Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2011; 17(29): 3431-3440
Published online Aug 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3431
Published online Aug 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3431
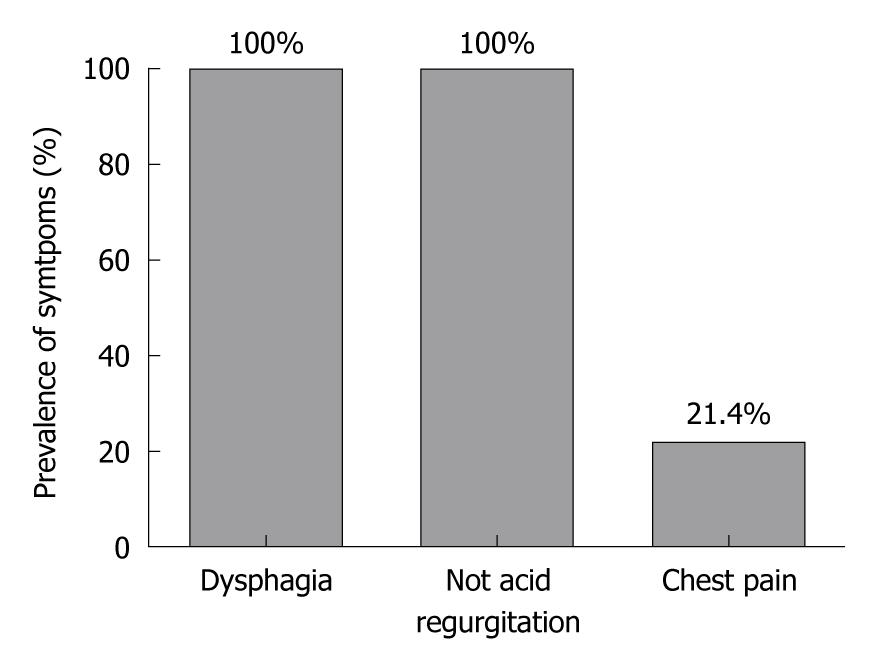
Figure 1 Preoperative symptoms.
Prevalence of dysphagia, regurgitation and heartburn in patients enrolled in the study.
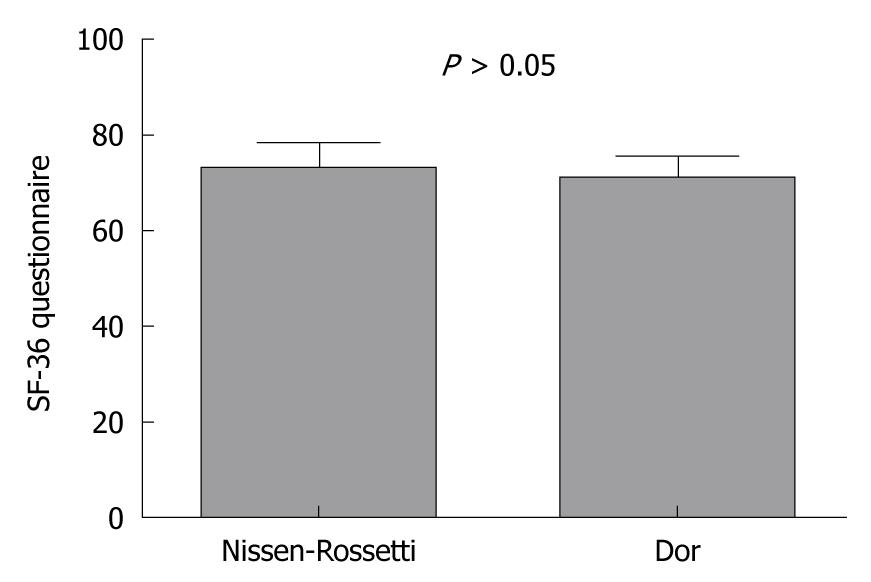
Figure 2 Quality of life at 24 mo follow-up.
Postoperative Qol (as measured by the SF-36 questionnaire) in patients with a partial anterior fundoplication and with a total fundoplication (P > 0.05; unpaired t-test).
