Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7341-7360
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7341
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7341
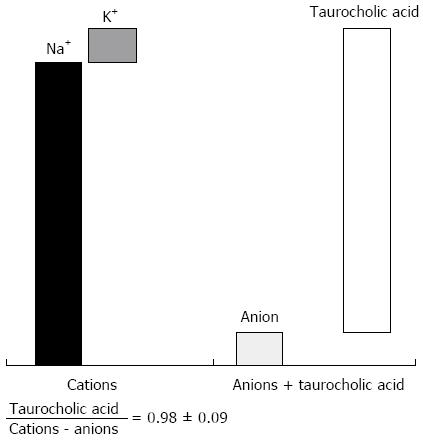
Figure 1 The bile content of anions, cations and taurocholic acid.
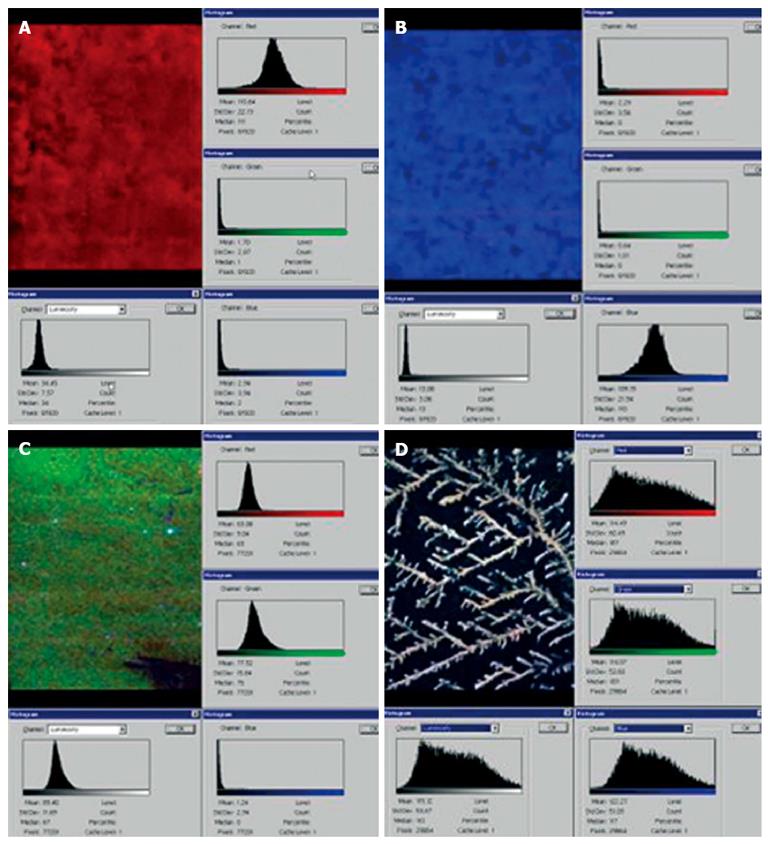
Figure 2 Color cathode-luminescence scanning electron microscopy images.
Color cathode-luminescence scanning electron microscopy (CCL SEM) micro images of unconjugated bilirubin (A), unesterified cholesterol (B), high-molecular-weight protein (C), and dehydrated sample of normal human cystic bile (D).
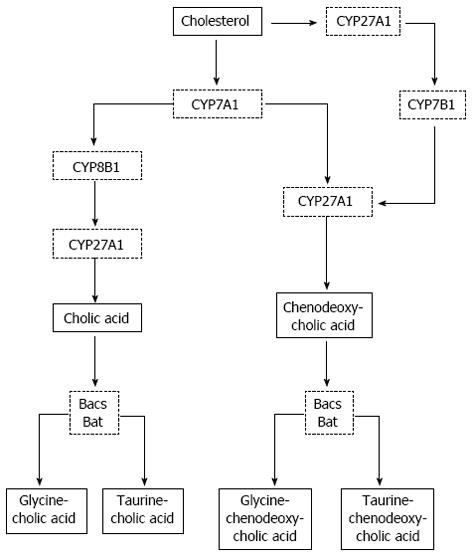
Figure 3 Bile acid synthesis.
CYP7B1: 7α-hydroxylase; CYP7A1: Enzyme cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase; CYP8B1: Sterol 12 α-hydroxylase; CYP27A1: Mitochondrial sterol 27 hydroxylase.
