Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2013; 19(29): 4827-4831
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4827
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4827
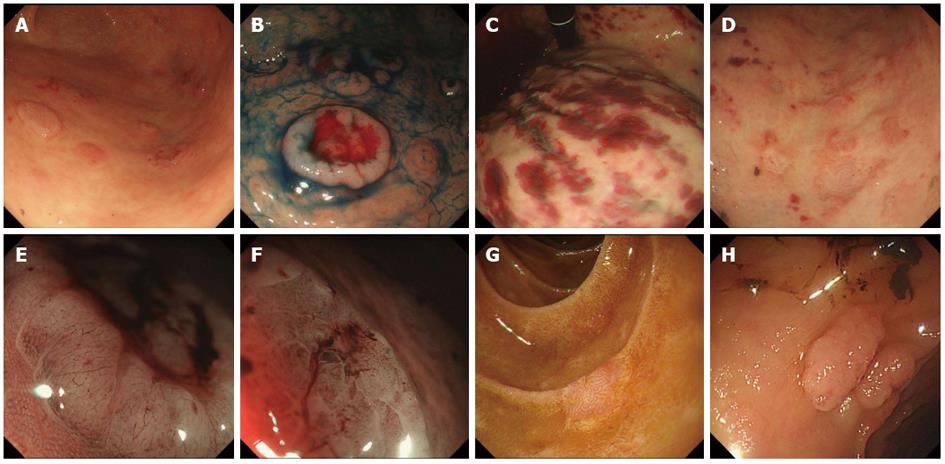
Figure 1 Upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopic findings.
A: Multiple elevated lesions in the body of the stomach; B: Multiple dish-like lesions with bleeding dyed with indigo carmine; C: Bloody spots in the body of the stomach; D: Ulceration with bleeding in the upper body of the stomach; E: Narrow band imaging (NBI) with magnification showing a honeycomb-like pattern at the edge of the elevated lesion; F: Irregular microsurface pattern in ulceration with NBI; G: Erythematous flat lesions in the duodenum; H: Multiple nodular masses in the colon and rectum.
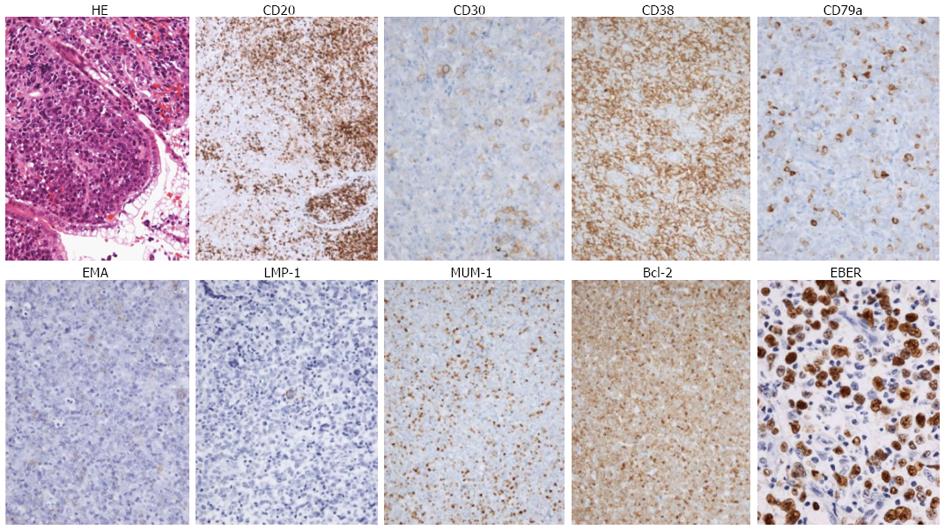
Figure 2 Histological findings and immunostaining of the biopsy specimen.
Pleomorphic, atypical lymphoid cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, marked nucleoli, and vesicular nuclei with hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 10). Immunohistochemistry shows positive staining for CD20 (× 4), CD30 (× 20), CD38 (× 10), CD79a (× 20), EMA (× 10), LMP-1 (× 10), MUM-1 (× 10), and BCL2 (× 10). Biopsy specimens revealed positive EBER-in situ hybridization (× 40). LMP-1: Latent membrane protein 1; MUM-1: Multiple myeloma oncogene 1; EMA: Epithelial membrane antigen.
-
Citation: Tanaka S, Nagata N, Mine S, Igari T, Kobayashi T, Sugihara J, Honda H, Teruya K, Kikuchi Y, Oka S, Uemura N. Endoscopic appearance of AIDS-related gastrointestinal lymphoma with c-
MYC rearrangements: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(29): 4827-4831 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i29/4827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4827