Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2011; 17(27): 3267-3270
Published online Jul 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3267
Published online Jul 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3267
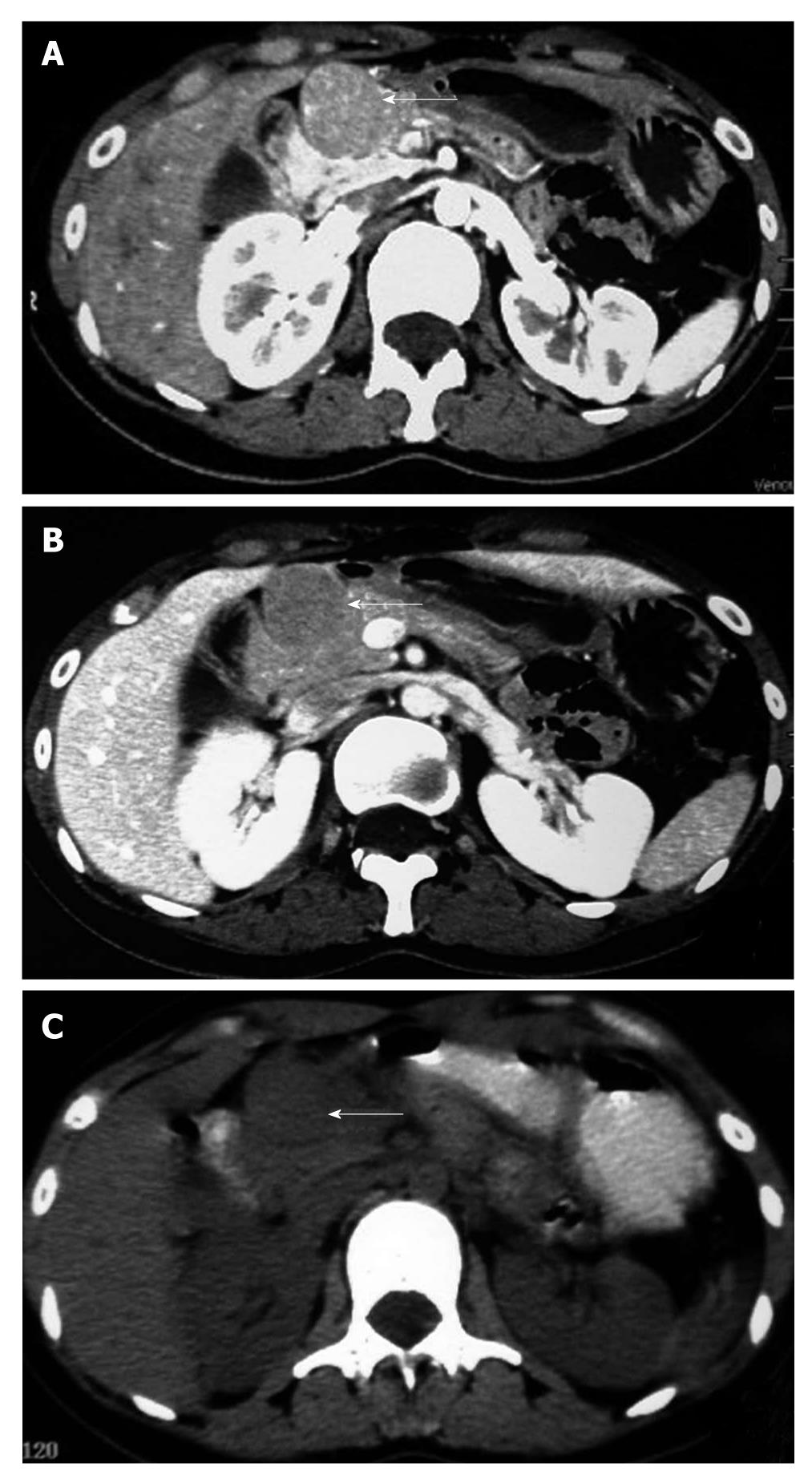
Figure 1 The abdominal imaging examination.
