Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2011; 17(14): 1848-1857
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1848
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1848
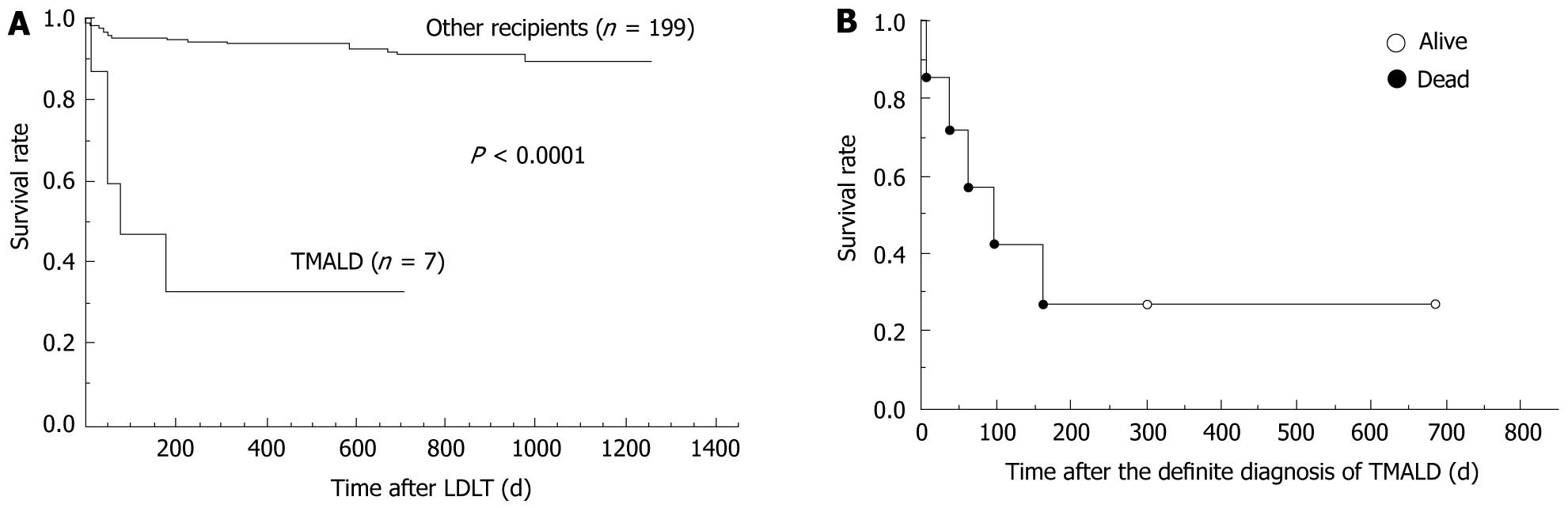
Figure 1 Outcomes of thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder after living-donor liver transplantation.
A: The seven thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder (TMALD) patients clearly showed a poor prognosis compared with the other 199 patients (P < 0.0001). TMALD after living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT) therefore had a negative impact upon the LDLT outcomes. A total of 206 LDLT recipients at Kyoto University Hospital (from April 2006 to March 2009) were evaluated; B: The thrombotic microangiopathy patients showed a poor prognosis despite intensive treatments after the diagnosis of TMALD. The open circles represent two recipients who were successfully treated, and the closed circles represent five recipients who finally died.
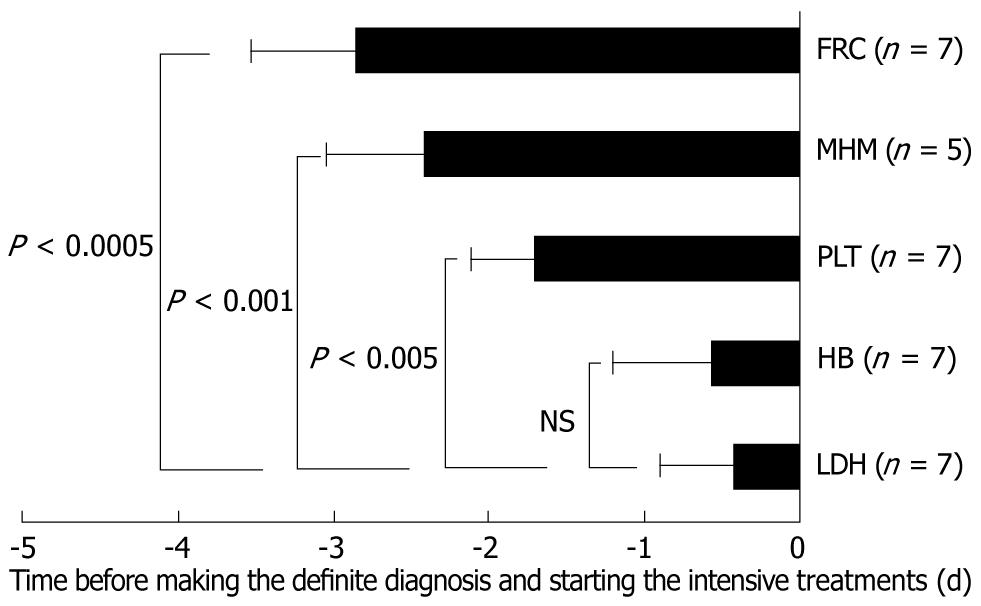
Figure 2 Temporal changes in important markers and signs for thrombotic microangiopathy.
