Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2013; 19(39): 6604-6612
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6604
Published online Oct 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6604
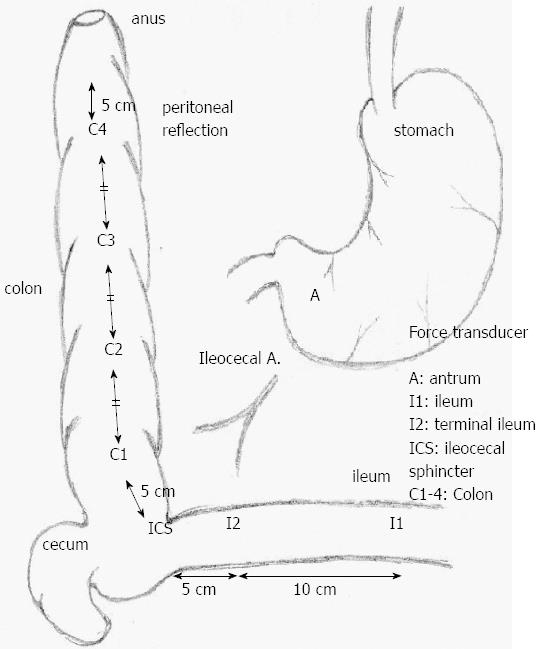
Figure 1 Scheme of the dog model and the locations of the force transducers implanted in the canine gastrointestinal tract.
Force transducers were implanted in the colon on the serosal surfaces of the gastric antrum (A), terminal ileum [5 and 15 cm proximal to ileocecal sphincter (ICS); I1-I2], ICS and colon (C1-C4); C1 was placed 5 cm distal to the ICS and C4 5 cm proximal to the peritoneal reflection. C2 and C3 were implanted equidistantly between C1 and C4.
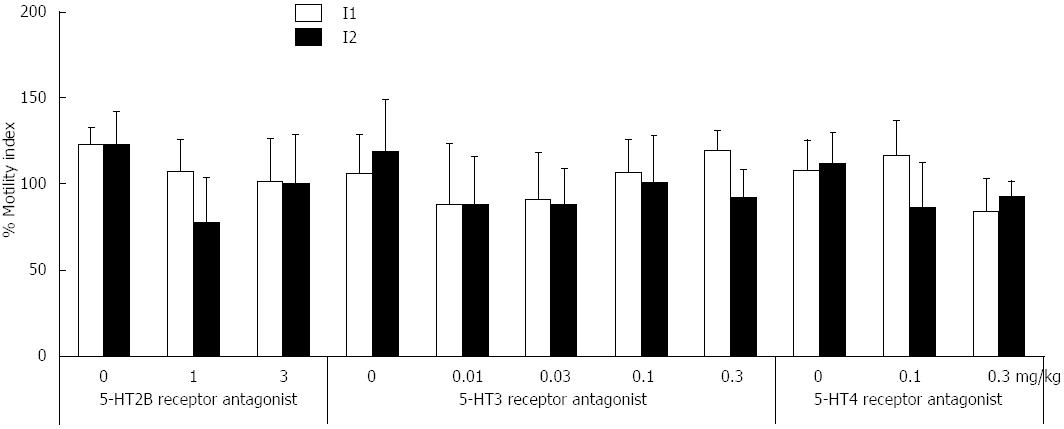
Figure 2 Inhibition ratio based on comparing the drug effects to before 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonist administration in the terminal ileum (I1-I2).
A systematic change was not observed. Values are mean ± SE. 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; I1:Ileum; I2: Terminal ileum.
