Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4737-4744
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4737
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4737
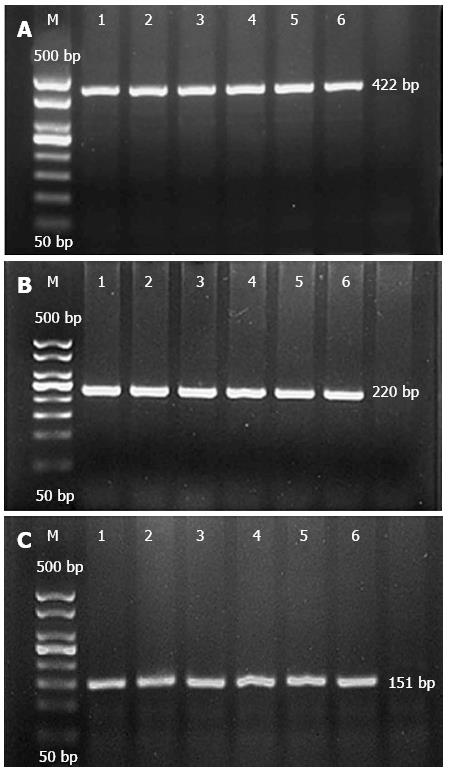
Figure 1 Electrophoresis of P268S, JW1, and N852S PCR products.
A: P268S; B: JW1; C: N852S. M: Marker; 1, 2: Ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD) of Han; 3, 4: UC, CD of Zhuang; 5, 6: healthy controls.
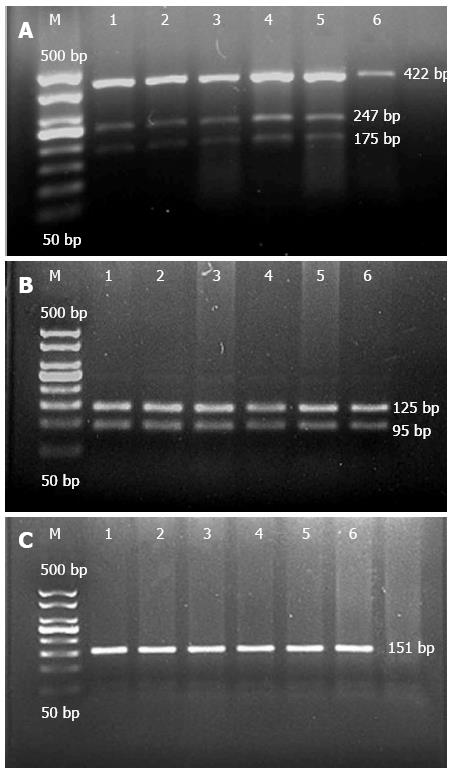
Figure 2 Electrophoresis of P268S, JW1, and N852S digestion products.
A: M: Marker; 1-5: Heterozygote of P268S, 6: Wild-type of P268S. B: M: Marker; 1-6: Wild-type of JW1. C: M: Marker; 1-6: Wild-type of N852S.
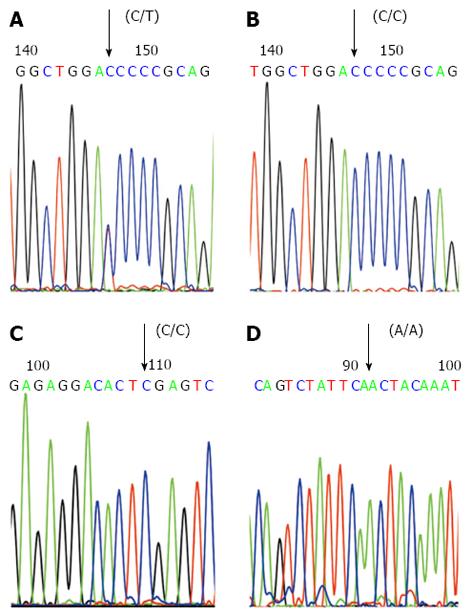
Figure 3 Gene sequencing analysis of P268S, JW1 and N852S polymerase chain reaction products.
A: The forward sequencing map of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product of heterozygote P268S (C/T); B: The forward sequencing map of the PCR product of wild-type P268S (C/C); C: The forward sequencing map of the PCR product of wild-type JW1 (C/C); D: The forward sequencing map of the PCR product of wild-type N852S (A/A).
-
Citation: Long WY, Chen L, Zhang CL, Nong RM, Lin MJ, Zhan LL, Lv XP. Association between
NOD2/CARD15 gene polymorphisms and Crohn's disease in Chinese Zhuang patients. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4737-4744 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4737.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4737