Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2013; 19(8): 1239-1246
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1239
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1239
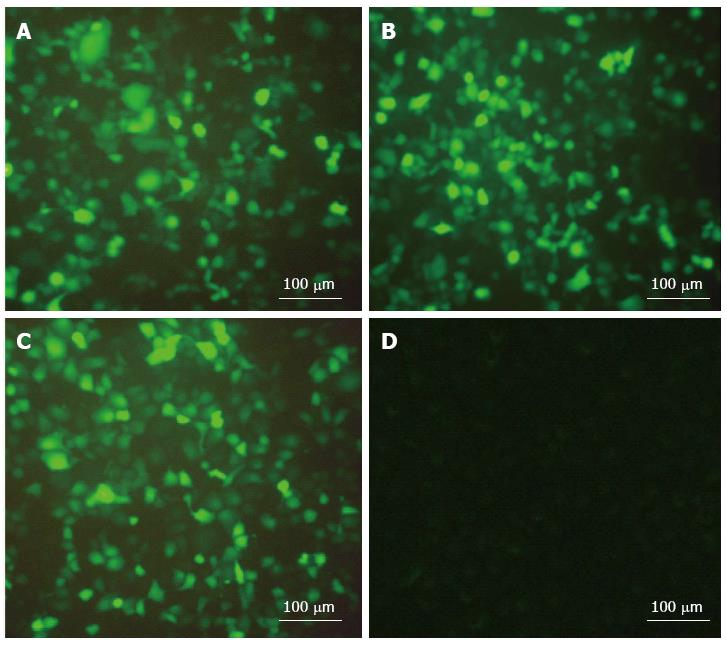
Figure 1 Cell transfection under the fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×400).
A: Transfected group 24 h after transfection; B: Transfected group 48 h after transfection; C: Transfected group 72 h after transfection; D: Scrambled sequence group 48 h after transfection.
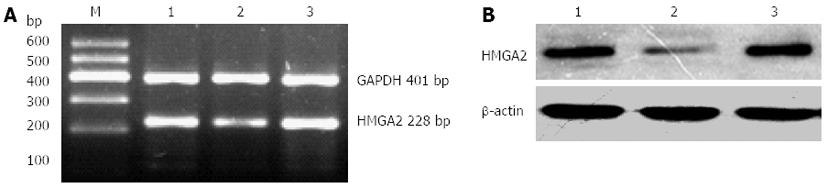
Figure 2 Expression of high mobility group A2 messenger RNA and high mobility group A2 protein.
A: Expression of high mobility group A2 (HMGA2) messenger RNA (mRNA); B: Expression of HMGA2 protein. M: Marker; 1: Blank control group; 2: Transfected group; 3: Scrambled sequence group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
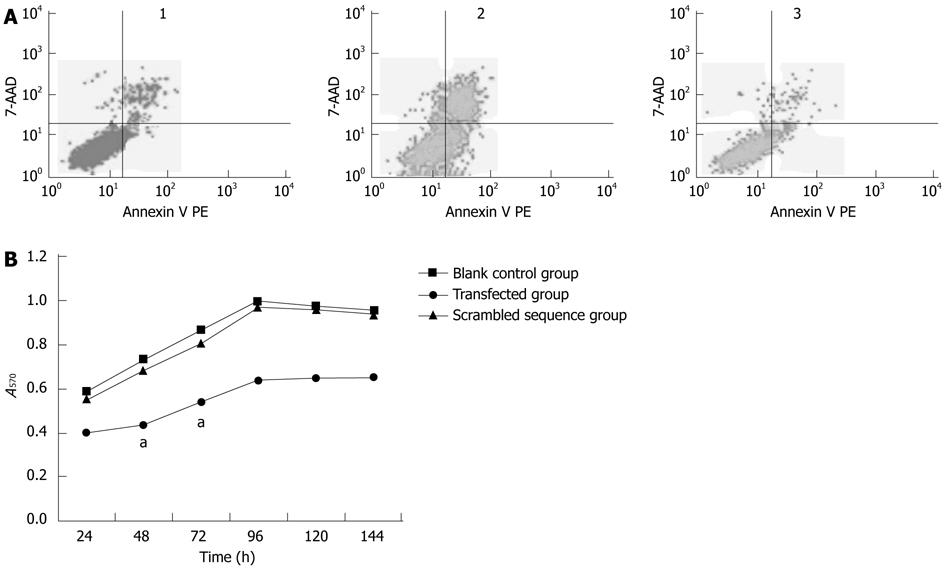
Figure 3 Apoptosis and cell proliferation analysis.
A: Flow cytometry. The cell apoptotic rate of the transfected group was significantly higher than those of the blank control group and the scrambled sequence group; B: Cell proliferation analysis. aP < 0.05 vs black control group. 1: Blank control group; 2: Transfected group; 3: Scrambled sequence group.
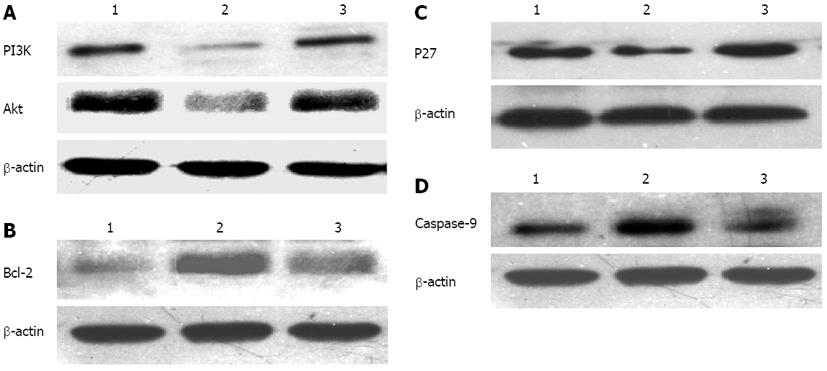
Figure 4 Western blotting analysis of protein expression.
A: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt); B: B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2); C: P27; D: Caspase-9. 1: Blank control group; 2: Transfected group; 3: Scrambled sequence group.
- Citation: Wei CH, Wei LX, Lai MY, Chen JZ, Mo XJ. Effect of silencing of high mobility group A2 gene on gastric cancer MKN-45 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(8): 1239-1246
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i8/1239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1239