Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2013; 19(11): 1845-1849
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1845
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1845
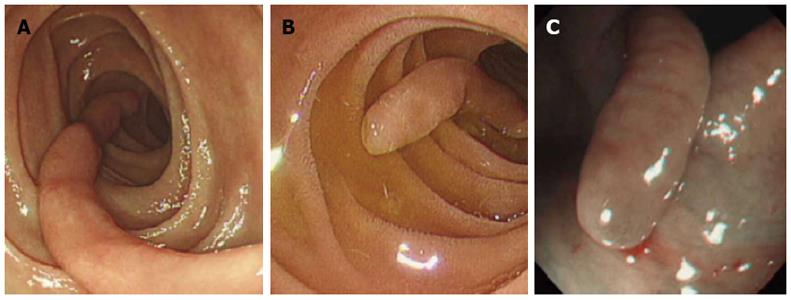
Figure 1 Endoscopic views of the polyps.
A: Gastroduodenoscopy revealed a 4 cm long, slender, “worm-like” polyp in the second part of the duodenum; B: Gastroduodenoscopy showed a 2.2 cm long, slender polyp in the duodenum; C: Colonoscopy showed a 1.4 cm long, slender polyp in the descending colon.
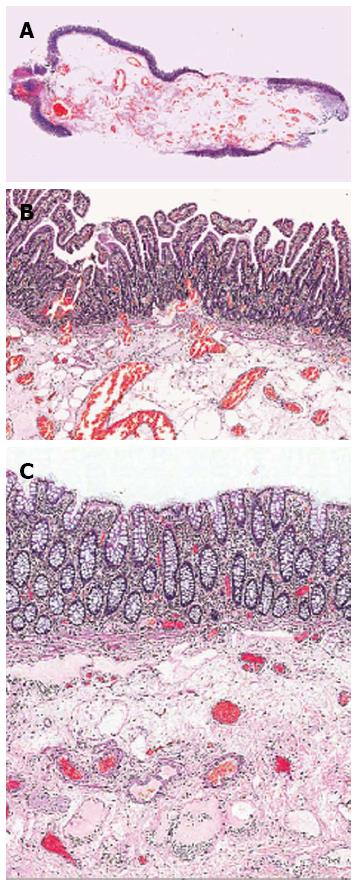
Figure 2 Histological section (hematoxylin and eosin staining).
A: Case 1; B: Case 1 with normal small intestinal mucosal lining; C: Case 3 with normal large bowel mucosa overlying the submucosa which contains a prominent vascular component.
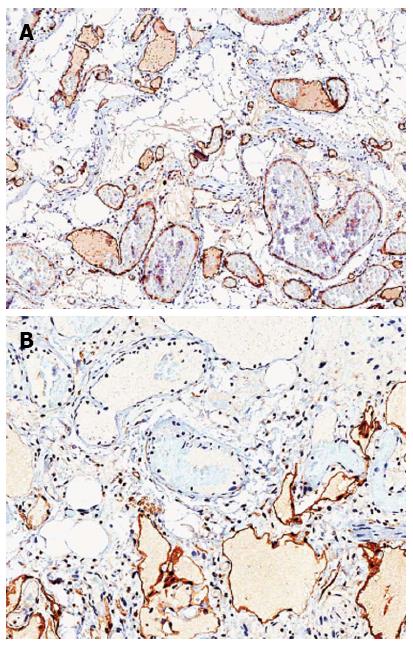
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry.
A: Positivity for CD31 in the endothelial cells of both vascular components; B: Positivity for D2-40/podoplanin selectively expressed by the endothelial cells in the lymphatic vessels.
- Citation: Tan CL, Tan SH, So JB, Petersson F. Muco-submucosal elongated polyps of the gastrointestinal tract: A case series and a review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(11): 1845-1849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i11/1845.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1845