Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2014; 20(2): 486-497
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.486
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.486
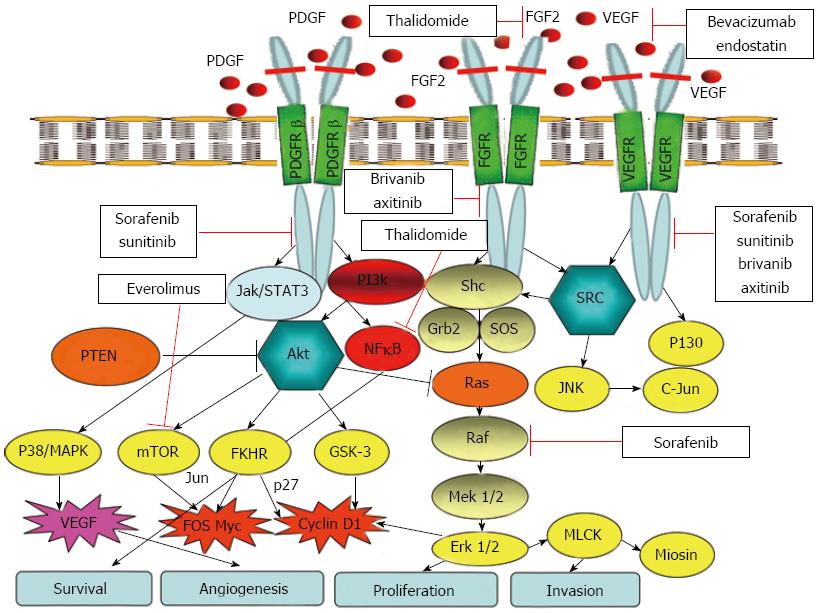
Figure 1 Fundamental pathways involved in development of hepatocellular cancer and their molecular targeting agents.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; VEGFR: VEGF receptor; PDGFR: PDGF receptor; FGF2: Fibroblast growth factor 2; PI3k: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; SRC: Steroid receptor coactivator; JNK: c-JUN terminal kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensinhomologue; STAT 3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase-3.
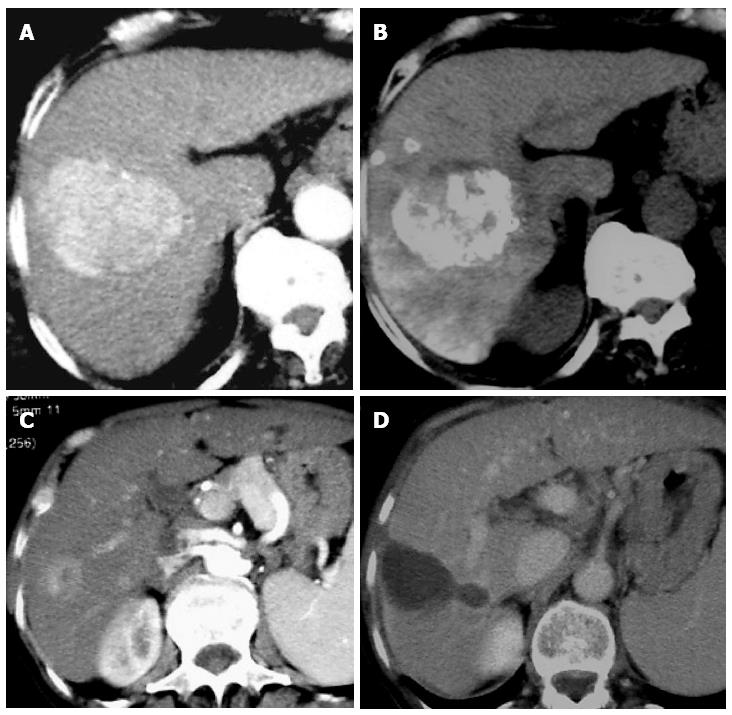
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan.
A: An intermediate hepatocellular cancer (HCC) is showed at liver segment VII before transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Note the HCC hyperdensity in arterial phase; B: The same tumor showed in A was observed 1 mo after TACE. Note the lipiodol impregnation of the tumor in computed tomography scan without intravenous contrast; C: An early hepatocellular cancer is showed at liver segment V before radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Note the HCC hyperdensity in arterial phase; D: The same tumor showed in C was observed 1 mo after RFA. Note the cavitation of the tumor as an image with no density.
- Citation: Ranieri G, Marech I, Lorusso V, Goffredo V, Paradiso A, Ribatti D, Gadaleta CD. Molecular targeting agents associated with transarterial chemoembolization or radiofrequency ablation in hepatocarcinoma treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(2): 486-497
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i2/486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.486