Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2012; 18(31): 4118-4126
Published online Aug 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4118
Published online Aug 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4118
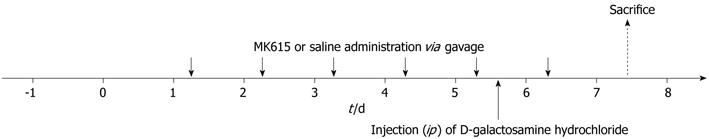
Figure 1 Experiment protocol of D-galactosamine hydrochloride-induced acute hepatic injury in rats.
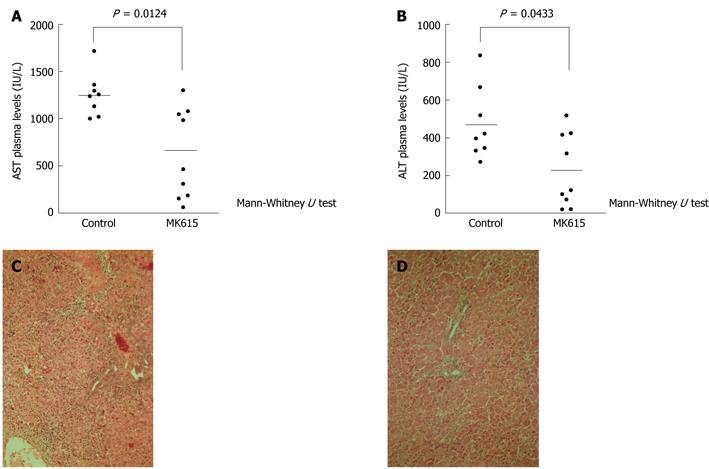
Figure 2 Effect of MK615 in D-galactosamine hydrochloride-induced acute hepatic injury in rats.
A: AST plasma levels; B: ALT plasma levels; C: Control group (liver); D: MK615 group (liver). AST:Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
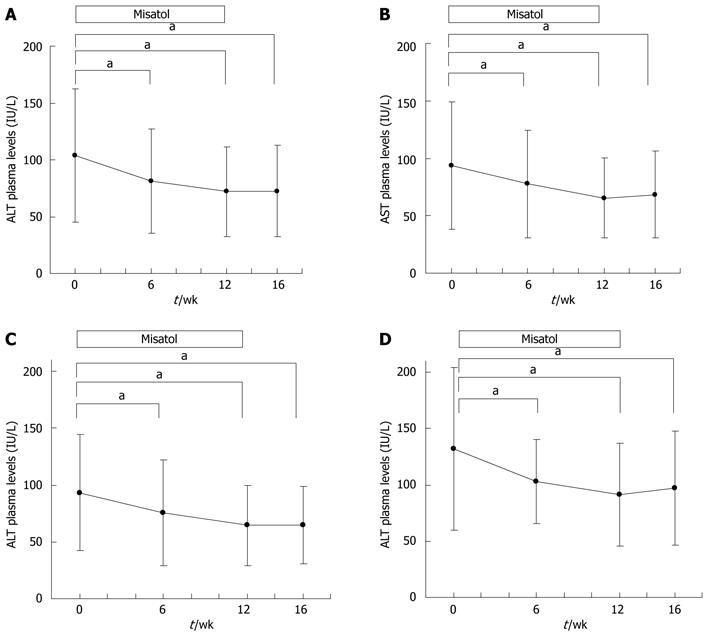
Figure 3 Effects of MK615 in patients with liver disorder, chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
A: Alanine aminotransferase (ALT); B: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST); C: Chronic hepatitis C group (ALT); D: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease group (ALT). aP < 0.05 vs 0 wk group. Dunnett’s test.
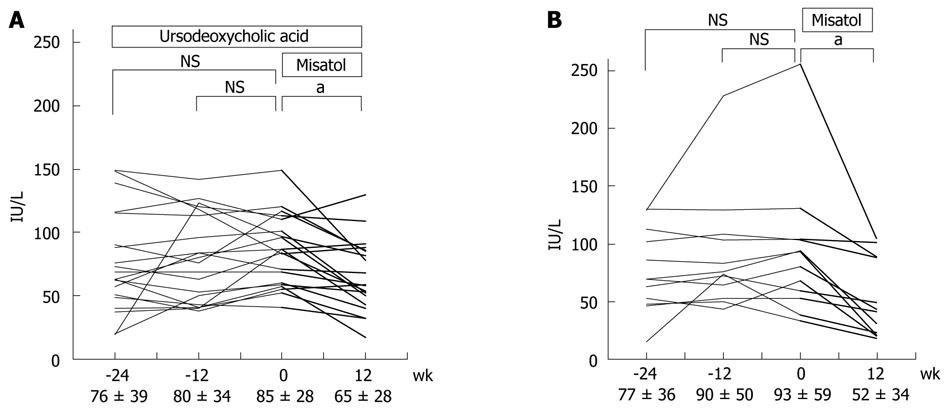
Figure 4 Effects of MK615 in patients with chronic hepatitis C (alanine aminotransferase).
A: Misatol was added on ursodeoxycholic acid; B: Only Misatol was used. aP < 0.05 vs 0 wk group. Dunnett’s test. NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Hokari A, Ishikawa T, Tajiri H, Matsuda T, Ishii O, Matsumoto N, Okuse C, Takahashi H, Kurihara T, Kawahara KI, Maruyama I, Zeniya M. Efficacy of MK615 for the treatment of patients with liver disorders. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(31): 4118-4126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i31/4118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4118