A, B: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) showing a lesion in front of the pancreatic head; C: Positron emission tomography-CT showing a lesion in front of the pancreatic head.
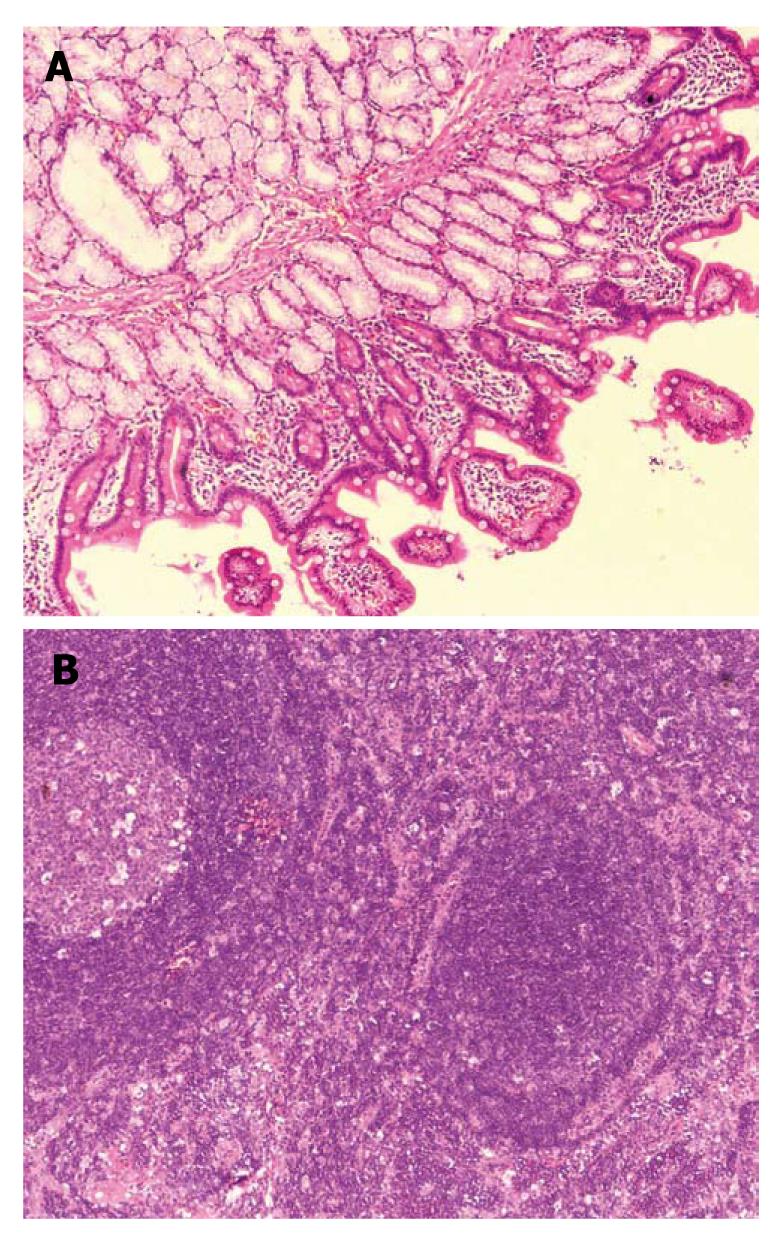
Figure 2 The histological examination.
A: Duodenal pseudolymphoma was confirmed by histopathologic examination, HE × 100; B: Lymph nodes showing reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, HE × 100.
