Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2012; 18(47): 7009-7014
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7009
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7009
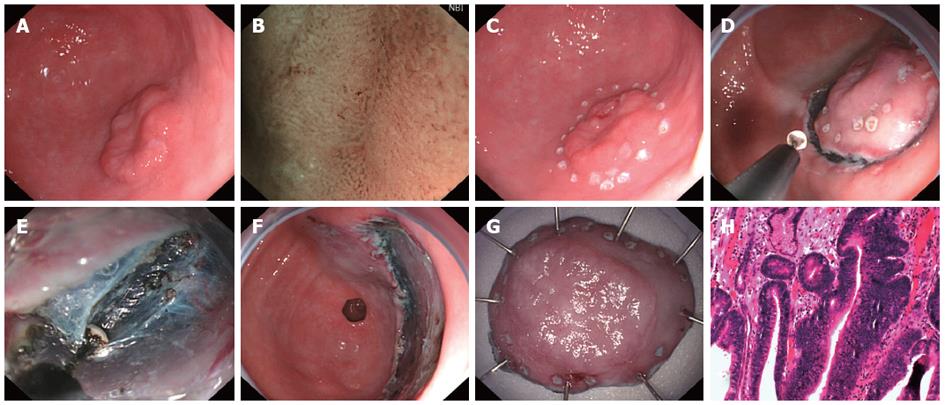
Figure 1 Procedure of endoscopic submucosal dissection: A male patient aged 56 years.
A: Gastroscopy showed a type 0-IIa (2.5 cm × 1.8 cm) lesion in the greater curvature of the stomach and pathology revealed differentiated adenocarcinoma; B: Magnification was performed using narrow band imaging to determine the borderline; C: Point-like electric coagulation was done at 0.5 cm away from the borderline of lesion for marking; D: Following submucosal injection, a circumferential incision was made in the mucosa and submucosa at 0.5 cm away from the marks; E: The mucosas were dissected from submucosa using an insulation tipped-2 knife; F: Artificial ulcer following resection; G: The sample (4 cm × 3 cm) was unfolded and the marks were found in the sample; H: Pathological type was high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (× 40).
- Citation: Lu ZS, Yang YS, Feng D, Wang SF, Yuan J, Huang J, Wang XD, Meng JY, Du H, Wang HB. Predictive factors of endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure time for gastric superficial neoplasia. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(47): 7009-7014
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i47/7009.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7009