The statistical significances of the differences in each factor in comparison with the time points for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are shown. Note that although microhemorrhagic macules (MHMs) were only observed in five of the seven cases (71.4%), the MHMs unexpectedly appeared at the early phase of thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder (TMALD) onset after living-donor liver transplantation, as well as fragmentation of red cells (FRC). In each case, the LDH levels proved decisive for making a diagnosis of TMALD, while the appearance of sufficient elevations of the LDH level were mostly late, similar to the case for hemoglobin (HB). PLT: Primary platelet.
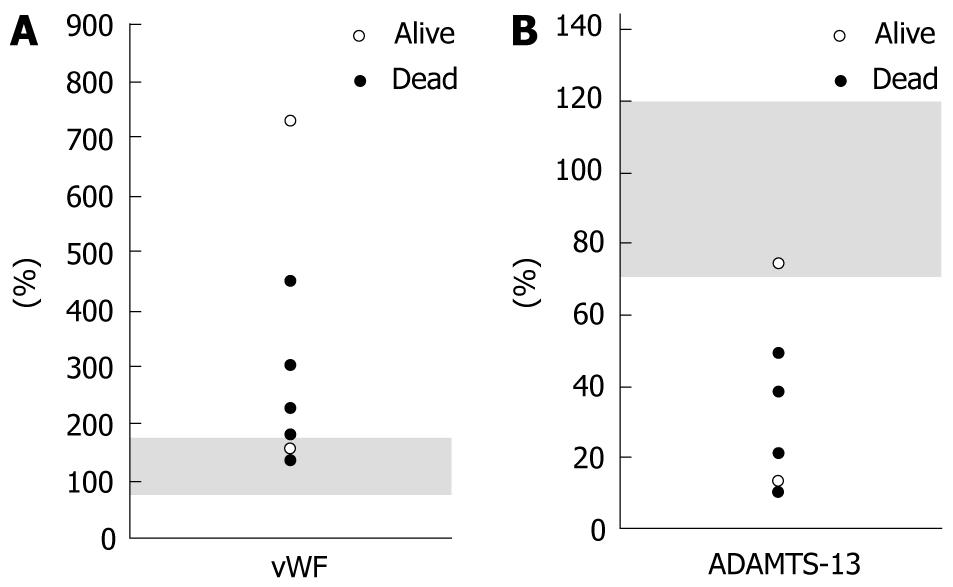
Figure 3 Absolute values of von willebrand factor and a disintegrin-like domain and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs-13.
A The mean absolute value of von Willebrand factor (WF) was 306.6% ± 212.0% (range, 135%-723%), and the vWF levels were within the normal range in two cases. The shaded area represents the normal range of vWF. The open circles represent two recipients who were successfully treated, and the closed circles represent five recipients who finally died; B The mean absolute value of a disintegrin-like domain and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs (ADAMTS)-13 was 31.1% ± 24.3% (range, 10%-75%), and the level of ADAMTS-13 was within the normal range in one case. The shaded area represents the normal range of ADAMTS-13. The open circles represent two recipients who were successfully treated, and the closed circles represent five recipients who finally died. Consequently, the degrees of abnormalities in the absolute values of both vWF and ADAMTS-13 did not seem to precisely reflect the thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder outcomes after living-donor liver transplantation.
