Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2013; 19(33): 5500-5507
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500
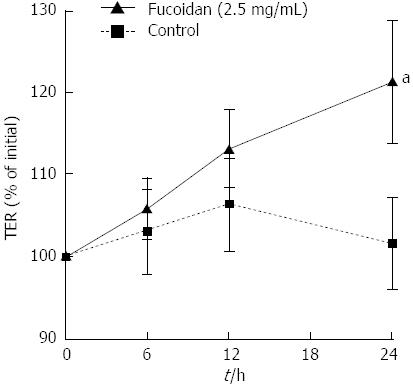
Figure 1 Fucoidan directly enhanced intestinal epithelial barrier function.
Polarized Caco-2 cell monolayers were incubated in the presence or absence of fucoidan (2.5 mg/mL) for 24 h. Changes in intestinal epithelial barrier function were monitored by measuring the trans-epithelial resistance (TER). The data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. aP < 0.05 compared with control (Student’s t test).
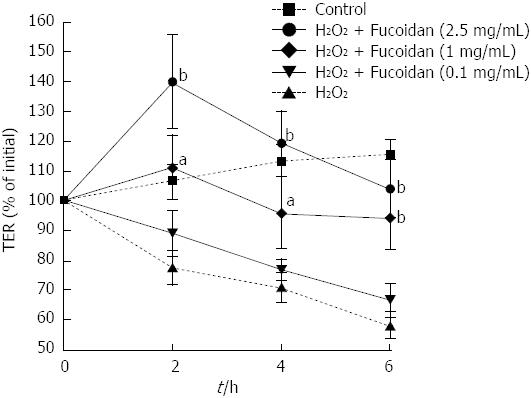
Figure 2 Fucoidan prevented H2O2-induced destruction of intestinal epithelial barrier function in a dose-dependent manner.
Polarized Caco-2 cell monolayers were injured by H2O2 (500 μmol/L) on the apical side of Caco-2 cell monolayers. Fucoidan was added into the basolateral side 30 min prior to H2O2 stimulation and cultured for 6 h. Changes in intestinal epithelial barrier function were monitored by measuring the trans-epithelial resistance (TER). The data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 compared with cells exposed to H2O2 alone at respective time point (Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
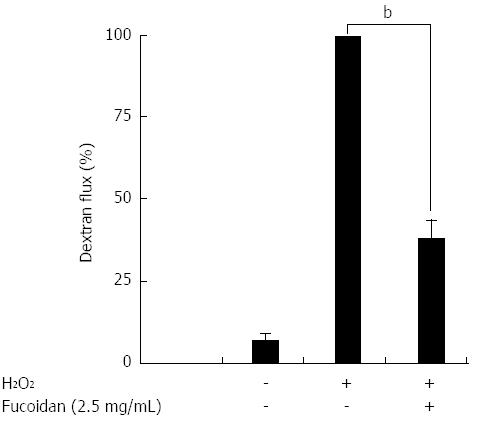
Figure 3 Fucoidan prevented H2O2-induced increases in paracellular permeability.
First, 0.5 mg/mL 4-kDa FITC-labeled dextrans (FD4) were added into the apical well and cultured for 6 h with or without H2O2 (500 μmol/L) and/or fucoidan (2.5 mg/mL). After 6 h of incubation, the basal medium was collected, and the fluorescence was measured as fluxed-FD4. H2O2-induced FD4 flux was considered 100%. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. bP < 0.01 (Student’s t test).
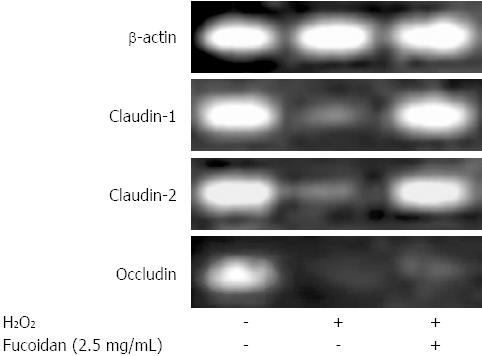
Figure 4 Fucoidan promoted intestinal epithelial barrier function via direct upregulation of tight junction proteins in intestinal epithelial cells Polarized Caco-2 cell monolayers injured by H2O2 (500 μmol/L) for 24 h with or without pretreatment of fucoidan (2.
5 mg/mL) 30 min prior to H2O2 administration. The expression of tight junction proteins, including claudin-1, claudin-2, and occludin, was examined using reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. The data shown are representative and are from 1 of the 3 independent experiments.
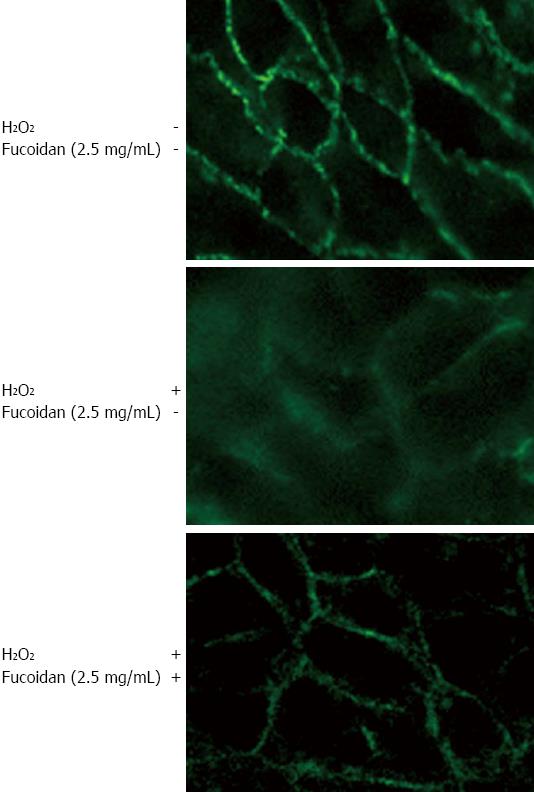
Figure 5 Fucoidan prevented the H2O2-induced destruction of tight junction protein claudin-1.
Caco-2 cells were grown on a Lab-Tek chamber plate. Polarized Caco-2 monolayers were injured by H2O2 (500 μmol/L) for 6 h with or without pretreatment of fucoidan (2.5 mg/mL). Immunofluorescence staining for claudin-1 was evaluated using confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data shown are representative and are from 1 of the 3 independent experiments.
- Citation: Iraha A, Chinen H, Hokama A, Yonashiro T, Kinjo T, Kishimoto K, Nakamoto M, Hirata T, Kinjo N, Higa F, Tateyama M, Kinjo F, Fujita J. Fucoidan enhances intestinal barrier function by upregulating the expression of claudin-1. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(33): 5500-5507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i33/5500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500