Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2011; 17(7): 898-905
Published online Feb 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.898
Published online Feb 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.898
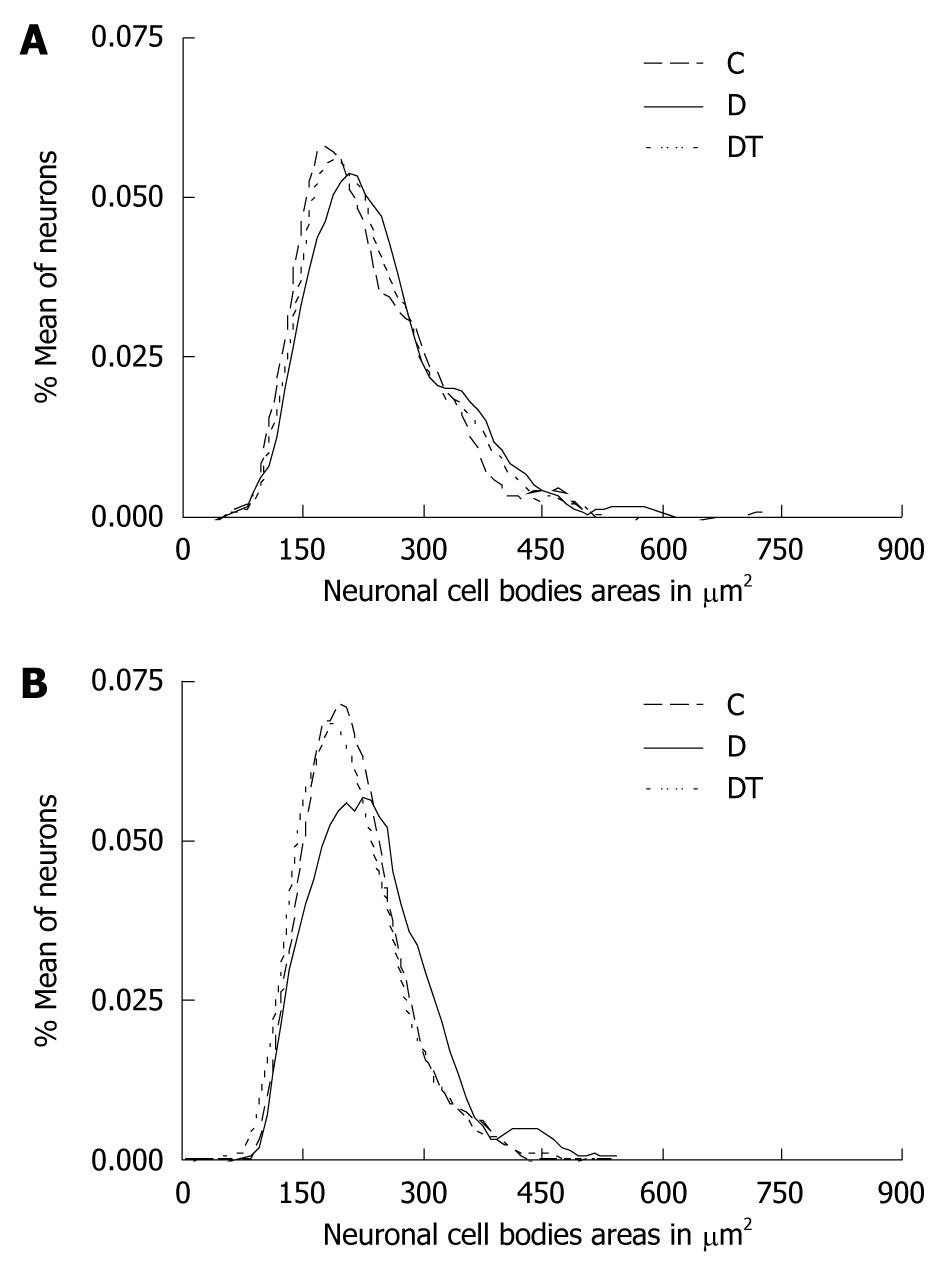
Figure 1 Neuronal behavior: area of cell body of myenteric (A) and submucosal (B) neurons, myosin-V immunoreactive in the jejunum, of control (C), diabetic (D) and diabetic-treated with EGb 761 (DT).
Figure 2 Neuronal behavior: area of cell body of myenteric (A) and submucosal (B) neurons, myosin-V immunoreactive in the ileum, of control (C), diabetic (D) and diabetic-treated with EGb 761 (DT).
