Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2011; 17(44): 4911-4916
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4911
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4911
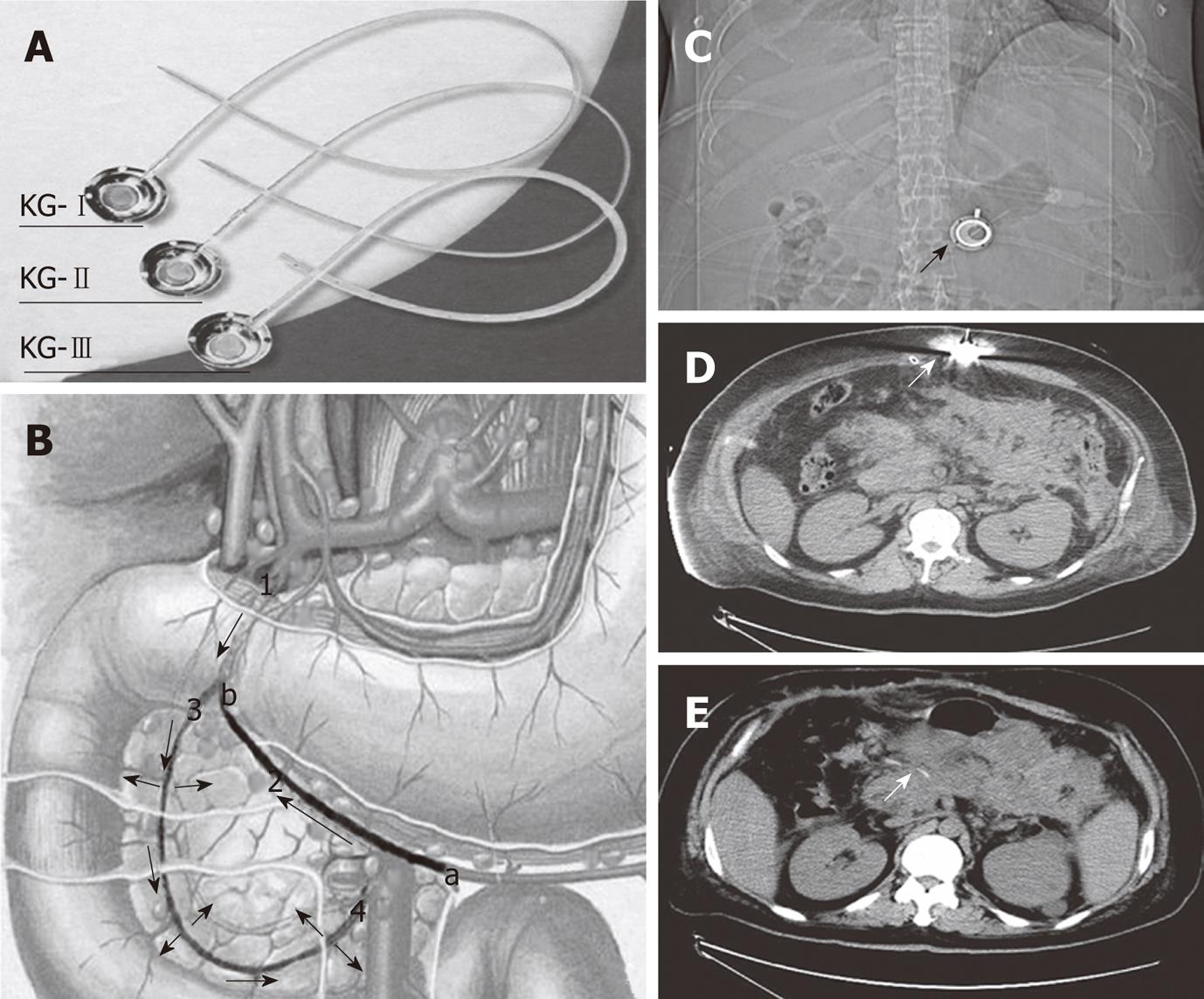
Figure 1 Procedure of placing drug delivery system and imaging after drug delivery system was inserted.
A: Drug delivery system; B: Anatomy and how it is inserted; 1: Gastroduodenal artery; 2: Right gastroepiploic artery; 3: Superior pancreatico-duodenal artery; and 4: Inferior pancreatico-duodenal artery (arrows indicate the direction of drug delivery and blood flow); a: The inserting point; and b: The end in which the catheter should be inserted; C: Abdominal X-ray film showed the subcutaneous drug delivery system (DDS) head (arrow); D: Computed tomography (CT) scan showed the subcutaneous DDS and the drug delivery needle inside the DDS (arrow); E: DDS catheter around the pancreas (arrow) in the CT scan.
