Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2013; 19(8): 1210-1218
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1210
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1210
Figure 1 Effects of AH6809 or NG-Nitro-L-arginine Methyl Ester on lipopolysaccharide-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) at a holding potential of -70 mV in control condition; B: Pacemaker currents of ICCs incubated at 37 °C with 200 μg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 12 h; C: Pacemaker currents in ICCs pretreated with AH6809 (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation; D: Pacemaker currents in ICCs pretreated with NG-Nitro-L-arginine Methyl Ester (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; L-NAME: NG-Nitro-L-arginine Methyl Ester.
Figure 2 Expression of TLR4, iNOS and COX-2 in c-Kit positive cells.
A: Double labeling of TLR4- and c-Kit-like immunoreactivity in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs). Green (c-Kit) and red (TLR4) result in the mixed color yellow, indicating the colocalization of both peptides; B: Double labeling of iNOS and c-Kit-like immunoreactivity in ICCs. Green (c-Kit) and red (iNOS) result in the mixed color yellow, indicating the colocalization of both peptides; C: Double labeling of COX-2 and c-Kit-like immunoreactivity in ICCs. Green (c-Kit) and red (COX-2) result in the mixed color yellow, indicating the colocalization of both peptides (bar = 20 μm).
Figure 3 Effects of catalase on lipopolysaccharide-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) incubated at 37 °C with 200 μg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 12 h; B: Pacemaker currents in ICCs pretreated with catalase (3000 unit/mL) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation. The effects of catalase on the LPS-induced action in ICCs are summarized in C and D. Bars represent mean ± SE values (n = 4 per group).
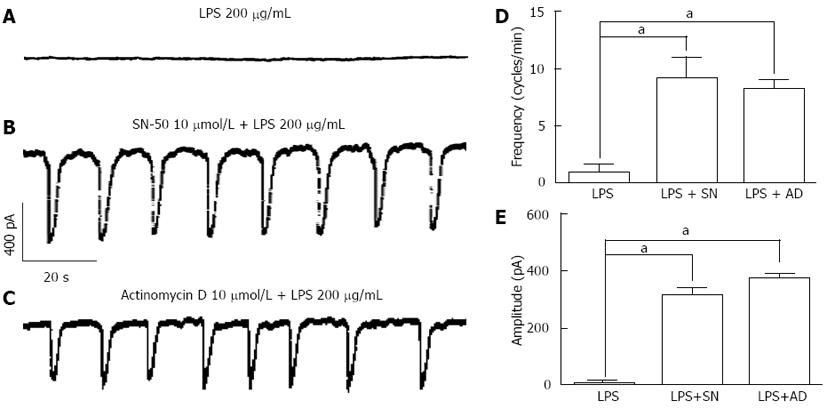
Figure 4 Effects of SN-50 or actinomycin D on lipopolysaccharide-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) incubated at 37 °C with 200 μg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 12 h at a holding potential of -70 mV; B: Pacemaker currents in ICCs pretreated with SN-50 (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation; C: Pacemaker currents in ICCs pretreated with actinomycin D (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation. The effects of SN-50 or actinomycin D on the LPS-induced action in ICCs are summarized in D and E. Bars represent mean ± SE values (n = 5 per group). aP < 0.05 vs LPS alone treatment. SN: SN-50, AD: Actinomycin D.
