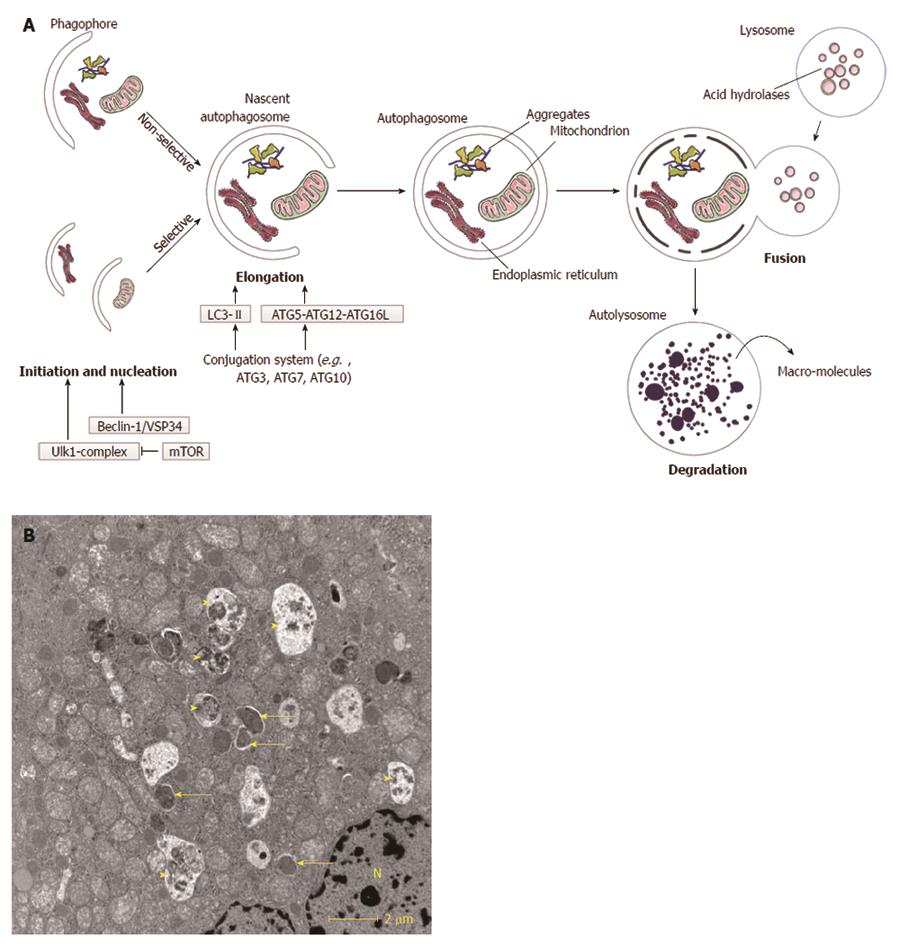
Figure 1 Macroautophagy.
A: Schematic overview of macroautophagy. Macroautophagy starts with the formation of a double-layered membrane, the phagophore (isolation membrane). Phagophore formation is regulated by the ULK1 complex (initiation), which is under control of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex, and the beclin-1/VSP34 interacting complex (nucleation). Two major ubiquitine-like conjugated complexes take care of the elongation of the double membrane: light chain 3 (LC3)-II and ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L1. ATG7 is one of the proteins necessary for formation of both elongation complexes. When an autophagosome is formed, it will fuse with a lysosome. The inner membrane of the autophagosome and the sequestered cytoplasm will be degraded and macromolecules can subsequently be (re-)used. Macroautophagy can be non-selective (random uptake of intracellular material) or selective [uptake of specific cargo, e.g., mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)]; B: Transmission electron microsocopy (TEM)-image of a normal mouse liver fasted overnight. The arrows indicate autophagosomes, the arrowheads indicate autolysosomes. N: Nucleus.
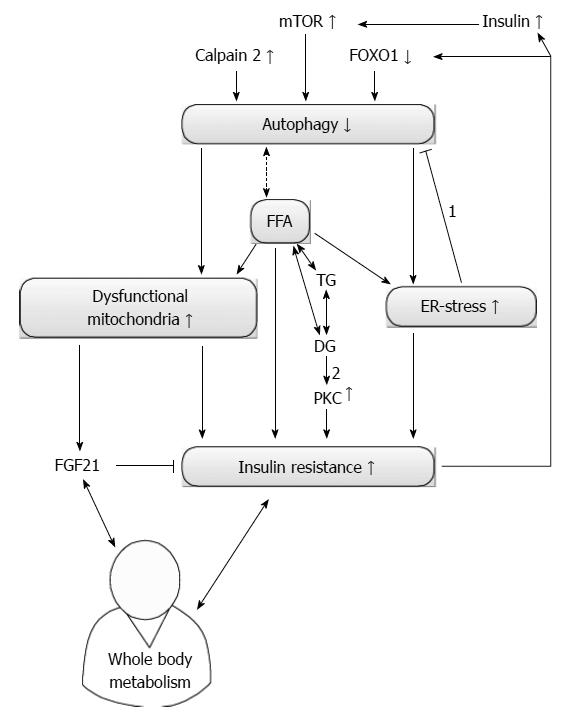
Figure 2 Current knowledge of autophagy and insulin resistance.
Autophagy and insulin resistance (IR) seem to influence each other reciprocally. On one hand, an increased level of calpain 2 reduces autophagy and increases IR by increasing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The amount of dysfunctional mitochondria will also increase and contribute to IR. On the other hand, secondary hyperinsulinism due to IR can decrease autophagy if the insulin sensitivity remains present. Furthermore, autophagy can also be suppressed via an IR-mediated reduction in forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1). Free fatty acids (FFA) can induce IR directly or by increasing ER stress. Correct stereoisomers of diacylglycerol (DG) can induce protein kinase c (PKC) dependent IR. Controversy exists on how autophagy influences the level of FFA and if subsequent correct stereoisomers of DG can be formed. Dysfunctional mitochondria can increase the level of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which is able to reduce IR. FGF21 and IR interact with whole body metabolism. Arrows indicate a consequence of a certain alteration, bar headed arrows denote an inhibition. Double-headed arrows present a reciprocal influence. The dashed and double-headed arrow denotes the uncertain relation between FFA and autophagy. 1: ER stress actually increases autophagy; 2: Only right stereoisomers induce PKC. mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Kwanten WJ, Martinet W, Michielsen PP, Francque SM. Role of autophagy in the pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A controversial issue. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7325-7338
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7325.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7325