Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2010; 16(9): 1063-1069
Published online Mar 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1063
Published online Mar 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1063
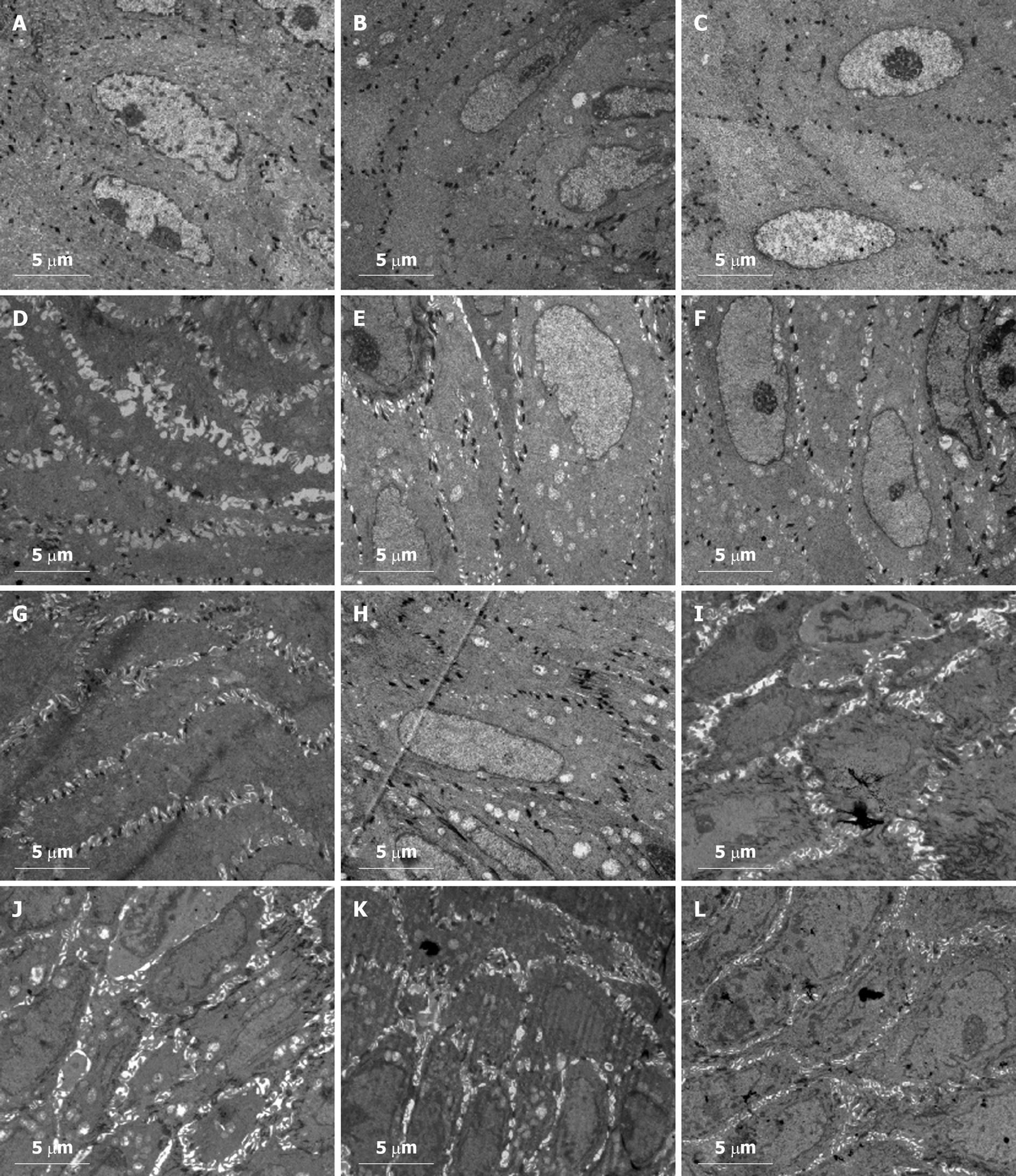
Figure 1 Transmission electron photomicrographs of the esophageal epithelium, showing intercellular spaces in rats of different groups in Part I (A-H) and Part II (I-L) (magnified at × 5000 by transmission electron microscopy).
A: Normal control group; B: Normal saline (NS) intragastric administration group; C: NS hypodermic injection group; D: Water immersion and restraint stress (WRS) group; E: Hydrochloric acid intragastric administration group; F: Ethanol intragastric administration group; G: Aspirin intragastric administration group; H: Prednisolone hypodermic injection group; I: NS + WRS group; J: Esomeprazole + WRS group; K: NS + aspirin group; L: Esomeprazole + aspirin group.
- Citation: Zhang DH, Zhou LY, Dong XY, Cui RL, Xue Y, Lin SR. Factors influencing intercellular spaces in the rat esophageal epithelium. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(9): 1063-1069
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i9/1063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1063