Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2012; 18(48): 7409-7412
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7409
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7409
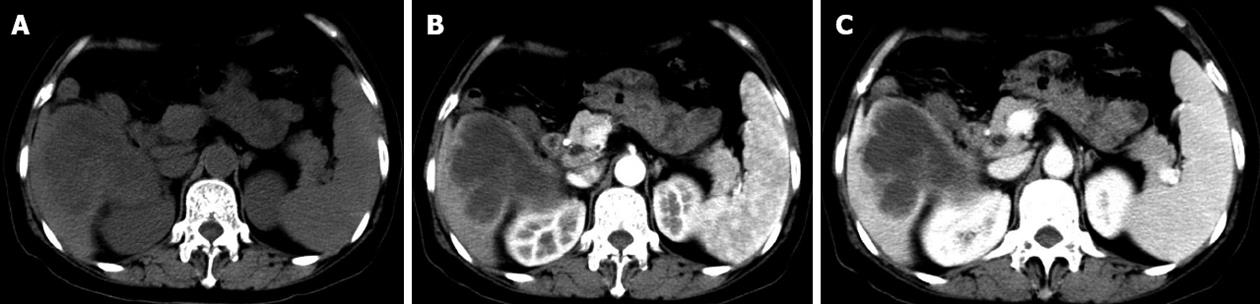
Figure 1 Obvious enhancement in the portal venous phase was observed.
A: A hypodense area in the right liver lobe was seen on plain computed tomography; B: The hypodense lesion showed mild rim enhancement in the arterial phase; C: Obvious enhancement was seen in the portal phase.
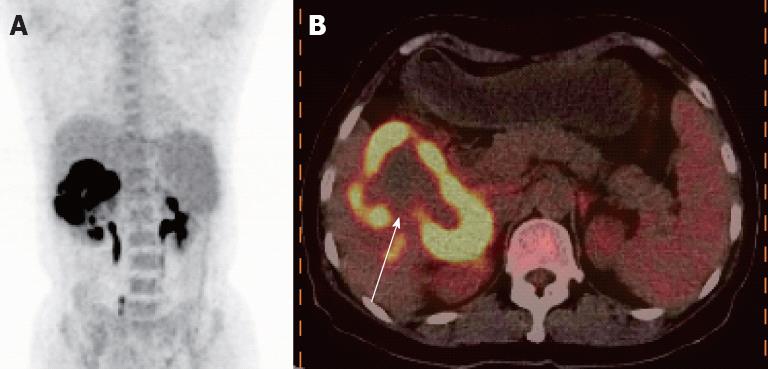
Figure 2 An abnormal ring-like metabolic focus in the right liver lobe was observed, with a maximum fluorodeoxyglucose uptake of 17.
7. A: Positron emission tomography/ computed tomography imaging showed a high metabolic focus in the right liver lobe; B: Fusion imaging revealed a ring-like high uptake focus with lower uptake in the center of the lesion (as shown by the white arrow).
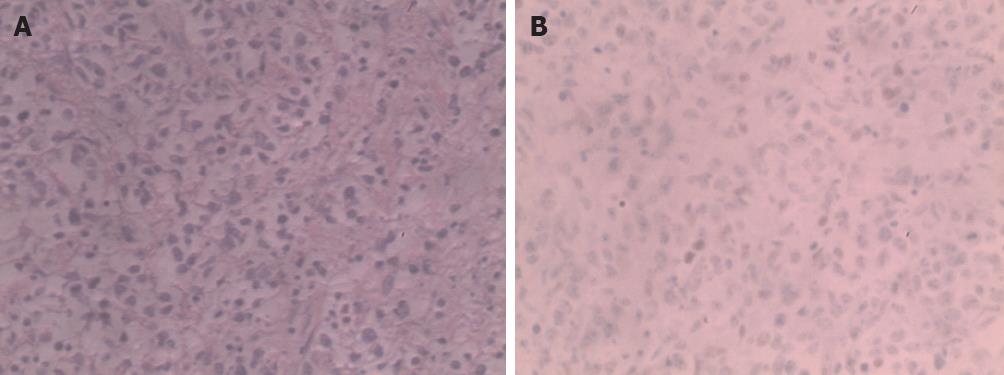
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD20, Bc1-6, Mum-1, Ki-67 and negative for CD30, Bcl-2, cytokeratin.
A: The normal structure of liver tissue was damaged, and showed dysplastic, almost naked nuclear lymphocytes, diffuse infiltration of liver tissue, tumor cells were mainly composed of round and oval cells, and spindle, polygonal, and multinucleated giant tumor cells were also seen (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); B: Bcl-6 was positive, and CD10 as well as Mum-1 were negative (immunohistochemistry, ×400).
- Citation: Pan B, Wang CS, Han JK, Zhan LF, Ni M, Xu SC. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT findings of a solitary primary hepatic lymphoma: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(48): 7409-7412
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i48/7409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7409