Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2013; 19(8): 1200-1209
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1200
Published online Feb 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1200
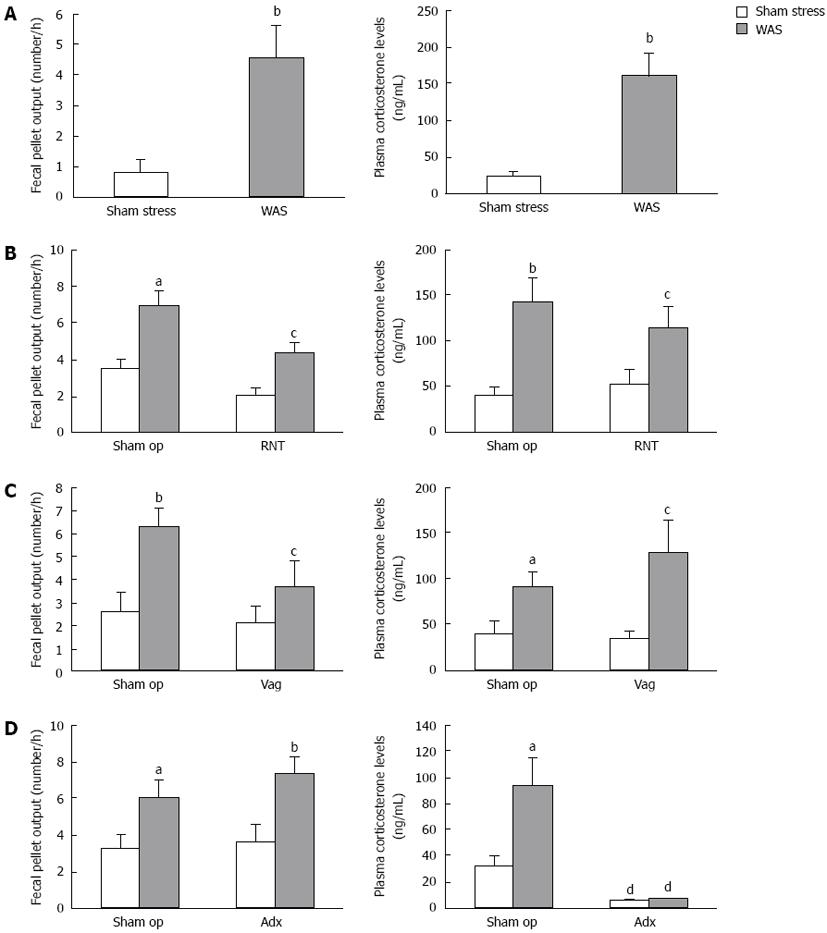
Figure 1 Involvement of parasympathetic nerves and corticosterone in the accelerated defecation induced by acute water avoidance stress.
A: The naive rats showed increases in defecation and corticosterone levels after 1-h of water avoidance stress (WAS) compared with sham stress; B-D: Effects of rectal nerve transection (RNT), vagotomy (Vag) and adrenalectomy (Adx) on WAS-induced increases in defecation and plasma corticosterone in rats. Each value represents the mean ± SE (n = 6-12 per group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the response of sham stress rats; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs sham-operated (sham op) rats.
