Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2013; 19(39): 6689-6692
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6689
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6689
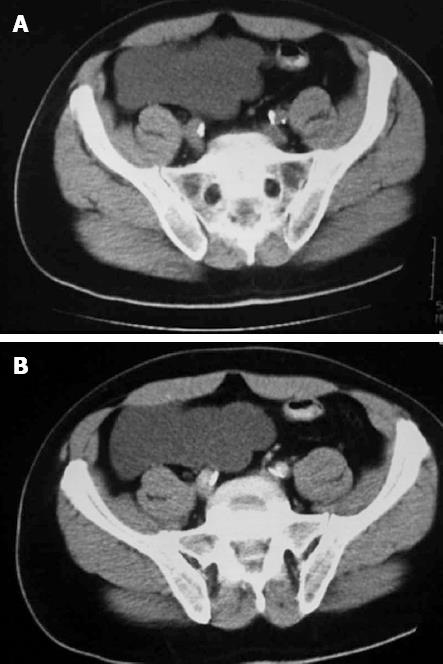
Figure 1 Computed tomography axial image results.
A: Plain computed tomography axial image showing a hypodense mass; B: Contrast enhancing computed tomography axial image demonstrating an intra-peritoneal hypodense non-enhancing tumor.
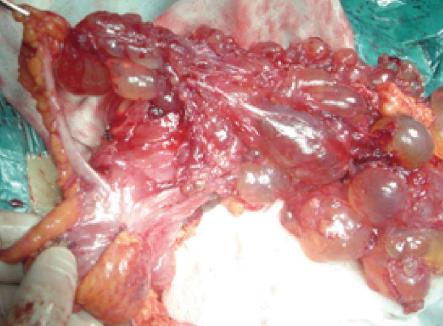
Figure 2 Intraoperative image showing a multicystic mass.
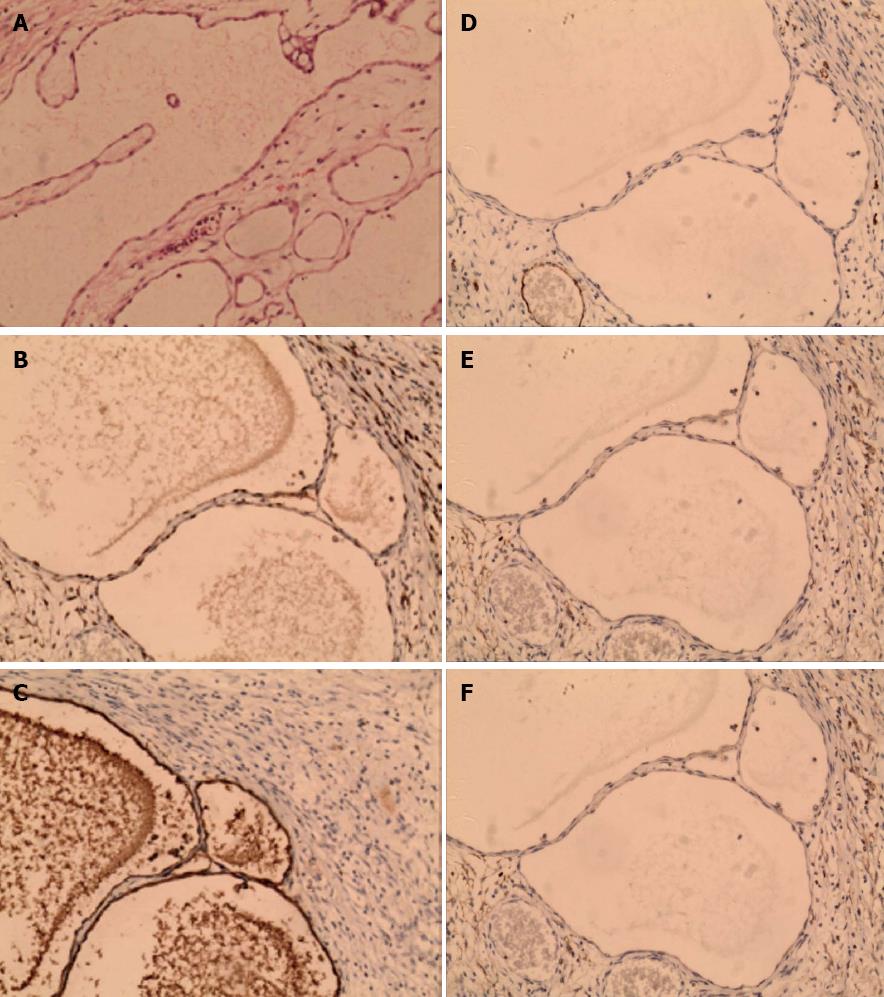
Figure 3 Histological examination revealed results.
A: Mesothelial cells lining the cysts (× 400); B-F: Immunohistochemical analysis documented positive expression of mesothelial cells (B, × 400) and calretinin (C, × 400), while expressions of D2-40, CD31, and CD34 were negative (D, F, × 400).
- Citation: Wang TB, Dai WG, Liu DW, Shi HP, Dong WG. Diagnosis and treatment of benign multicystic peritoneal mesothelioma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(39): 6689-6692
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i39/6689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6689