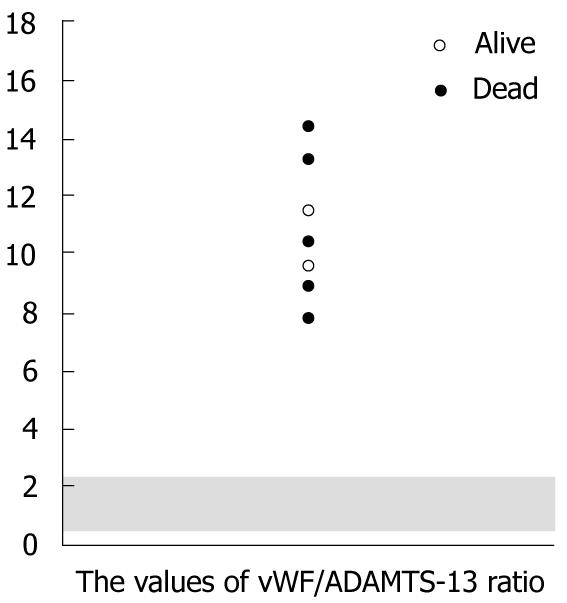
Figure 4 Balance between von willebrand factor and a disintegrin-like domain and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs-13.
From the viewpoint of an imbalance between von Willebrand factor (vWF) and a disintegrin-like domain and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs (ADAMTS)-13, the ratio of vWF/ADAMTS-13 strictly revealed the abnormalities in all thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder (TMALD) recipients after living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT). The shaded area represents the normal range. The mean value of the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio was 11.0 ± 2.4 (range, 7.8-14.6). The open circles represent two recipients who were successfully treated, and the closed circles represent five recipients who finally died.
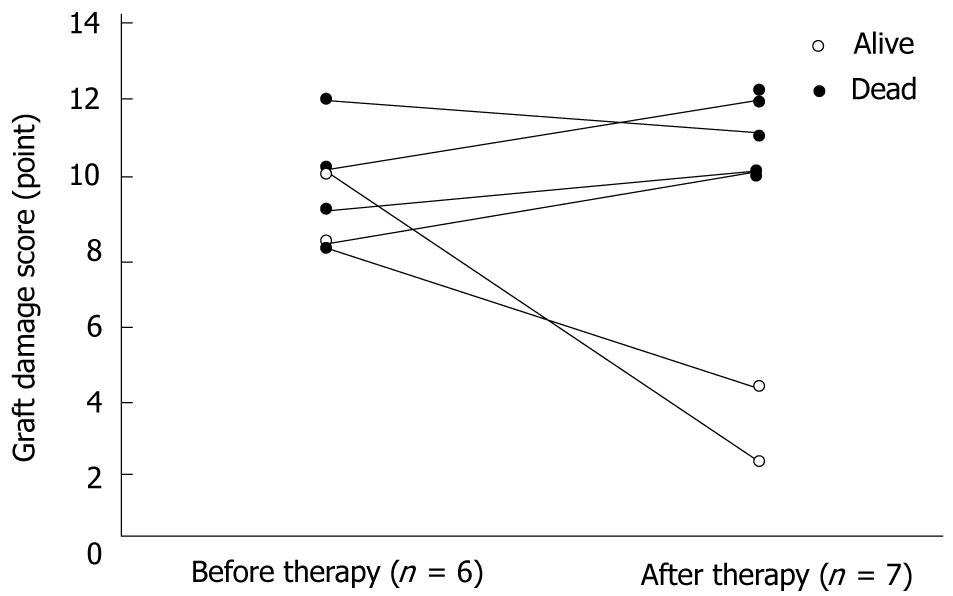
Figure 5 Graft parenchymal damage before and after thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder treatments.
The mean graft damage scores before and after thrombotic microangiopathy like disorder (TMALD) treatments in all patients were 8.9 ± 2.2 points (range, 5-12 points) and 8.7 ± 4.0 points (range, 2-12 points), respectively. In comparisons of the histopathological findings before and after TMALD treatments, the graft damage scores clearly demonstrated that five recipients who had poor outcomes (closed circles) showed no improvements despite repeated plasma exchange (PE). The mean graft damage score after TMALD treatments in these five recipients was 8.8 ± 2.6 points (range, 5-12 points). On the other hand, the two surviving recipients (open circles) recovered from their graft parenchymal damage. The graft damage scores after TMALD treatments in these two recipients were two and four points.
- Citation: Hori T, Kaido T, Oike F, Ogura Y, Ogawa K, Yonekawa Y, Hata K, Kawaguchi Y, Ueda M, Mori A, Segawa H, Yurugi K, Takada Y, Egawa H, Yoshizawa A, Kato T, Saito K, Wang L, Torii M, Chen F, Baine AMT, Gardner LB, Uemoto S. Thrombotic microangiopathy-like disorder after living-donor liver transplantation: A single-center experience in Japan. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(14): 1848-1857
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i14/1848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1848