Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2013; 19(28): 4464-4474
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4464
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4464
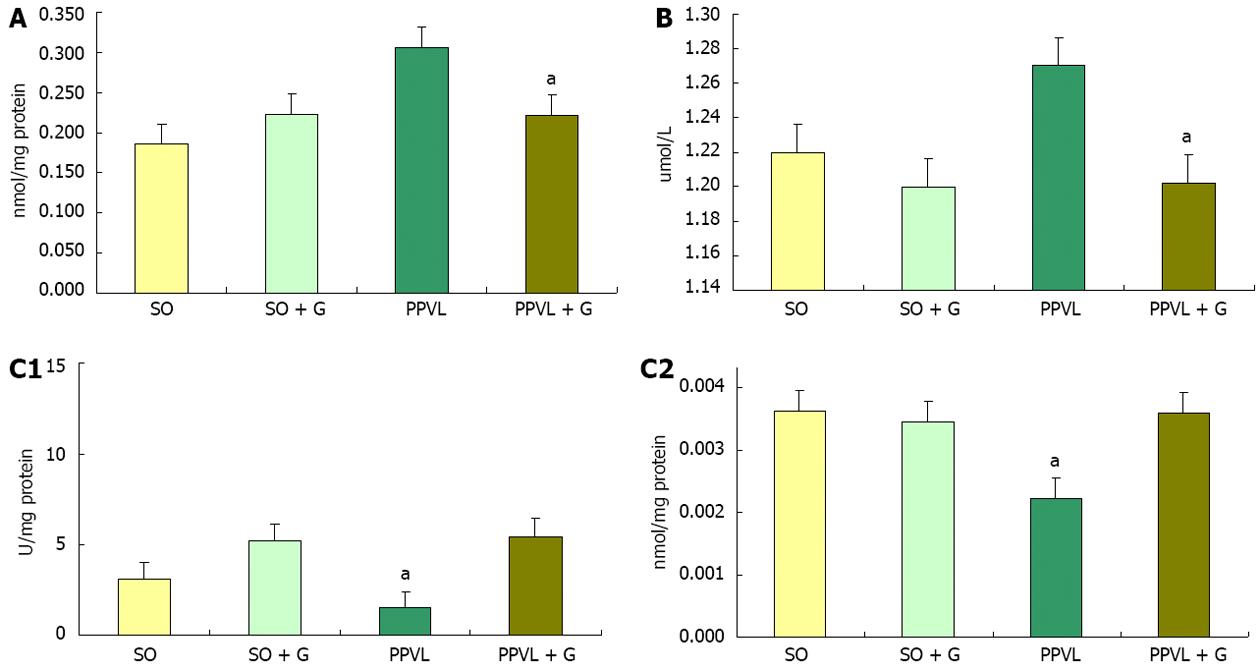
Figure 1 Effect of partial portal vein ligation and glutamine administration on gastric oxidative stress, nitric oxide production, antioxidant enzyme activities.
A: Effect of partial portal vein ligation and glutamine administration on gastric oxidative stress; B: Effect of partial portal vein ligation and glutamine administration on gastric nitric oxide production; C: Effect of partial portal vein ligation and glutamine administration on gastric antioxidant enzyme activities: (1) SOD activity; and (2) GSH activity. TBARS concentration. Values are the mean ± SE for 14 rats. aP < 0.05 vs the sham-operated group. PPVL: Partial portal vein ligation; G: Glutamine; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; TBARS: Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; SO: Sham-operated.