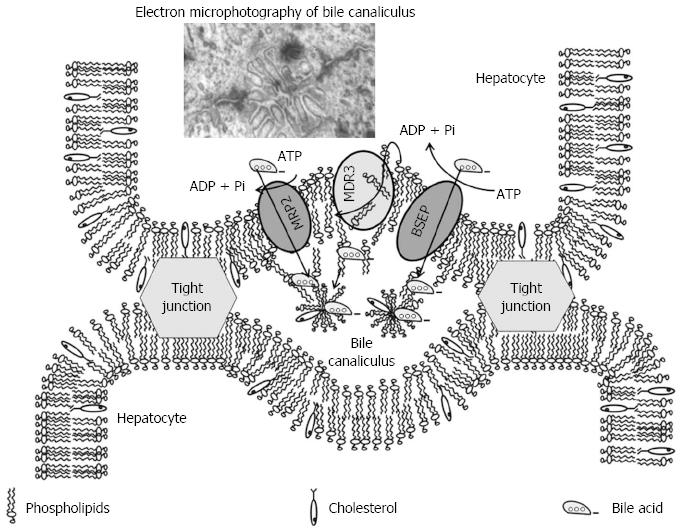
Figure 4 Proposed model for lipid secretion into bile[58].
BSEP: Bile salt export pump; MDR3: Multidrug-resistance protein 3; MRP2: Multidrug-resistance-associated protein 2; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; Pi: Inorganic phosphate.
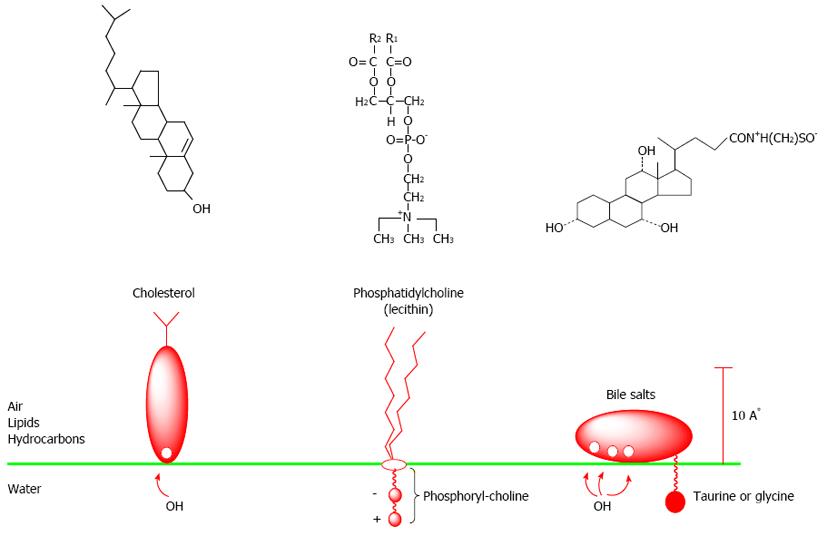
Figure 5 Chemical formulas and simple images of cholesterol, lecithins, and bile salts on a boundary of two phases-water: lipids (air, hydrocarbons).
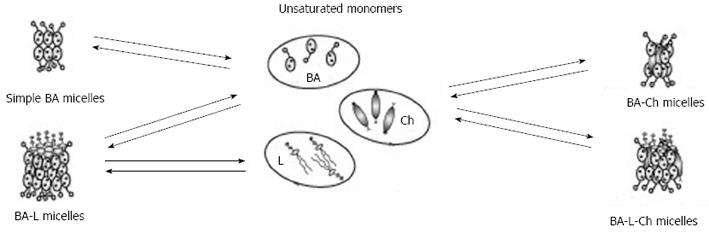
Figure 6 Formation of micelles structures in the system containing bile acids, lecithin, and cholesterol.
BA: Bile acids; Ch: Cholesterol; L: Lecithin.
Figure 7 Mechanisms of the transport of bile acids, water, and electrolytes through the hepatocyte (transcellular pathway) and intercellular space (paracellular pathway).
