Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 5092-5097
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5092
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5092
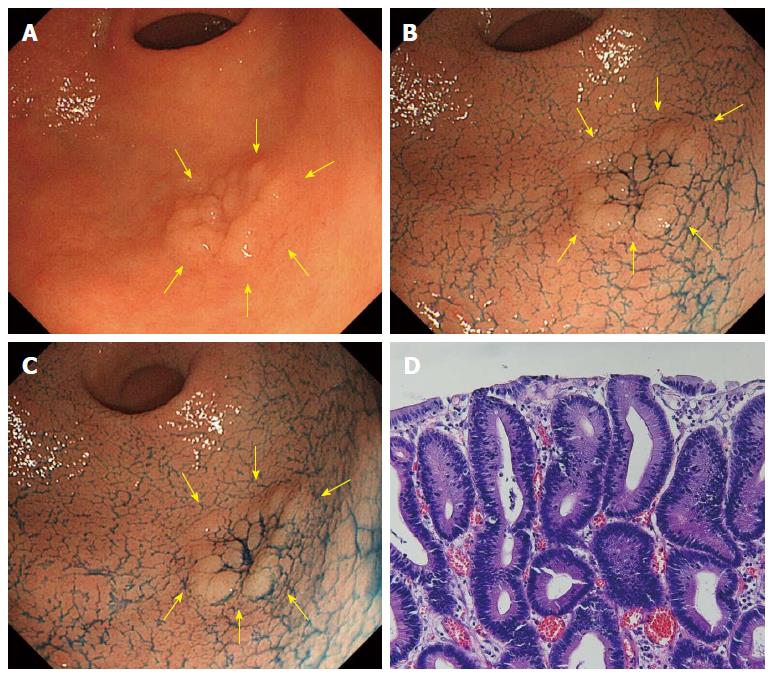
Figure 1 A case of tubular adenoma (no change in acetic acid indigocarmine mixture-chromoendoscopy).
A: Whitish superficial elevated lesion is shown at the greater curvature of the antrum in white light endoscopy (indicated by yellow arrows); B: After sprinkling indigo carmine solution; C: 3 min after sprinkling acetic acid indigocarmine mixture (AIM) solution. Compared to B, there was no surface color change (no change in AIM-chromoendoscopy); D: Histology after endoscopic submucosal dissection.
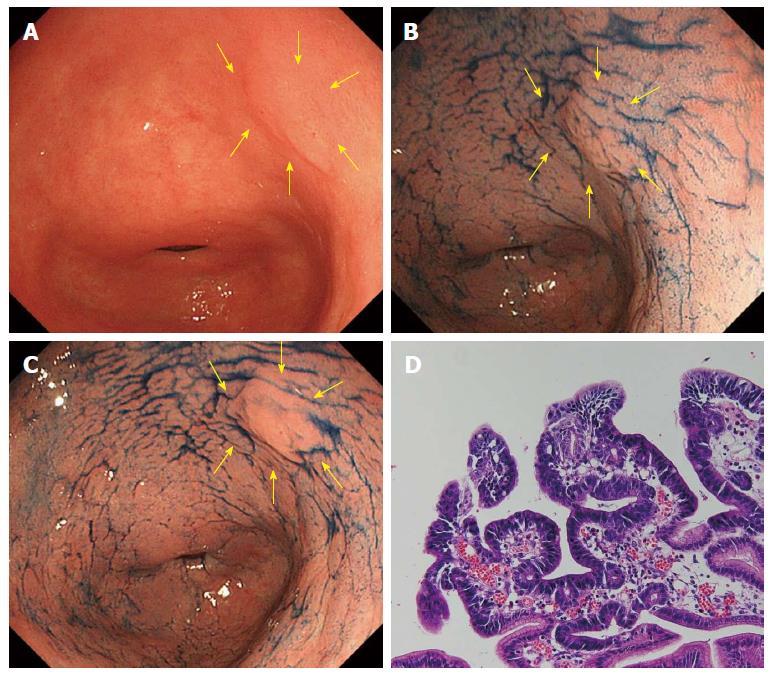
Figure 2 A case of well-differentiated adenocarcinoma (reddish color change in acetic acid indigocarmine mixture-chromoendoscop).
A: A normochromic superficial elevated lesion is shown at the lesser curvature of the antrum in white light endoscopy (indicated by yellow arrows); B: After sprinkling indigo carmine solution. The margin of the lesion was not clear; C: 3 min after sprinkling acetic acid indigocarmine mixture (AIM) solution. The margin of the lesion became clear and the surface color turned reddish (reddish change in AIM-chromoendoscopy); D: Histology after endoscopic submucosal dissection.
- Citation: Kono Y, Takenaka R, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Hori K, Kawano S, Yamasaki Y, Takemoto K, Miyake T, Fujiki S, Yamamoto K. Chromoendoscopy of gastric adenoma using an acetic acid indigocarmine mixture. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 5092-5097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/5092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5092