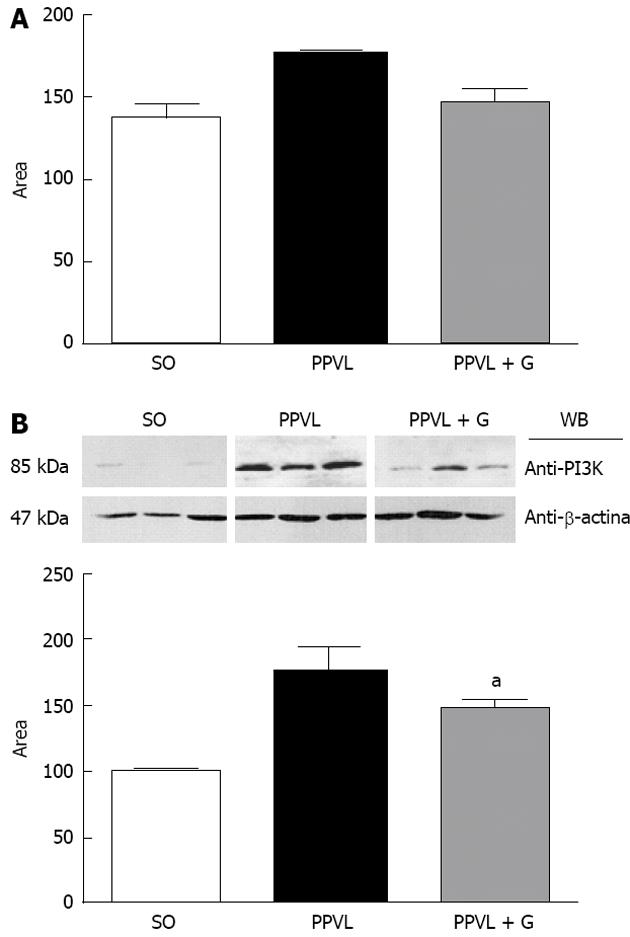
Figure 2 Expression of P-Akt and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase determined by Western blotting in gastric tissue from rats in the sham-operated group, the partial portal vein ligation group and rats subjected to portal vein ligation and glutamine treatment.
A: An increase in P-Akt protein expression was detected in the PPVL group vs the SO group; B: An increase in PI3K protein expression was found in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group showed reduced expression of this enzyme vs the PPVL group. SO: Sham-operated; PPVL: Partial portal vein ligation; G: Glutamine; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; WB: Western blotting. aP < 0.05 vs the SO group.
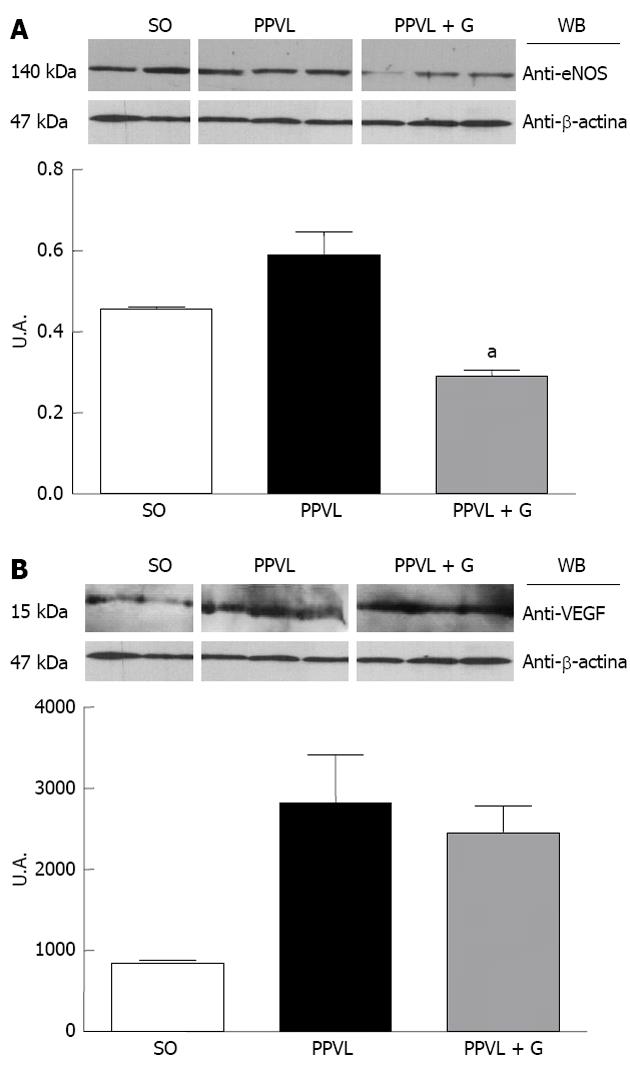
Figure 3 Expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor determined by Western blotting in gastric tissue from rats in the sham-operated group, the partial portal vein ligation group and rats subjected to partial portal vein ligation and glutamine treatment.
