Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2013; 19(15): 2307-2312
Published online Apr 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2307
Published online Apr 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2307
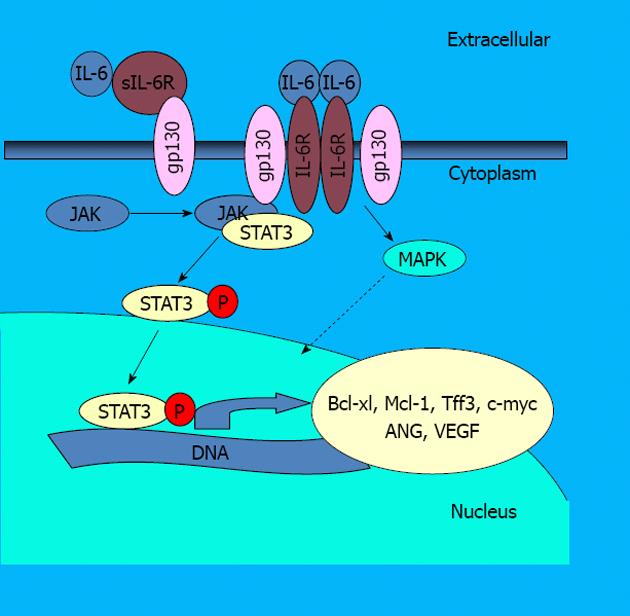
Figure 1 Interleukin 6 signaling scheme of the interleukin 6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway.
IL-6: Interleukin 6; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; sIL-6R: Soluble IL-6 receptor; IL-6R: IL-6 receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; ANG: Angiopoietin.
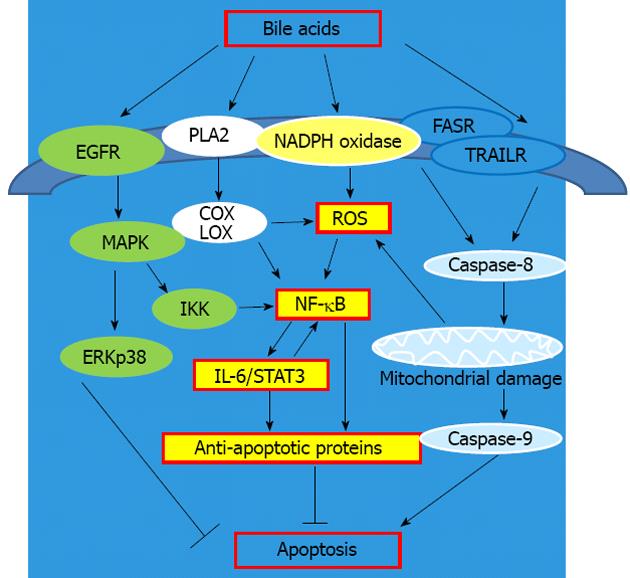
Figure 2 Apoptosis and the signaling pathways activated by bile acids.
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IL-6: Interleukin 6; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; COX: Cyclooxygenase; LOX: Lipooxygenase; IKK: IκB kinase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PLA2: Phospholipase A2; NAPDH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; FASR: FAS receptor; TRAILR: TRAIL receptor.
- Citation: Dvorak K, Dvorak B. Role of interleukin-6 in Barrett’s esophagus pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(15): 2307-2312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i15/2307.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2307