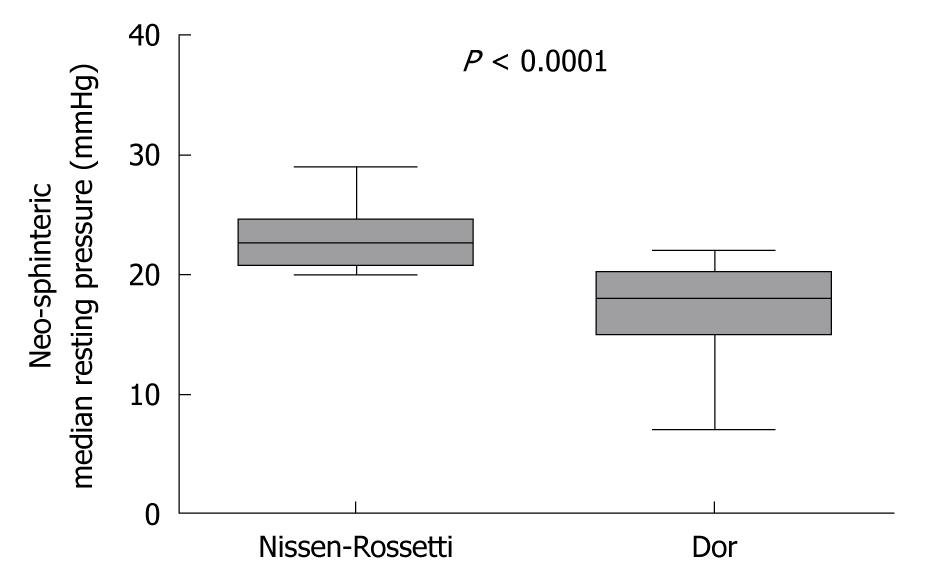
Figure 3 Postoperative oesophageal manometry.
Neo-sphinteric median resting pressure in patients with a Dor and with a Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication (P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test).
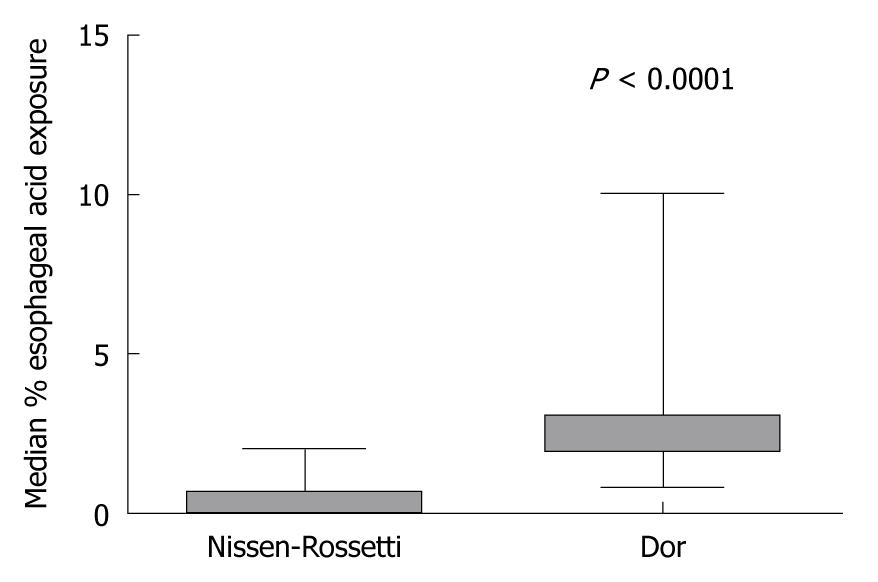
Figure 4 Oesophago-gastric pH monitoring at 24-mo follow-up.
Median percentage of total time with oesophageal acid exposure in patients with partial and total fundoplication (P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test).
- Citation: Martino ND, Brillantino A, Monaco L, Marano L, Schettino M, Porfidia R, Izzo G, Cosenza A. Laparoscopic calibrated total vs partial fundoplication following Heller myotomy for oesophageal achalasia. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(29): 3431-3440
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i29/3431.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3431