Localization and function of sinusoidal and canalicular hepatocellular transporters. The Na+-dependent sinusoidal uptake of bile salts (BS) is mediated by Na+-dependent taurocholate cotransport peptide. The Na+-independent hepatic uptake of organic anions (OA-), BSs and type II organic cations (OC+) is mediated by members of the OATP family. Sinusoidal uptake of type I OC+ is mediated by OCT1. Transport across the canalicular membrane is driven mainly by ATP-dependent export pumps. MDR1 mediates canalicular excretion of amphiphilic type II OC+ and other hydrophobic compounds. MDR3 functions as a PC flippase. BSEP mediates apical excretion of BSs. MRP2 transports non-bile-salt organic anions, such as bilirubin glucuronides (BGs), GSH, and sulfated/glucuronidated bile salts. Canalicular transport of HCO3- is mediated by the Cl-/HCO3- exchanger AE2. AQP9 and AQP8 are involved in the transport of water across the sinusoidal and the canalicular membrane, respectively. The nature of the water channels in human liver has been characterized[84]. GC: Golgi apparatus (complex); ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; N: Nucleus.
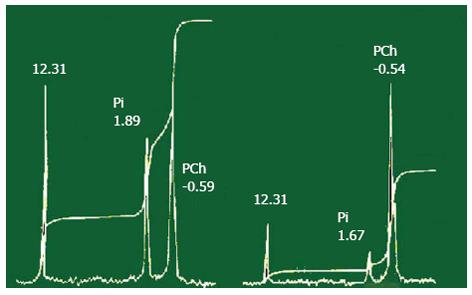
Figure 8 31P-NMR spectroscopy hepatic (left part of figure) and gallbladder (right part of figure) bile.
Signals: 12,31 (standard); inorganic phosphate (Pi); phosphatidilcholine (PCh). PCh signal of gallbladder bile is increased with respect to such signals from hepatic bile. Signal of standard and inorganic phosphate of gallbladder bile are decreased with respect to such signals of hepatic bile. The concentration of lipids is increased by water absorption by gallbladder mucosa.
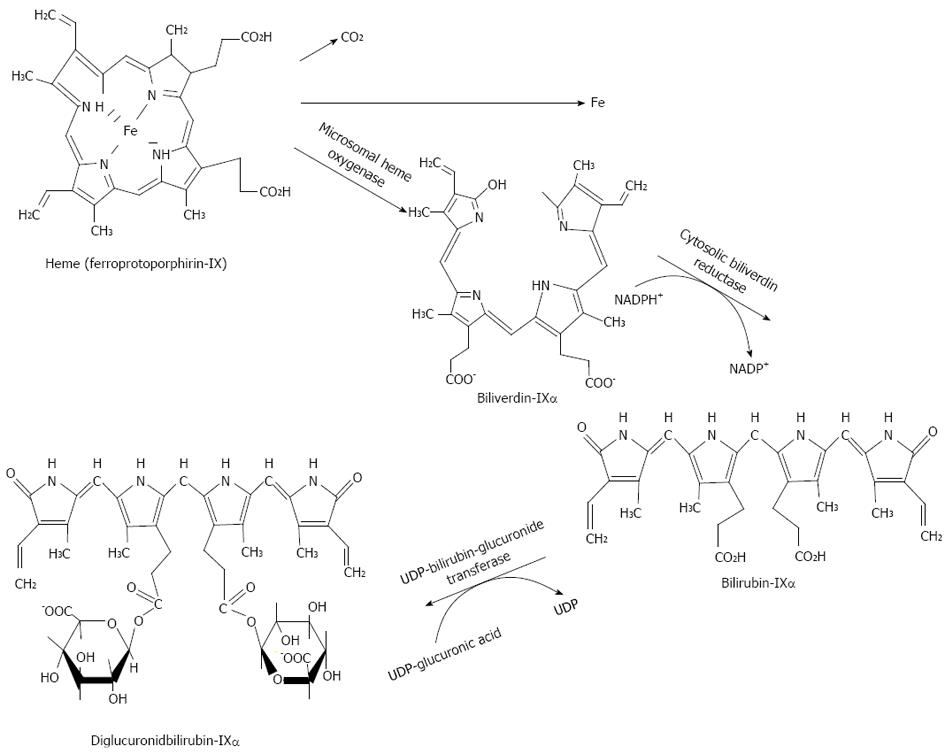
Figure 9 Formation of IXα bilirubin from heme.
- Citation: Reshetnyak VI. Physiological and molecular biochemical mechanisms of bile formation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7341-7360
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7341