Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2012; 18(47): 7113-7117
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7113
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7113
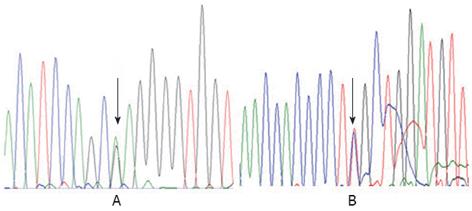
Figure 1 Genomic DNA sequences in exon 7 of the aldo-keto reductase 1D1 gene in patient 1.
A: The arrow identified a heterozygote mutation for c.797G>A (p.R266Q) in this patient; B: The reverse strand sequence shows the same result.
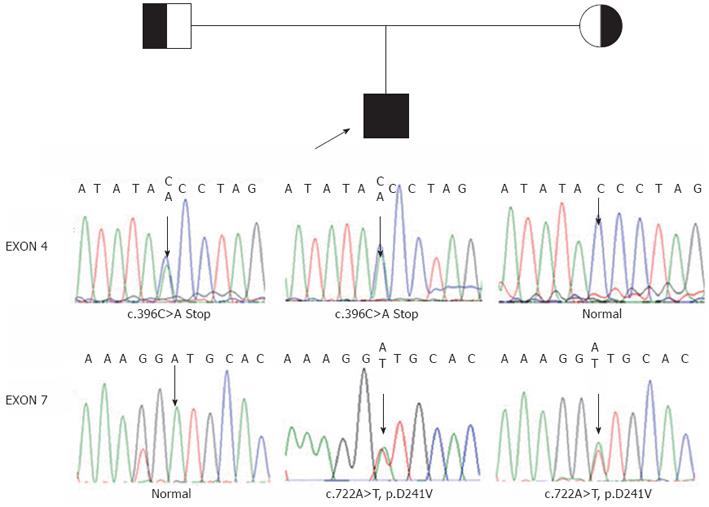
Figure 2 Pedigree for patient 2 shown with genomic DNA sequences in exons 4 and 7 of the aldo-keto reductase 1D1 gene in patient 2 and his parents.
The arrow in exon 4 identified C/A in patient 2s and his father, but C in his mother. The arrow in exon 7 identified A/T in patient 2 and his mother, but T in his father. These represent compound heterozygote with c.396C>A (nonsene mutation) from his father and c.722A>T (p.D241V) from his mother.
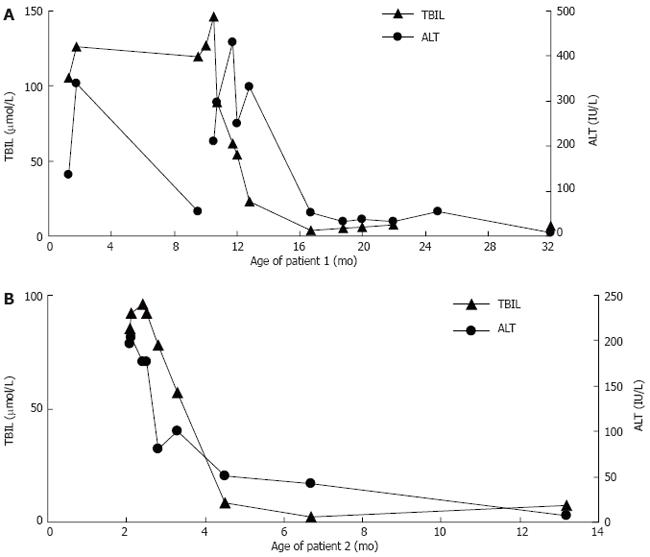
Figure 3 The responds of total bilirubin and alanine aminotransferase to treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid and/or chenodeoxycholic acid.
A: Patient 1; B: Patient 2. TBIL: Total bilirubin; ALT: Alanine aminotransaminase.
- Citation: Zhao J, Fang LJ, Setchell KD, Chen R, Li LT, Wang JS. Primary ∆4-3-oxosteroid 5β-reductase deficiency: Two cases in China. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(47): 7113-7117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i47/7113.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7113