Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2013; 19(39): 6665-6678
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6665
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6665
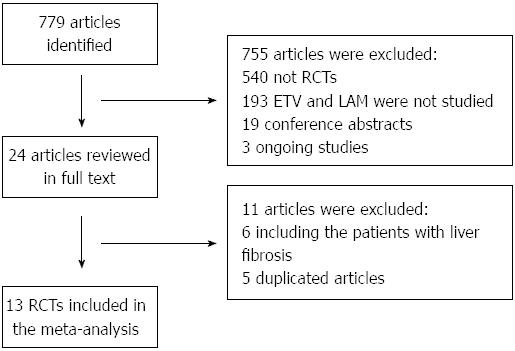
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the randomized controlled trials reviewed.
RCT: Randomized controlled trial; ETV: Entecavir; LAM: Lamivudine.
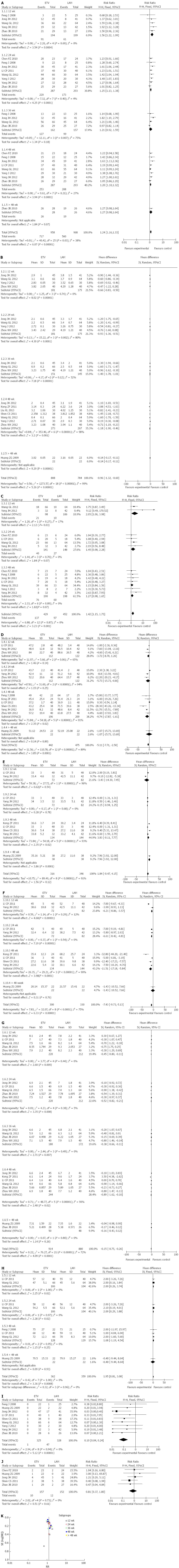
Figure 2 Meta-analysis.
A: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA undetectability in the two treatment groups; B: HBV DNA levels in the two treatment groups; C: Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion in the two treatment groups; D: Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in the two treatment groups; E: Albumin (ALB) levels in the two treatment groups; F: Total bilirubin (TBIL) levels in the two treatment groups; G: The child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score in the two treatment groups; H: Prothrombin time activity (PTA) levels in the two treatment groups; I: Drug-resistance in the two treatment groups; J: Mortality in the two treatment groups; K: The two treatment groups included in the Randomized controlled trials (RCTs). ETV: Entecavir; LAM: Lamivudine.
- Citation: Ye XG, Su QM. Effects of entecavir and lamivudine for hepatitis B decompensated cirrhosis: Meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(39): 6665-6678
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i39/6665.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6665