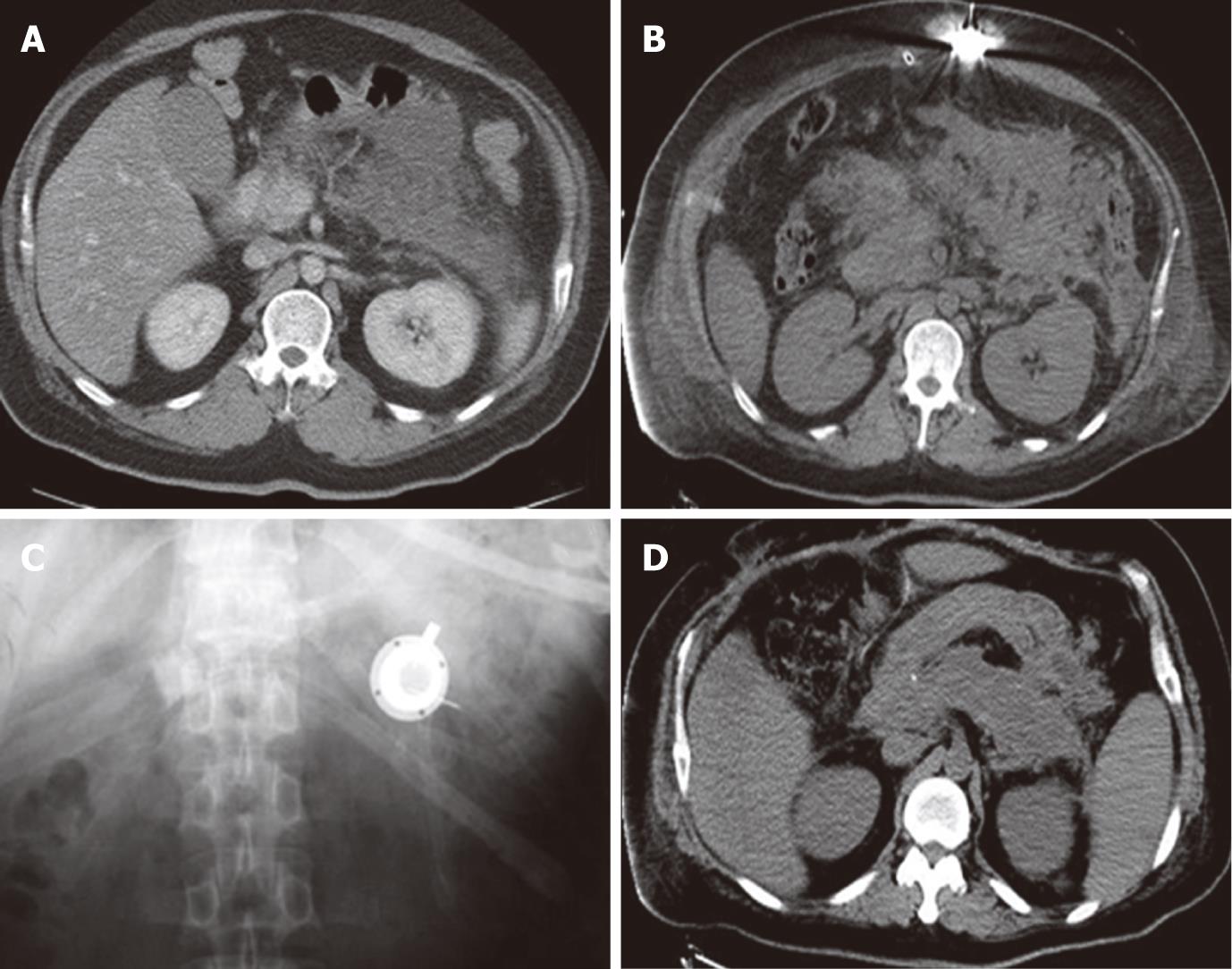
Figure 2 Imaging comparison between preoperation and postoperation.
A: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan before the operation; B: Abdominal CT scan after the operation with the drug delivery system (DDS) inserted; C: Abdominal X-ray film showing the subcutaneous DDS head (white); D: CT scan showing the recovered pancreas. No more fluid could be seen around the pancreas (CT scan before discharge).
- Citation: Deng ZG, Zhou JY, Yin ZY, Peng YY, Wang FQ, Wang XM. Continuous regional arterial infusion and laparotomic decompression for severe acute pancreatitis with abdominal compartment syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(44): 4911-4916
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i44/4911.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4911