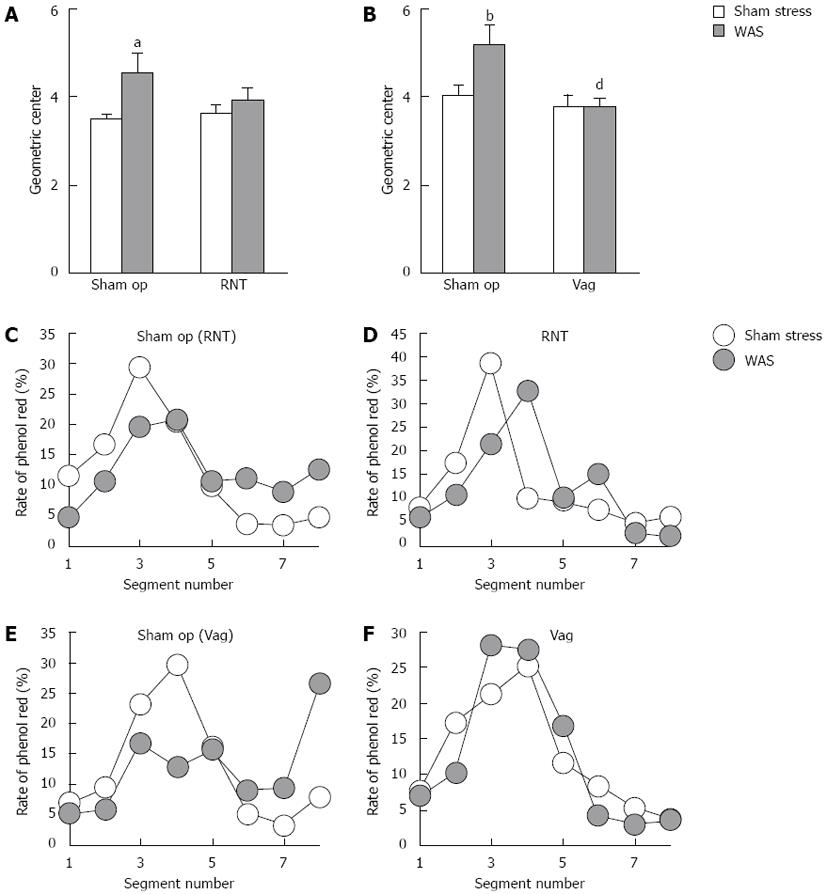
Figure 2 Involvement of parasympathetic nerves in the bowel movement.
A, B: Effects of rectal nerve transection (RNT) (A) and vagotomy (Vag) (B) on the colonic transit presented by geometric center of moved phenol red; C-F: Relative distribution of phenol red through the entire colon and rectum after water avoidance stress (WAS) in sham-operated rats (C, E), RNT-rats (D) and Vag-rats (F). Each value represents the mean of 6-8 rats. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the response of sham stress rats; dP < 0.01 vs sham-operated (sham op) rats.
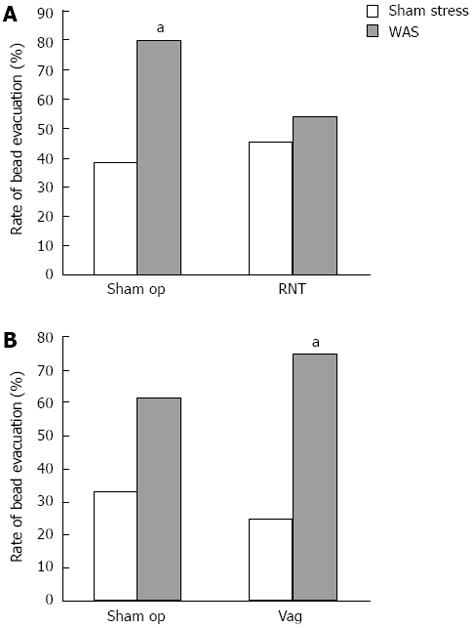
Figure 3 Involvement of parasympathetic nerves in the fecal expulsion through the distal colon.
A, B: Effects of rectal nerve transection (RNT) (A) and vagotomy (Vag) (B) on the rate of bead evacuation from the distal colon during 2-h water avoidance stress (WAS). The increased rate of bead evacuation in sham-operated rats was inhibited in RNT-rats. Each value represents the mean ± SE (n = 11-15 per group). aP < 0.05 vs sham stress rats.
