Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2013; 19(45): 8219-8226
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8219
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8219
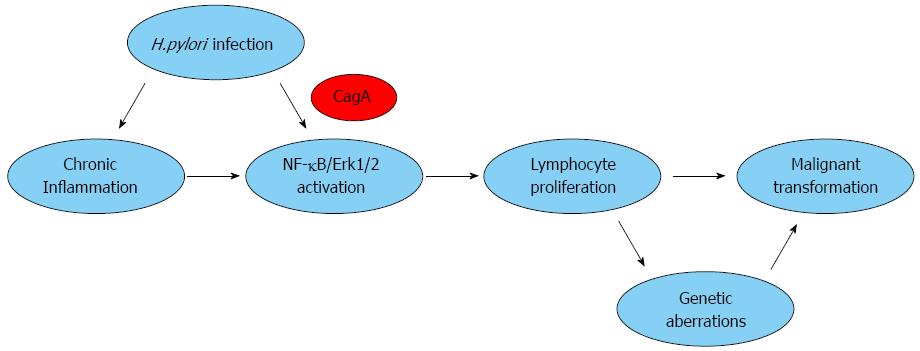
Figure 1 Oncoprotein cytotoxin-associated gene A is involved in the gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma development.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Erk1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2.
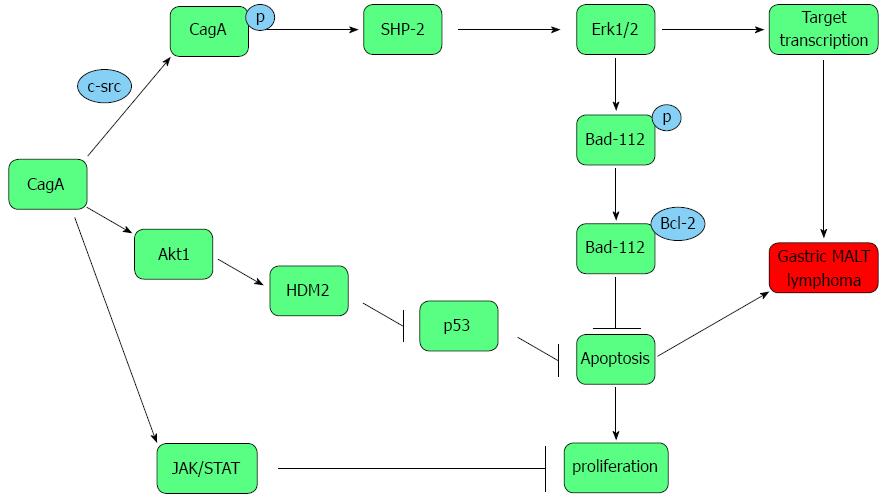
Figure 2 Cytotoxin-associated gene A deregulates intracellular signaling pathways in tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent and -independent manners to initiate lymphomagenesis.
CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A; Erk1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2; MALT: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; SHP-2: Protein-tyrosine phosphatase-2.
-
Citation: Wang HP, Zhu YL, Shao W. Role of
Helicobacter pylori virulence factor cytotoxin-associated gene A in gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(45): 8219-8226 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i45/8219.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8219