Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2012; 18(24): 3081-3088
Published online Jun 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3081
Published online Jun 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3081
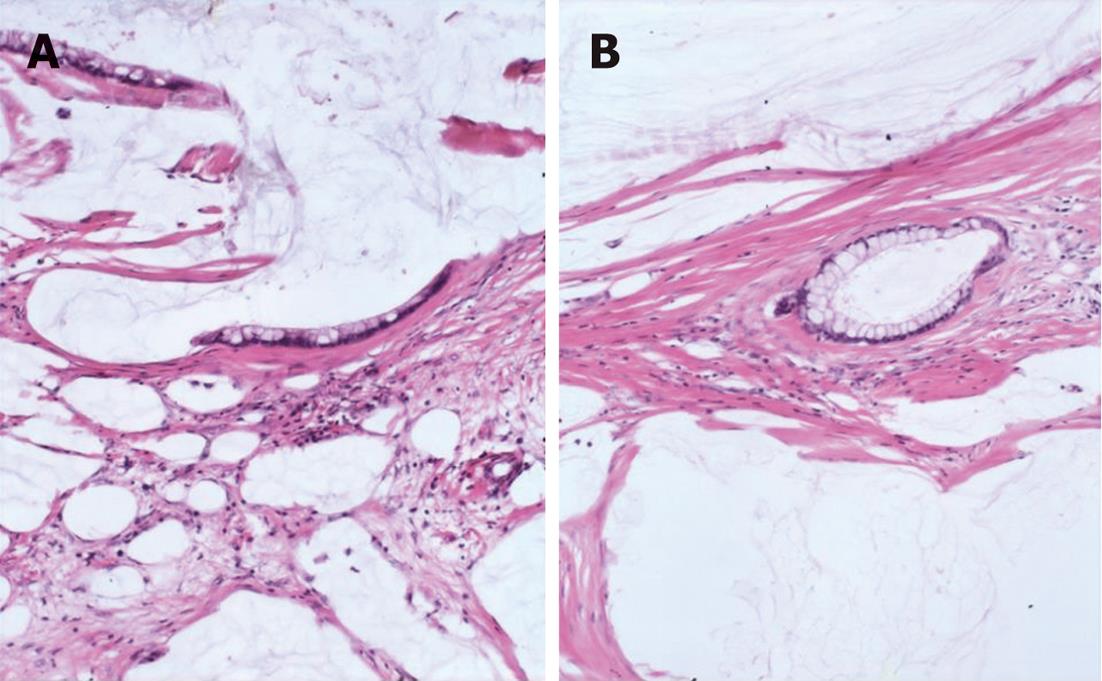
Figure 1 Peritoneal lesions consist of scant strips (A) and gland (B) of histologically bland mucinous epithelium associated with abundant extracellular mucin and fibrousis in disseminated peritoneal adenomucinosis (HE, × 40).
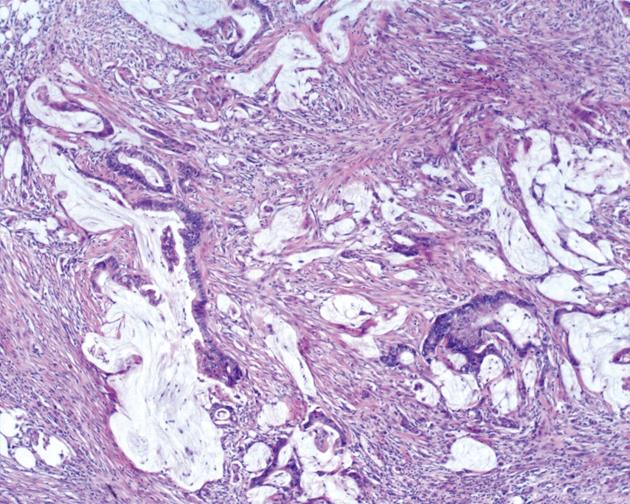
Figure 2 Markedly atypical epithelial fragments are suspended in pools of extracellular mucin in peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis (HE, × 40).