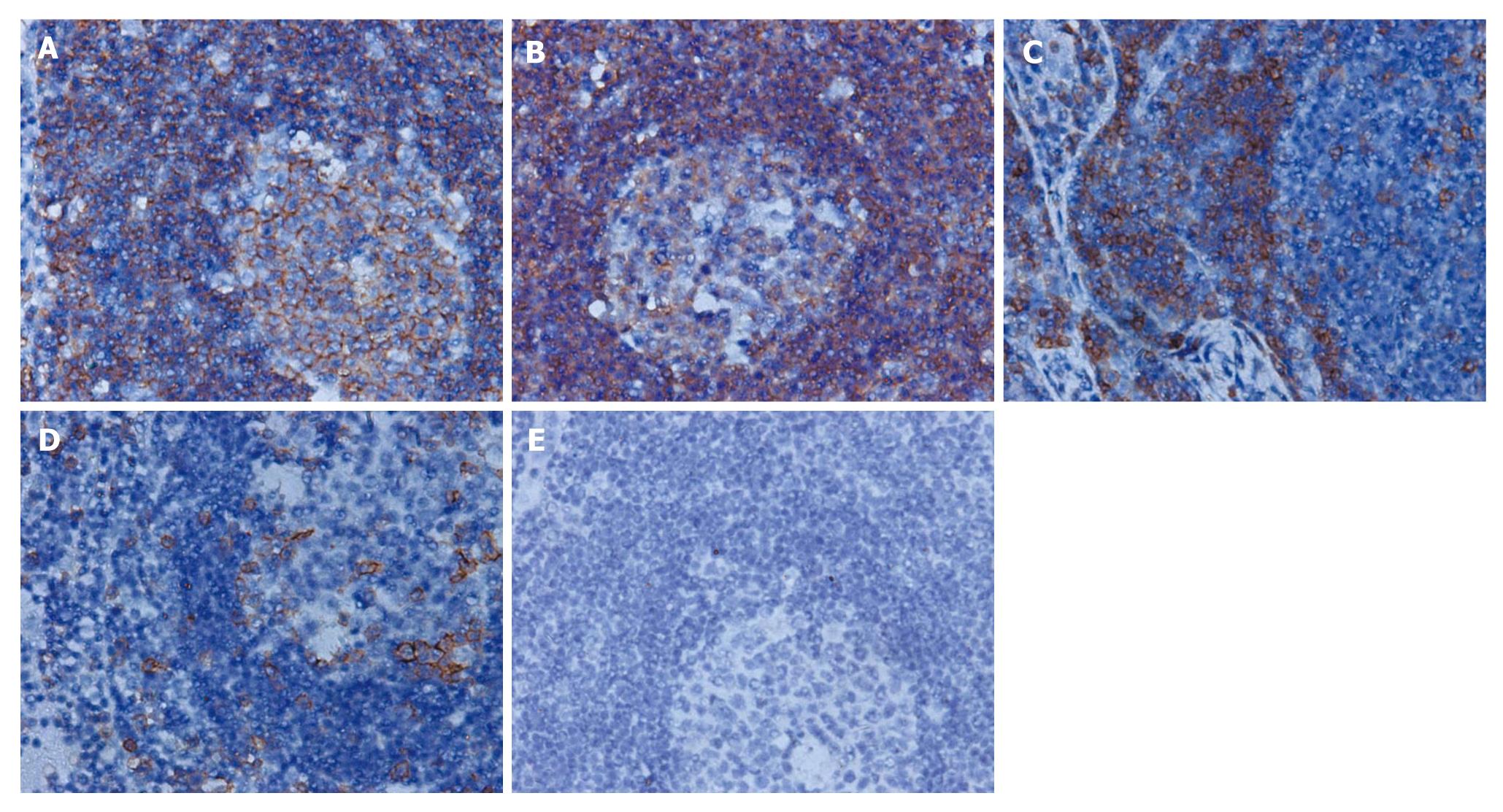
Figure 3 The immunohistochemical finding of the lesion.
A, B: Immunohistochemical study revealed follicles mainly consisting of L-26 and CD79a positive B cells, × 400; C, D: Interfollicular distributed CD3 and ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 positive T cells, × 400; E: Negative staining for terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, × 400.
- Citation: Huang YH, Long TZ, Xiao ZY, Ye H, Wan YL, Wang J. Duodenal pseudolymphoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(27): 3267-3270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i27/3267.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3267