Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2012; 18(7): 609-615
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.609
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.609
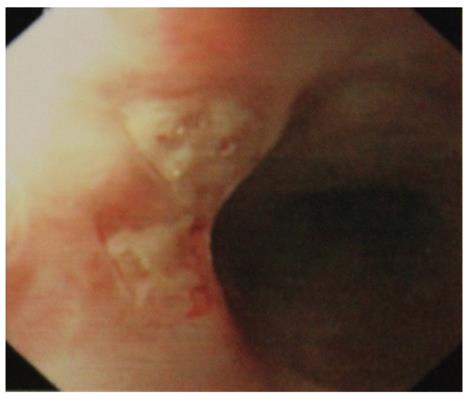
Figure 1 Esophageal involvement of Adamantiades-Behcet’s disease.
Endoscopic examination reveals two small punched-out, active ulcerations in the middle esophagus of the patient.
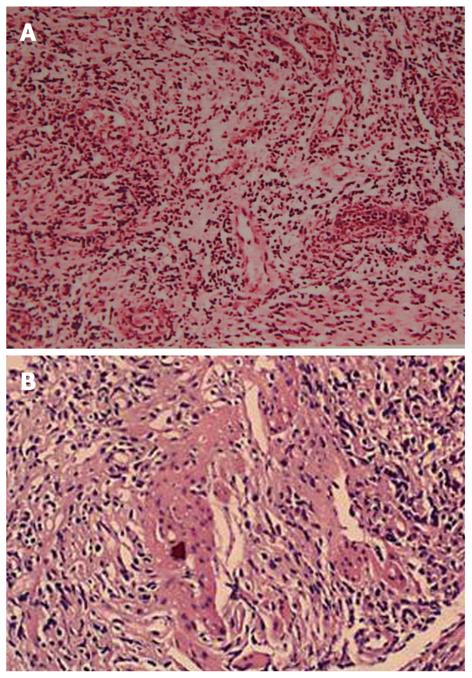
Figure 2 Ileum biopsy reveals lymphocyte-predominant inflammatory cells infiltration (A: HE, × 150) and fibrinoid vasculitis (B: HE, × 200).
HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
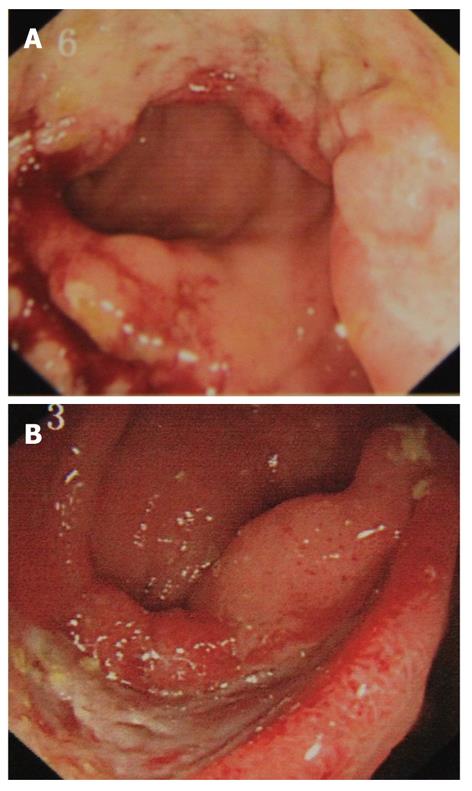
Figure 3 Typical colonoscopic findings of intestinal Behçet’s disease.
A: A single, large, and oval-shaped ulceration in the ileocecal region; B: A single annular-shaped ulcer in the ileum.
- Citation: Wu QJ, Zhang FC, Zhang X. Adamantiades-Behcet's disease-complicated gastroenteropathy. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(7): 609-615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i7/609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.609