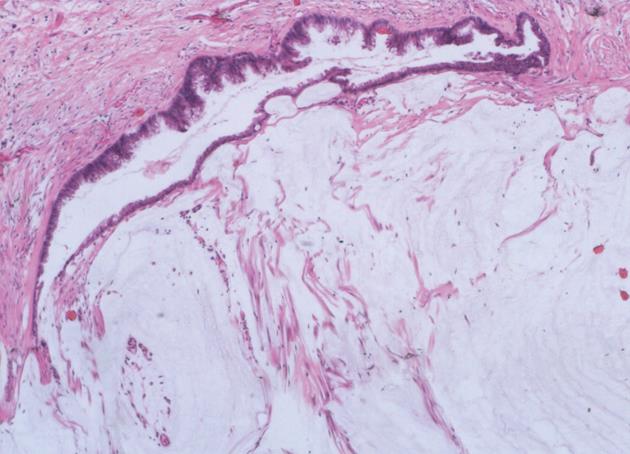
Figure 3 The mucinous epithelium displays nuclear stratification and cytologic atypia in peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis-I/D (HE, × 40).
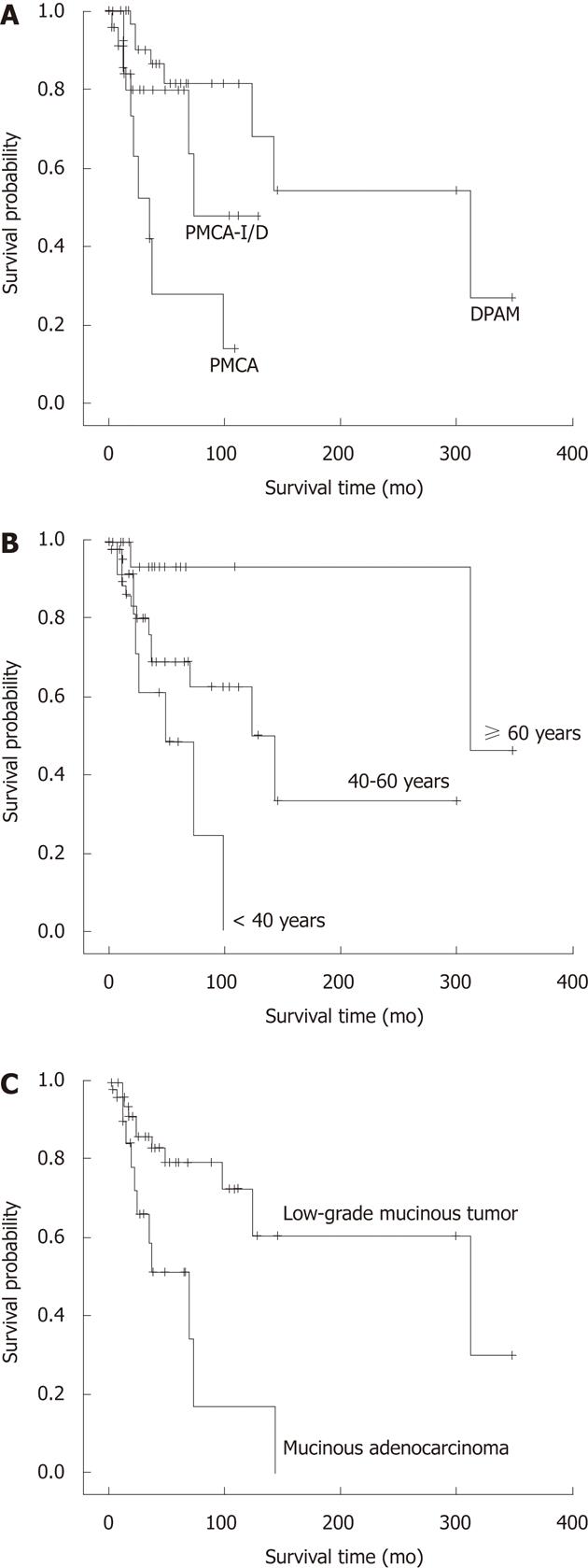
Figure 4 Survival related to histological classification, age and appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma.
A: Overall survival of the three histologic groups: Disseminated peritoneal adenomucinosis (DPAM), peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis with intermediate or discordant features (PMCA-I/D) and peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis (PMCA) (P = 0.001); B: Overall survival of the three age groups: < 40, 40-59 and ≥ 60 years (P = 0.011); C: Overall survival of the two appendiceal tumor groups: low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm and mucinous adenocarcinoma (P = 0.008).
- Citation: Guo AT, Li YM, Wei LX. Pseudomyxoma peritonei of 92 Chinese patients: Clinical characteristics, pathological classification and prognostic factors. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(24): 3081-3088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i24/3081.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3081