Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2010; 16(32): 3987-3994
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.3987
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.3987
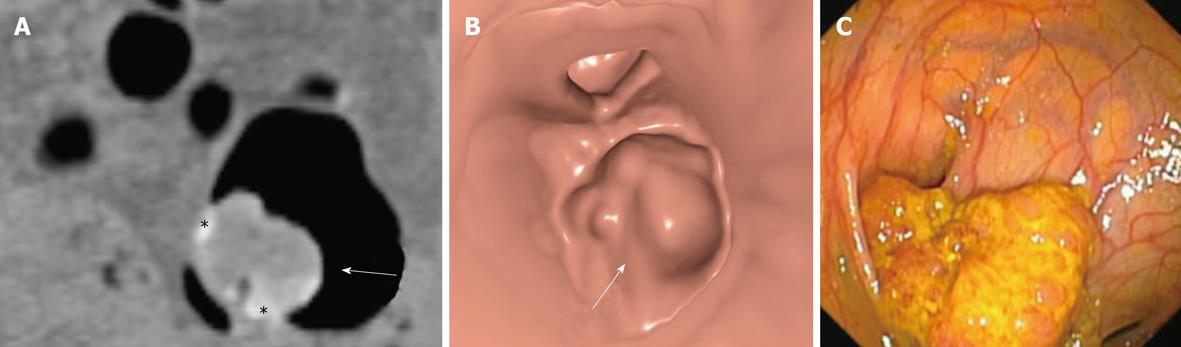
Figure 1 Sessile polyp: adenoma with low-grade dysplasia.
A: Coronal reformatted image showing a polypoid lesion (arrow), partly surrounded by tagged fluid (asterisks); B: The same lesion as shown on 3D endoluminal view (arrow); C: Conventional colonoscopy.
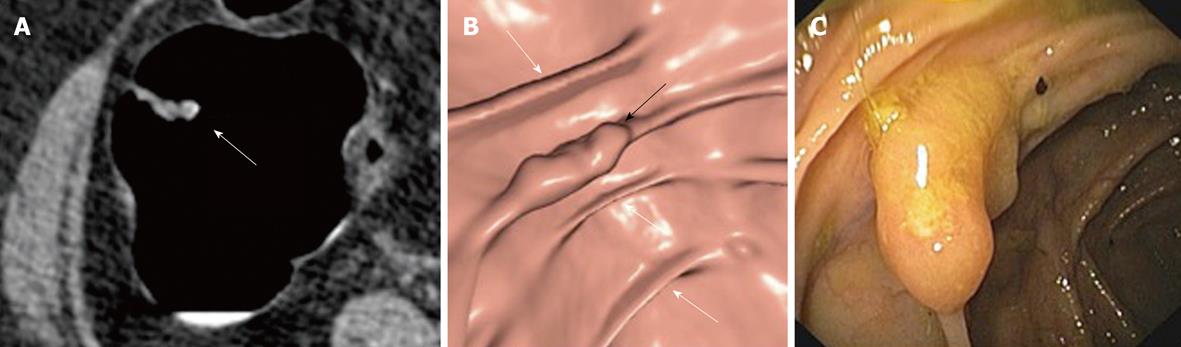
Figure 2 Non-polypoid (flat) lesion: advanced adenoma.
A: On 2D axial computed tomography image an irregularly thickened fold (arrow) is detected; B: On 3D endoluminal image the lesion is better appreciated (black arrow), in particular if compared with the normal adjacent colonic folds (white arrows); C: The same lesion at colonoscopy before removal.
- Citation: Laghi A, Iafrate F, Rengo M, Hassan C. Colorectal cancer screening: The role of CT colonography. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(32): 3987-3994
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i32/3987.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i32.3987