Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2013; 19(39): 6693-6698
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6693
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6693
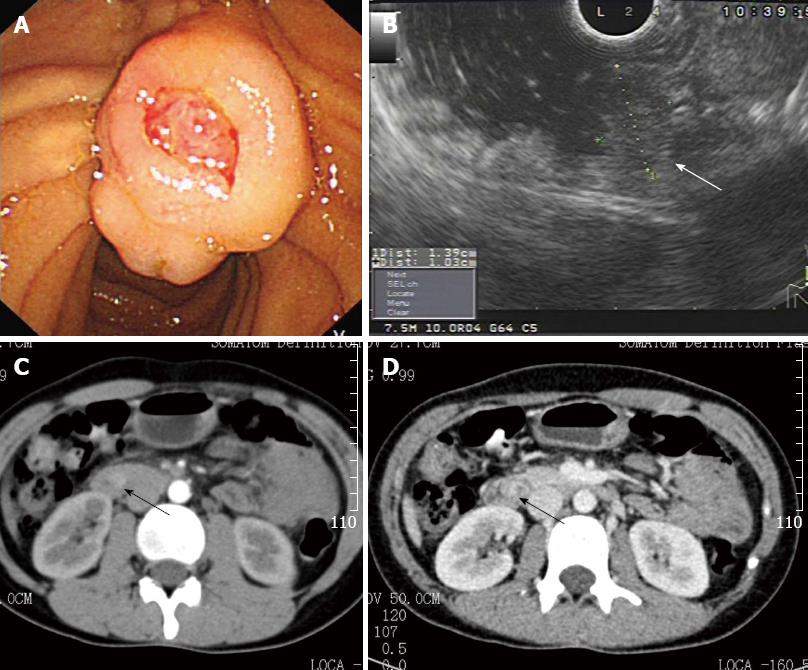
Figure 1 Periampullary tumor (arrow) was detected by gastroscope, endoscopic ultrasonography, and computed tomography.
A: Gastroscope; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography; C, D: Computed tomography.
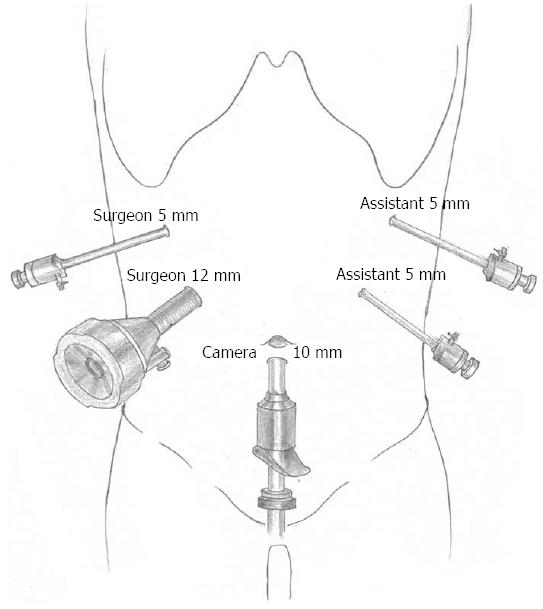
Figure 2 Location of trocars placement.