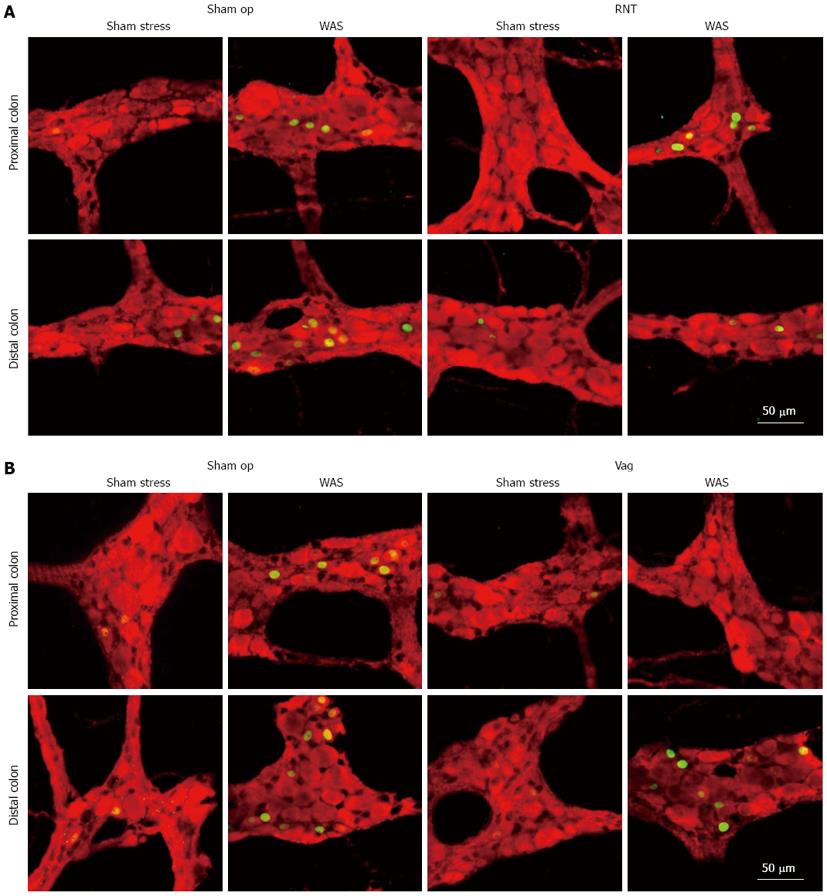
Figure 4 Induction of c-Fos expression after exposure to water avoidance stress.
Confocal microscope images showing the staining of c-Fos (green) and protein gene product 9.5 (PGP9.5, red) in whole mount preparations of longitudinal muscle myenteric plexus in rectal nerve transection (RNT) (A) and vagotomy (Vag) rats (B). WAS: Water avoidance stress; Sham op: Sham-operated.
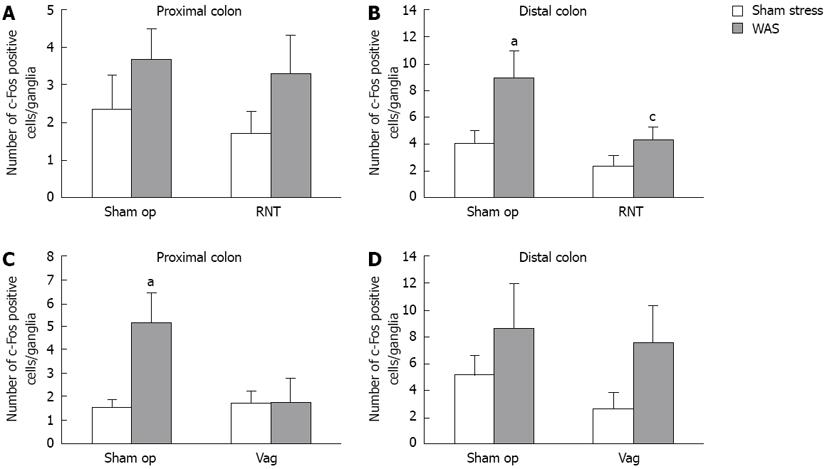
Figure 5 Effects of vagotomy and rectal nerve transection on the induction of c-Fos-expressing cells in the colon after water avoidance stress.
Using whole mount preparations of longitudinal muscle myenteric plexus in the proximal (A, C) and distal colons (B, D), numbers of c-Fos immunoreactive cells per ganglia in the proximal and distal colons of rectal nerve transection (RNT) rats (A, B) and vagotomy (Vag) rats (C, D) after water avoidance stress (WAS) treatment were counted and compared to those of sham stress rats. Each value represents the mean ± SE (n = 6-12 per group). aP < 0.05 vs sham stress rats; cP < 0.05 vs sham-operated (sham op) rats.
- Citation: Suda K, Setoyama H, Nanno M, Matsumoto S, Kawai M. Involvement of parasympathetic pelvic efferent pathway in psychological stress-induced defecation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(8): 1200-1209
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i8/1200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1200