Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2013; 19(39): 6679-6682
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6679
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6679
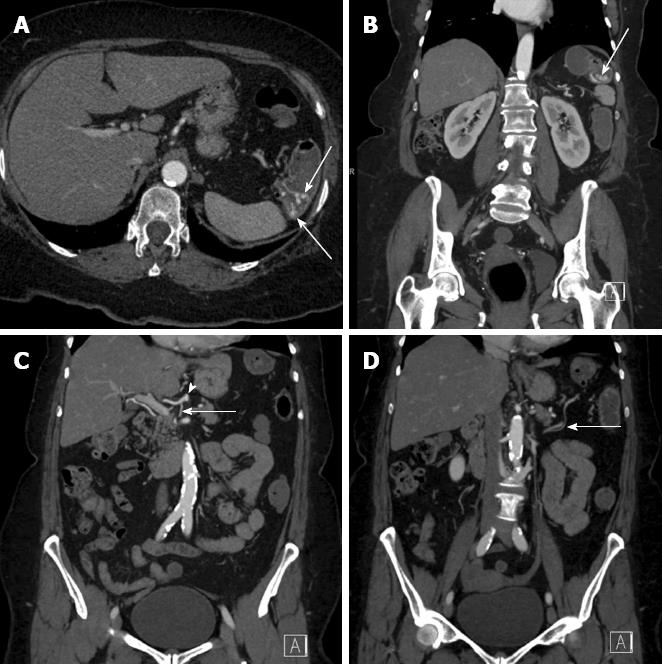
Figure 1 Computed tomography angiography with arterial phase (20 s following injection) acquisition.
A, B: Axial image (A) and coronal images (B) demonstrating active contrast extravasation (arrows) at the splenic flexure; C: Coronal reformatted image demonstrating a celio-mesenteric branch (arrow) arising from the common hepatic artery (arrowhead); D: Seen in the large bowel mesentery (arrow) and supplying the splenic flexure.
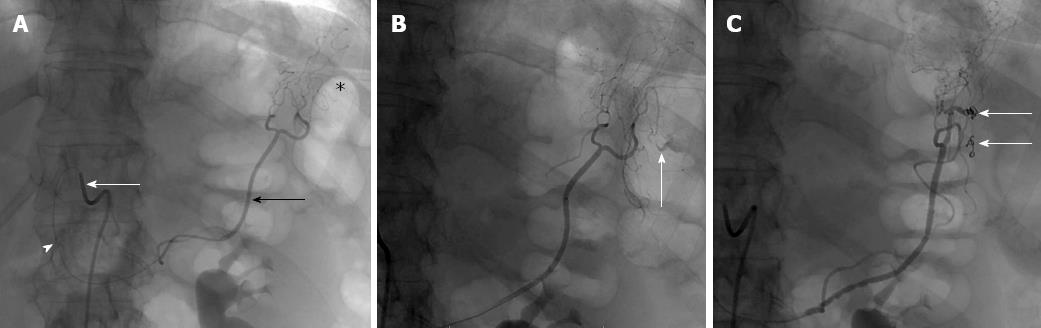
Figure 2 Digital subtraction angiogram.
A: Sim 1 catheter (white arrow) engaged in the common hepatic artery and a microcatheter (arrowhead) cannulating the celio-mesenteric trunk (black arrow) supplying the splenic flexure (asterisk) with no active hemorrhage seen; B: Active contrast extravasation (arrow) following instillation of 1 mg tPA; C: Angiogram following deployment of coils in branches of the celio-mesenteric vessel and no further active extravasation seen (arrow).
- Citation: Wu M, Klass D, Strovski E, Salh B, Liu D. Aberrant celio-mesenteric supply of the splenic flexure: Provoking a bleed. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(39): 6679-6682
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i39/6679.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6679