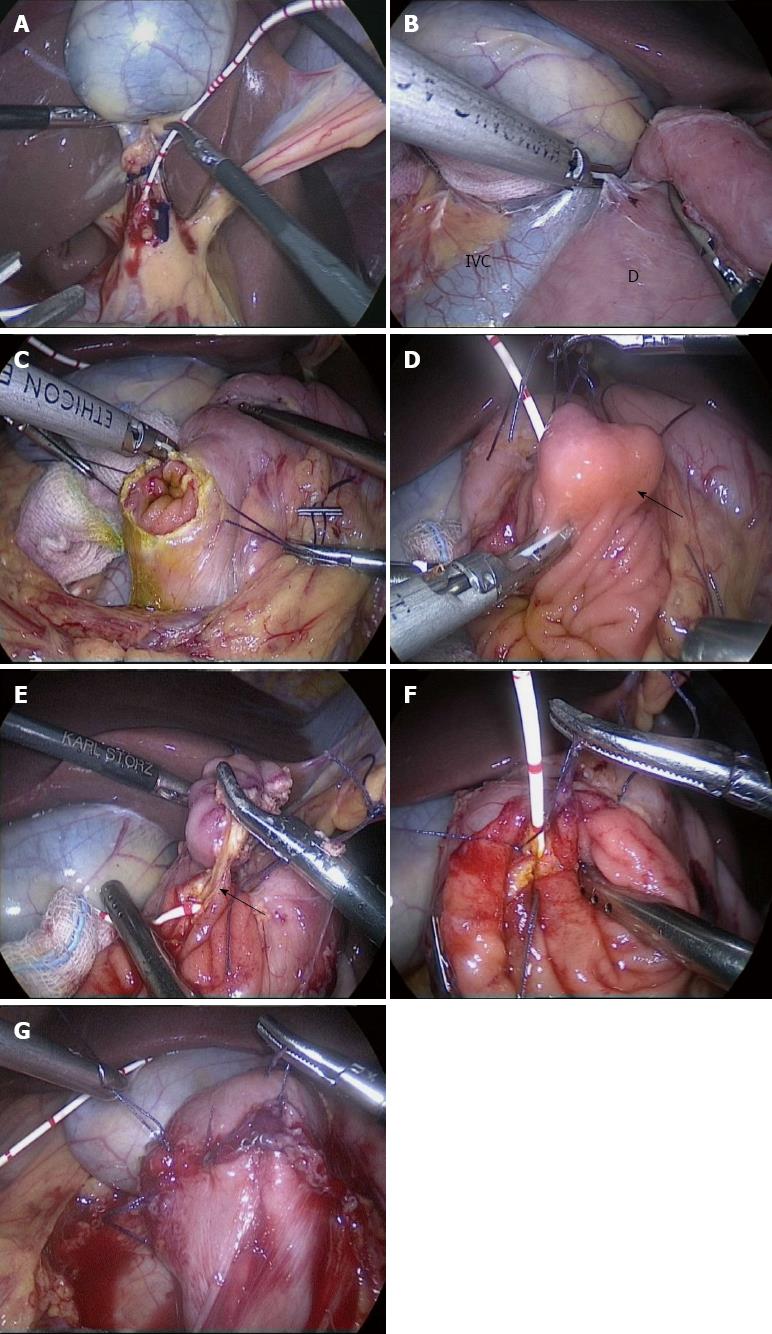
Figure 3 Steps of the surgical procedures.
A: Inserting a cholangiogram catheter through the cystic duct to the duodenum; B: Mobilizing duodenum by the Kocher maneuver; C: Making a longitudinal incision of duodenal wall on the opposite site of the duodenal papilla; D: Performing the resection circumferentially at a distance of 5 mm from the tumor (arrow); E: Identifying pancreaticobiliary duct (arrow) by the cholangiogram catheter; F: Suturing the pancreaticobiliary duct to the surrounding duodenal mucosa; G: After closure of the duodenotomy. IVC: Indicates inferior vena cava; D: Duodenum.
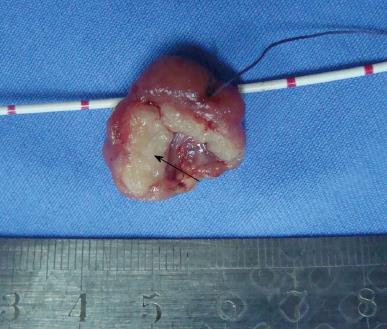
Figure 4 Resected specimen of periampullary neuroendocrine tumor (arrow).
- Citation: Zhang RC, Xu XW, Wu D, Zhou YC, Ajoodhea H, Chen K, Mou YP. Laparoscopic transduodenal local resection of periampullary neuroendocrine tumor: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(39): 6693-6698
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i39/6693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6693