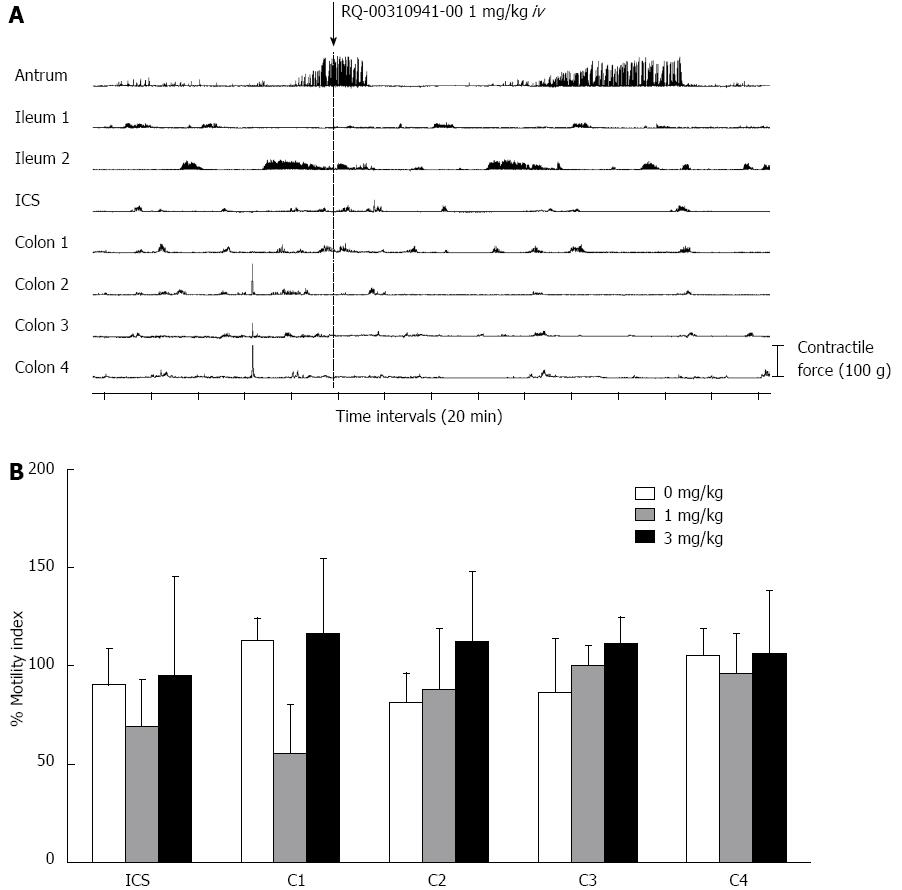
Figure 3 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor antagonists on normal colonic motor activity.
A: Typical effect of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) 2B receptor antagonist. The 5-HT2B receptor antagonist had no contractile effect on the whole intestine; B: The inhibition ratio compared with before 5-HT2B receptor antagonist administration. A systematic change was not observed. Values are mean ± SE. ICS: Ileocecal sphincter; C1-4: Colon 1-4.
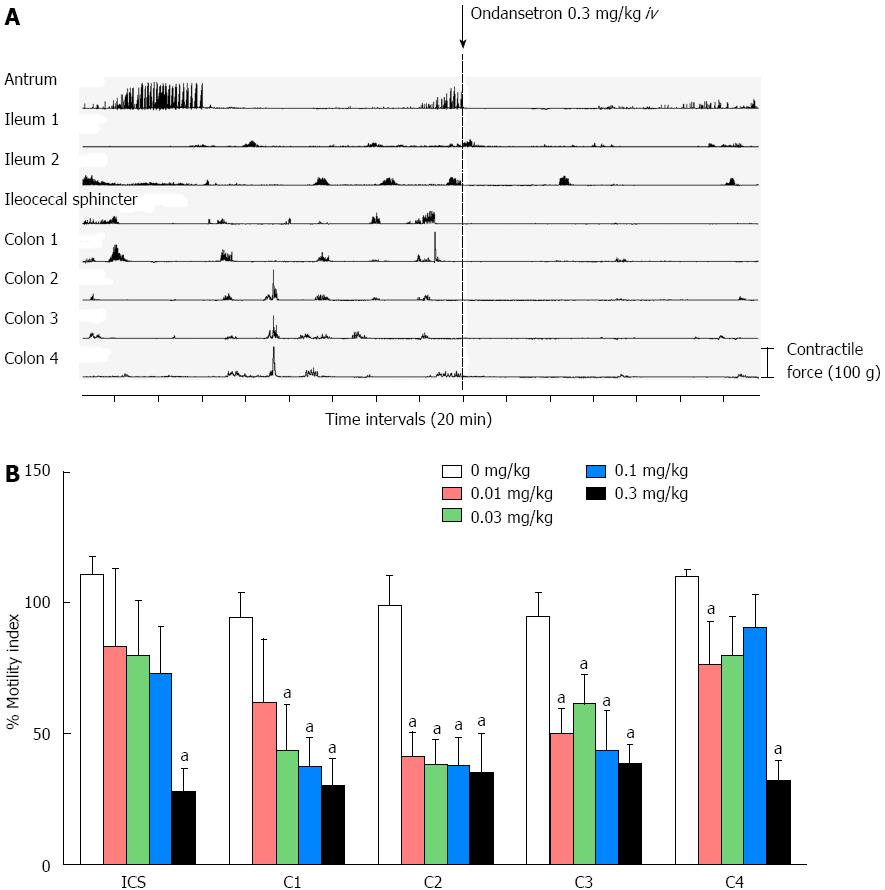
Figure 4 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor antagonists on normal colonic motor activity.