A: An increase in eNOS expression was observed in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group showed reduced expression of this enzyme vs the PPVL group; B: An increase in VEGF expression was detected in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group did not show a reduction in the expression of VEGF vs the PPVL group. SO: Sham-operated; PPVL: Partial portal vein ligation; G: Glutamine; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; WB: Western blotting. aP < 0.05 vs the SO group.
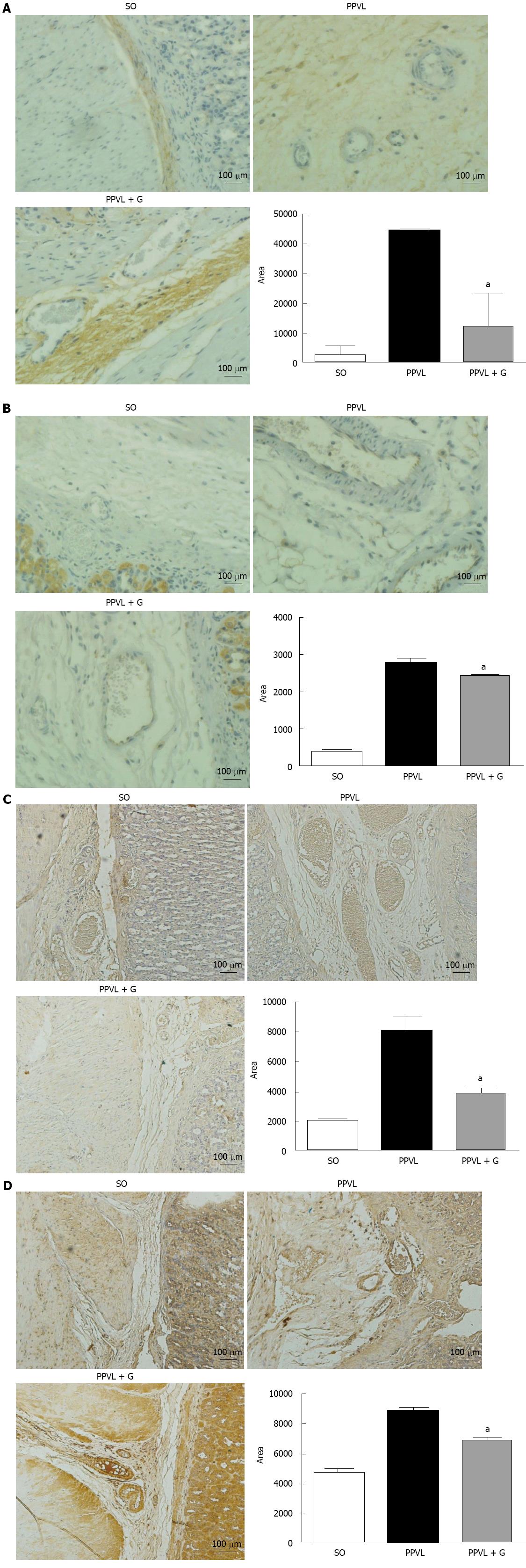
Figure 4 Representative expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, vascular endothelial growth factor, Akt and nitrotyrosine determined by immunohistochemical analysis of gastric tissue from rats in the sham-operated group, the partial portal vein ligation group and rats subjected to partial portal vein ligation and glutamine treatment.
A: An increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression was observed in the partial portal vein ligation (PPVL) group compared with the sham-operated (SO) group. The PPVL + glutamine (G) group showed reduced expression of this enzyme vs the PPVL group; B: An increase in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression was observed in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group did not show a reduction in the expression of VEGF vs the PPVL group; C: An increase in Akt protein expression was found in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group showed a reduction in the expression of this enzyme vs the PPVL group; D: An increase in nitrotyrosine expression was observed in the PPVL group vs the SO group. The PPVL + G group showed reduced expression of this enzyme vs the PPVL group. Analysis of the field was carried out precisely in the submucosal region, where there is evidence of edema and vasodilatation. eNOS staining; original magnification × 10. aP < 0.05 vs the SO group.
- Citation: Marques C, Licks F, Zattoni I, Borges B, de Souza LER, Marroni CA, Marroni NP. Antioxidant properties of glutamine and its role in VEGF-Akt pathways in portal hypertension gastropathy. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(28): 4464-4474
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i28/4464.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4464