Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2012; 18(47): 6951-6959
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.6951
Published online Dec 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.6951
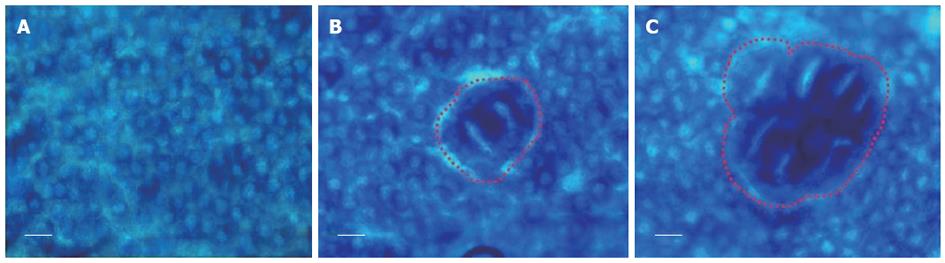
Figure 1 Topographical view of colon tissue.
A: Normal colon tissue; B: Aberrant crypt foci (ACF) with 2 crypts; C: Large ACF (crypt multiplicity containing more than 3 crypts per ACF). Scale bars = 25 μm.
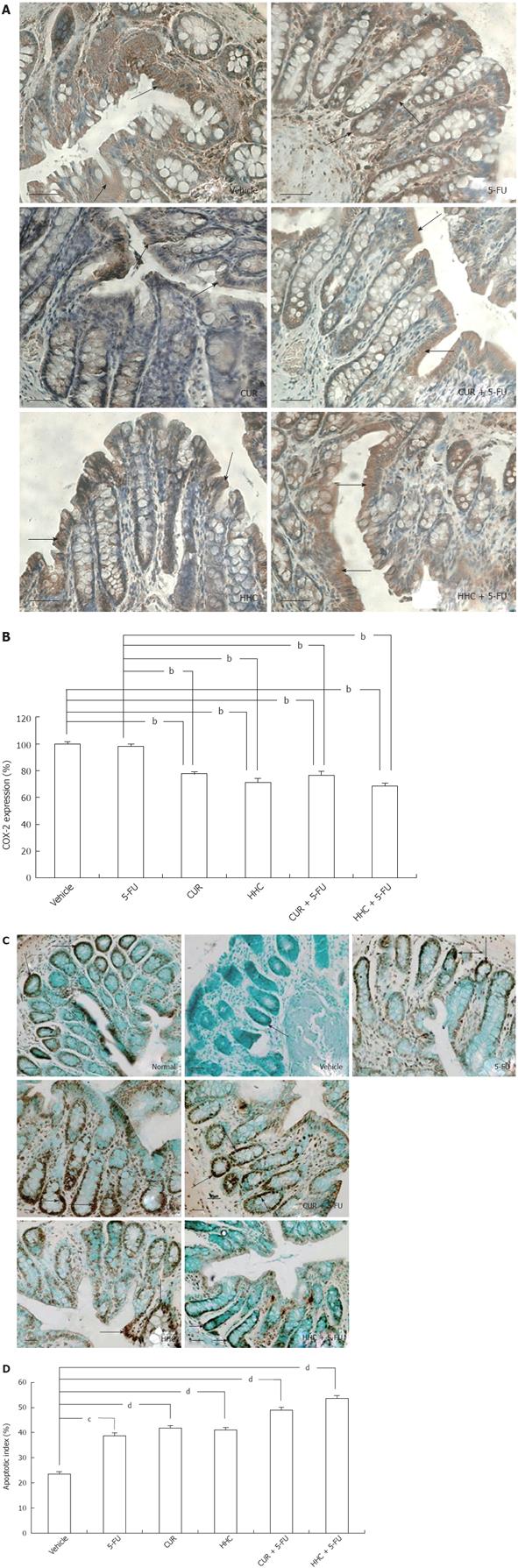
Figure 2 Effects of 5-fluorouracil, curcumin, and hexahydrocurcumin alone and their combined treatments on cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression and apoptosis.
A: Immunohistochemical staining of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein expression. Scale bars = 50 μm; B: Quantitative data of COX-2 protein expression (%). Each value is represented by mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs vehicle or 5-FU monotherapy; C: Apoptosis labeled using the dUTP-biotin nick end labeling method. Scale bars = 50 μm; D: Apoptotic index (%). Each value is represented by mean ± SE. cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs vehicle group. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; HHC: Hexahydrocurcumin; CUR: Curcumin.
- Citation: Srimuangwong K, Tocharus C, Tocharus J, Suksamrarn A, Yoysungnoen Chintana P. Effects of hexahydrocurcumin in combination with 5-fluorouracil on dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(47): 6951-6959
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i47/6951.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.6951