A: Typical effect of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) 3 receptor antagonist. The 5-HT3 receptor antagonist inhibited phase III of the interdigestive motor complex at the antrum and whole colonic motor activity; B: The inhibition ratio compared with before 5-HT3 receptor antagonist administration. The inhibitory effect of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist was dose dependent in the proximal colon (ICS-C2). At a dose of 0.3 mg/kg, whole colonic motor activity was inhibited significantly. Values are mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs control (0 mg/kg). ICS: Ileocecal sphincter; C1-4: Colon 1-4.
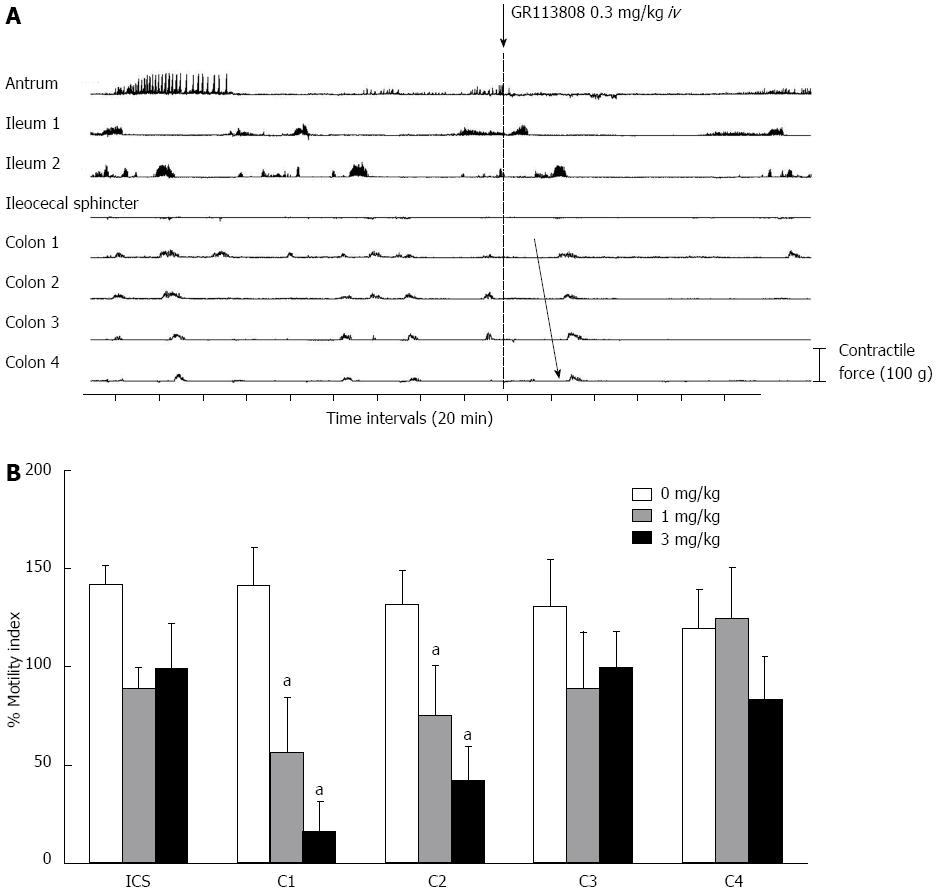
Figure 5 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor antagonists on normal colonic motor activity.
A: Typical effect of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) 4 receptor antagonist. The 5-HT4 receptor antagonist inhibited phase III of the interdigestive motor complex at the antrum and whole colonic motor activity, CMMCs corresponding to phase III of the migrating motor complex at the ileum were sometimes observed (see arrow); B: The inhibition ratio compared with before 5-HT4 receptor antagonist administration. The inhibitory effect of the 5-HT4 receptor antagonist was dose dependent in the proximal colon (C1-C2). Values are mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs control (0 mg/kg). ICS: Ileocecal sphincter; C1-4: Colon 1-4.
- Citation: Morita H, Mochiki E, Takahashi N, Kawamura K, Watanabe A, Sutou T, Ogawa A, Yanai M, Ogata K, Fujii T, Ohno T, Tsutsumi S, Asao T, Kuwano H. Effects of 5-HT2B, 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptor antagonists on gastrointestinal motor activity in dogs. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(39): 6604-6612
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i39/6604.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6604