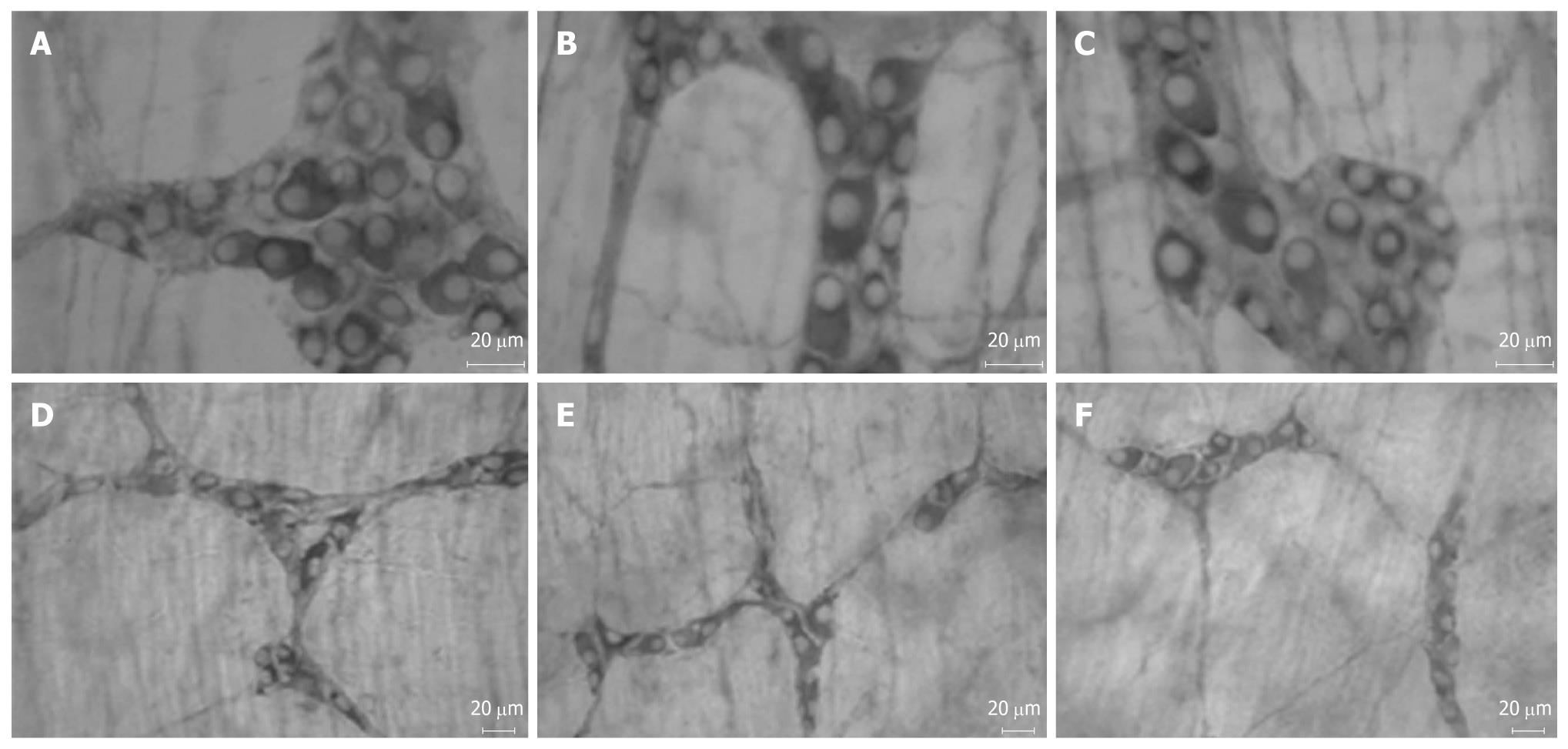
Figure 3 Myosin-V immunoreactive myenteric neurons in the jejunum (A-C) and myosin-V immunoreactive submucosal neurons in the jejunum (D-F).
There is a significant reduction in the neuronal density in the myenteric (B) and submucous (E) plexus in group diabetic. The neuronal density in the submucous plexus (F) was preserved in group EGb 76-treated (DT) (F). There was a significant reduction in the neuronal cell body area in group DT of both plexuses (C and F).
Figure 4 Myosin-V immunoreactive myenteric neurons in the ileum (A-C) and myosin-V immunoreactive submucosal neurons in the jejunum (D-F).
There is a significant reduction in the neuronal density in the myenteric plexus (B), but the neuronal density was preserved in this plexus in group EGb 76-treated (DT) (C). There is a significant increase in the neuronal cell body area in group diabetic in the myenteric (B) and submucous (E) plexuses. There was a significant reduction in the neuronal cell body area in group DT in the submucous plexus (F).
-
Citation: Silva GGPD, Zanoni JN, Buttow NC. Neuroprotective action of
Ginkgo biloba on the enteric nervous system of diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(7): 898-905 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i7/898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.898