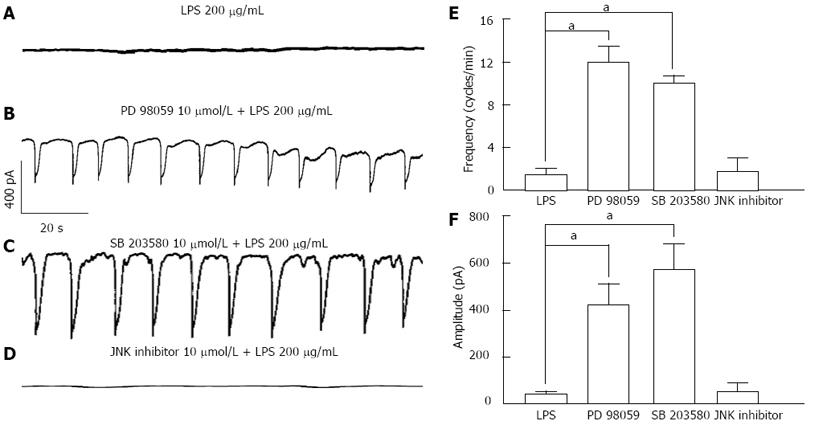
Figure 5 Effects of Mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on lipopolysaccharide-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) incubated at 37 °C with 200 μg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 12 h at a holding potential of -70 mV; B: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with PD 98059 (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation; C: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with SB 203580 (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation; D: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor II (10 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to LPS incubation. The effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on the LPS-induced action are summarized in E and F. Bars represent mean ± SE values (n = 7 per group). aP < 0.05 vs LPS.
Figure 6 Effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on prostaglandin E2-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) treated with 5 μmol/L prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) at a holding potential of -70 mV; B: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with PD 98059 (10 μmol/L) prior to PGE2 treatment; C: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with SB 203580 (10 μmol/L) prior to PGE2 treatment. The effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on the PGE2-induced action are summarized in D and E. Bars represent mean ± SE values (n = 4 per group). aP < 0.05 vs PGE2. Con: Control, PD: PD 98059, SB: SB203580.
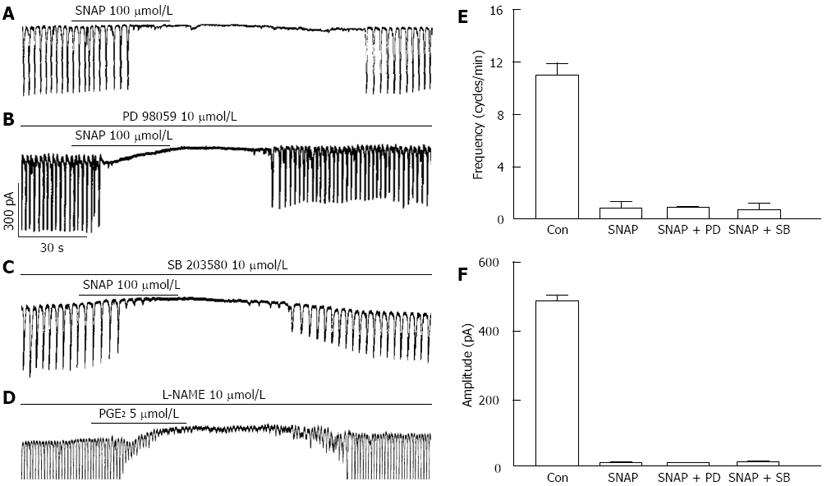
Figure 7 Effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on (±)-S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine-induced action in interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker currents of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) treated with 100 μmol/L SNAP at a holding potential of -70 mV; B: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with PD 98059 (10 μmol/L) prior to SNAP treatment; C: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with SB 203580 (10 μmol/L) prior to SNAP treatment; D: Pacemaker currents after pretreatment with L-NAME (10 μmol/L) prior to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (5 μmol/L) treatment. The effects of mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibitors on the (±)-S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine-induced action are summarized in E and F. Bars represent mean ± SE values (n = 5 per group). Con: Control, PD: PD 98059, SB: SB203580; SNAP: S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine; L-NAME: NG-Nitro-L-arginine Methyl Ester.
-
Citation: Zuo DC, Choi S, Shahi PK, Kim MY, Park CG, Kim YD, Lee J, Chang IY, So I, Jun JY. Inhibition of pacemaker activity in interstitial cells of Cajal by LPS
via NF-κB and MAP kinase. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(8): 1210-1218 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i8/1210.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1210